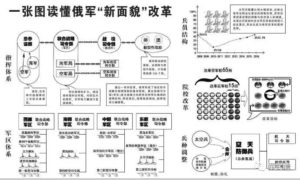
中國軍隊分析北韓軍隊朝鲜先军时代军事战略问题研究 //
Chinese Military Analysis of North Korean Army
The first part of the preface
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the drastic changes in the Eastern Europe, the disintegration of the Soviet Union and the socialist camp suffered great setbacks. In the mid-1990s, the Korean economy suddenly plunged into recession. In July 1994, Kim Il Sung died. At that time, people generally believe that North Korea is facing a serious crisis, the development prospects of North Korea is quite worrying. Nevertheless, North Korea has experienced three years of “mourning mourning”, and continue to missile test and nuclear test activities, and constantly strengthen its military power.
Into 2000, the DPRK has provoked the second, third Western war, carried out two nuclear tests, and the implementation of several missile test firing. In 2010, the DPRK in the West Sea (Korean Peninsula in the western waters) to create a “Cheonan ship incident” and “Yin Ping Island shelling incident.” North Korea’s military provocation, not only to South Korea, back to the surrounding countries to bring unease, but also to the security situation in Northeast Asia has brought great variables, and become an important factor in the regional arms competition.
September 1998, Kim Jong Il in the introduction of its regime, held high the banner of building a “strong power”, put forward a new political slogan – “first army politics.” To December 17, 2011 Kim Jong-il died, he had a long-17 years of strong rule of the DPRK. Kim Jong Il’s “first army politics” refers to all military work as the first, all military work as the most important, under the principle of military advance, to solve all the problems in the revolution and national construction, the people’s army as a pillar of the revolution , The political way of advancing the whole of socialism. It can be said that the first army politics is Kim Jong-Japanese political way. Its core content is that under the leadership of Kim Jong Il, the DPRK’s army actively responded to economic difficulties, social problems and security crisis, and strive to maintain the Korean-style socialist system. “Military strategy” is the DPRK in order to “first army politics” rooted in the Korean society, all to give priority to the development of national defense forces for all purposes, to give priority to the protection of national defense for the purpose of Kim Jong-Japanese military forces use.
In this paper, after the death of Kim Il Sung, Kim Jong-il system under the Korean military strategy development changes in the study, in particular, the DPRK in spite of the strong opposition from the international community, is still nuclear development and has a certain nuclear weapons after the strategic changes as a study Focus.
The second part of the Korean military strategy
First, the formation of the Korean military strategy background
The military strategy of the DPRK is gradually formed on the basis of Kim Il Sung’s military strategic thinking. Kim Il Sung’s military strategic thinking can be said to be the integration of formal warfare and guerrilla warfare. In the process of anti-Japanese activities in China and the former Soviet Union, Kim Il Sung accumulated a wealth of practical experience, which laid a solid foundation for the formation of its military strategic thinking. On the basis of these military experiences, Kim Il Sung put forward the “main tactics”, and stressed that “the main tactics” is the DPRK’s unique military strategy. In order to fully understand the DPRK’s military strategy, the study of Kim Il Sung’s military experience is very important.
In 1928, Kim Il Sung joined the Communist Youth League of China. Later, Kim Il Sung as a member of the Communist Party of China, in the East Manchuria, coastal state area carried out anti-Japanese activities behind enemy lines. Through the small Wangqing, the old Montenegro, Putian Fort fighting and other guerrilla warfare, Kim Il Sung from Mao Zedong’s military thinking to draw a wealth of wisdom and nutrition, and gradually realize the penetration war, guerrilla warfare, night war, behind enemy lines, large forces and small forces With the importance of tactics. Kim Il Sung was led behind the enemy’s anti-Japanese activities, the main fighting style for the ambush, raid, etc., but belong to the tactical category of guerrilla warfare. However, the DPRK will be these guerrilla warfare style exaggerated, propaganda into a large-scale battle, that is, a typical war in the revolutionary war. Because of this, today’s North Korean army still attaches great importance to guerrilla warfare.
In the late 1940s, Kim Il Sung had to flee to the former Soviet Union and was incorporated into the Red Army of the Soviet Union due to the encroachment of the Japanese Kwantung Army. At that time, Kim Il-sheng by learning Mikhail Nikolayevich Tukachevsky (1893 – 1939) prepared by the Marshal of the “workers and peasants Red Army field”, the military-style military organization , With the mobile combat-based battle compiled, the fire as the center of the weapons and equipment system and other content of the Soviet army’s regular war thinking has a certain understanding. Kim Il Sung’s military struggle in China and the former Soviet Union has played a very important role in the development of the military-based military forces in North Korea and the formation of military tactics such as speed warfare, raid warfare and cooperation. Through the Korean War, the DPRK in its military strategy to increase the annihilation of enemy forces surrounded by war, to promote political work, to ensure that the contents of war materials and so on. Through local conflicts, North Korea recognizes the need to strengthen the ability to cooperate with the war, strengthen the mechanized forces and air force. Based on the above, the DPRK continued to carry out the war to supplement and improve the method.
Source: Park Jung Pao, “North Korea’s Military Strategy Research”, “Korean Studies” Volume 6 (Seoul: Dongguo University, 2010), p.123.
Second, Kim Il Sung military strategy
1, preemptive attack strategy
Preemptive strategy is to choose the enemy completely unpredictable, or even if it can be expected but there is no time to respond to the timing, places and methods to attack each other’s strategy. Preemptive attack strategy can maximize the play to a sudden, fast, secret, camouflage, etc.. Often, the implementation of surprise operations, you can at the lowest cost, get the maximum combat effect. Kim Il Sung has repeatedly stressed that to do surprise success, usually must maintain a good fighting situation. Not only that, the combat troops have to really have the ability to completely destroy each other’s combat capability. This means that the purpose of pre-emptive surprise strategy is through the efficient and fast combat operations, in a short time focus on fighting forces, the complete destruction of enemy combat forces.
In order to implement pre-emptive surprise attacks, North Korea will be the deployment of most of the military forces in the front area. In the structure of the troops, but also highlights the rapid response, flexible and flexible features. It is particularly worth mentioning that North Korea will be about 70% of the military forces deployed in Pyongyang – Yuan Shan line south, if the DPRK made surprise attack decision, then the North Korean troops do not have another combat deployment, you can directly to South Korea to take military action.
2, with the strategy
“Coordination strategy” refers to a battle, two or more combat forms of mutual cooperation, mutual coordination strategy. On the basis of Mao Zedong ‘s guerrilla war ideas, summed up the experience of the Vietnam War, and fully considered the characteristics of the Korean Peninsula after the so – called “main tactics. The core of the war is in the large-scale regular warfare and guerrilla warfare, large forces and small forces with the launch of various forms of attack operations, such a battlefield will be no front and rear, making the other completely into a state of chaos.
In order to implement the war, North Korea has established the world’s largest special forces, and has AN-2 machine, hovercraft, submarines and other sea, air penetration means. In addition, the North Korean Navy, the Air Force also set up a sniper brigade, taking into account the characteristics of different services, and constantly strengthen the combat capability building. North Korea may take the type of war with a combination of regular warfare and guerrilla warfare, cooperation between large forces and small forces, cooperation between different services (land and sea air force), between different arms (arms), military and people force (Military and folk resources) and so on.
3, quick fix strategy
In the traditional military strategy theory, quick fix strategy has been highly valued by all parties. Quick tactical strategy is to focus on superior forces, each break the other main force, in a short time, with rapid tactical victory, the end of the war strategy. To this end, North Korea attaches great importance to the rapid development strategy, from the 20th century, 80 years, North Korea focused on the construction of armored forces, mechanized forces. In order to achieve the speed of war, North Korea’s military structure is also fully highlighted the rapid response, flexible and flexible features. The main combat forces of the warlords are tanks, armored vehicles, fighters, standing forces, compared with South Korea, in addition to armored vehicles, the DPRK in the number of obvious dominant. Therefore, if the DPRK launched a speed war on South Korea, then within a few days, the Korean army may sweep the whole of South Korea, and block the US military reinforcements involved.
Third, the evaluation of Kim Il Sung’s military strategy
Kim Il Sung’s military strategy is to sum up Kim Il Sung’s experience of military struggle in China and the former Soviet Union, taking into account the terrain characteristics of the Korean Peninsula and the gradual formation of local warfare. It can be said that Kim Il Sung’s military strategy is offensive offensive strategy. It is particularly worth emphasizing that the use of conventional combat power to occupy the number of advantages, the attack on South Korea launched a surprise attack, and then master the war dominance, and in the external reinforcements arrived in the Korean Peninsula before the end of the war speed strategy is Kim Il Sung’s military strategy core.
At present, the local war style is changing from long-term war, war of attrition, ground warfare to ground combat, maritime combat, air combat, space operations, network operations and other integrated all-round, multi-level modern three-dimensional operations. In addition, with the development of science and technology, the destruction of weapons and equipment, remote precision strike capability increased significantly, making the war style is developing into a rapid focus on precision strike style. In the past, the focus of the war was to use conventional military forces to win the victory of war and compete for the dominance of war. The focus of modern warfare is based on cutting-edge weapons and equipment system, to achieve the battlefield digital, efficient play the overall effectiveness of combat effectiveness. However, Kim Il Sung’s military strategy only embodies the conventional combat power of the implementation of the war, North Korea’s nuclear and missile areas are not included. Obviously, Kim Il Sung’s military strategy is very obvious, can not adapt to the needs of modern warfare. The army is an effective means for the DPRK to maintain its regime and to combat the threat of the system. Therefore, in order to give full play to the role of the military, Kim had to put forward a new military strategic concept.
The third part of the military era of military strategy and military strength construction
First, the military strategy
Kim Jong-il pointed out that the modern war was a new form of war, characterized by a highly expanded three-dimensional warfare, information warfare (reconnaissance, electronic warfare, cyber warfare, psychological warfare) Non-symmetrical warfare, non-contact warfare, precision strike, short time war decisive battle. In addition, Kim Jong Il also stressed that to do a good job in preparing for the new battle. It can be seen that Kim Jong-il has fully recognized that the modern war style is subject to qualitative changes, and that continue to use the existing conventional war tactics, can not guarantee the victory of future war. Therefore, in full consideration of the modern war style at the same time, in order to develop can cope with the United States and South Korea joint military forces, Kim Jong Il conceived the “large-scale destruction strategy”, “quick decision strategy”, “network strategy.”
(A), large-scale destruction strategy
Large-scale destruction strategy is to bring a huge destructive strategy to each other, is a “serious retaliation strategy” of a. To achieve a large-scale destruction strategy, need to have beyond the other side of the military power or have to give each other a decisive loss of military means. North Korea for large-scale destruction of the strategic forces, including nuclear weapons, including weapons of mass destruction and artillery units.
The massive destruction strategy is a strategy developed by the DPRK in order to protect the “victorious” battle of victory. In 1994, the DPRK was facing a major crisis because of the US threat to military attacks on North Korea’s nuclear facilities. It can be said that the emergence of this crisis directly promoted Kim Jong Il from the containment level to develop large-scale destruction of the military strategy.
The massive destruction strategy is the most representative strategy adopted by countries with nuclear weapons. In order to make up for the “blockade strategy” deficiencies, the former US President Eisenhower has proposed a “large-scale revenge strategy.” The United States, on the basis of its absolute nuclear superiority, pursued a large-scale retaliation strategy, reduced defense spending and established military hegemony in the international community. Former Soviet leader Khrushchev argues that the Soviet Union had failed in the “Cuban Missile Crisis” in 1962, mainly because the Soviet Union was at a disadvantage in terms of nuclear warfare compared with the United States. Therefore, Khrushchev actively promote nuclear weapons as the main force of large-scale retaliation strategy, trying to have the military strength with the United States. In 1964, China’s first atomic bomb after the success of China’s international influence, political status has been significantly improved. It can be said that through the nuclear development, to take a deterrent revenge strategy, China protects the security of its own country and establishes the status of the Asian military power based on it.
As mentioned above, countries with nuclear weapons, as a military power, can occupy a dominant position in the international community. Not only that, but also nuclear weapons as a primary means to promote large-scale retaliation strategy, in order to ensure their own national security. Therefore, the DPRK may be through the possession of nuclear weapons to promote large-scale destruction strategy. In other words, large-scale destruction strategy can not only make North Korea effective response to a variety of external threats, but also in the “something” to ensure that North Korea to win. 6.25 After the war, North Korea and the United States has maintained a truce. In recent years, the DPRK-US relations, due to nuclear problems, human rights issues, counterfeiting problems and other contradictions, the contest continued. In this context, the DPRK that at any time possible with the United States outbreak of war. Therefore, the DPRK’s massive destruction strategy is likely to play an important role in the future DPRK-US relations.
In 2006, the DPRK Labor Party Propaganda Department Deputy Minister has said that once the war broke out, the whole of Seoul will be 30 minutes into a flames, 100,000 US troops, 70% of South Korean residents face death, South Korea’s economic 90% Above into ashes. July 24, 2010, the DPRK National Defense Commission has also issued a threat that will be necessary when the start of nuclear-based North Korean retaliation “jihad”. This means that “something” when North Korea will use weapons of mass destruction to launch attacks.
(2) quick fix strategy
Kim Jong Il’s “quick fix strategy” is in the external forces reinforce the Korean Peninsula before the end of the war strategy, is Kim Il Sung’s strategy of succession, continuation and development. The Gulf War, the war in Afghanistan, the war in Iraq, the “quick fix strategy” has been widely used. Obviously, through the “quick fix strategy”, you can focus on attack and destroy hostile country command facilities and the main force, to master the war dominance, and in a very short time to end the war victory. The reason why North Korea will use quick fix strategy, the main reasons are as follows:
1, North Korea has a considerable scale can start the speed of combat forces
North Korea’s armored forces and mechanized forces with a high degree of mobility, can give each other a strong impact and deterrence, artillery forces can focus on the enemy’s core targets, can cause great losses and damage to each other. North Korea’s main battle of the speed of war – armored forces is 1.7 times the Han Jun, artillery units are Han Jun 2.5 times.
2, North Korea’s military system as a whole is conducive to maneuver
Despite North Korea’s economic difficulties, North Korea has been building military power. In recent years, not only the strength of military forces and equipment continued to increase, the army structure adaptation, also pay great attention to the construction of mobile combat capability. According to South Korea’s defense paper published in 2010, in order to improve the combat effectiveness of the troops, the DPRK reorganized part of the army, the two mechanized army reorganized as mechanized division, a tank army reorganized as armored division, an artillery army reorganized as artillery division. In addition, the DPRK has also strengthened the front forces of firepower building capacity. These changes in the Korean army provide a reliable guarantee for its speed warfare.
3, the Korean army most of the combat effectiveness deployed in the front area
North Korea has deployed more than 10 troops and more than 60 divisions / brigades in Pyongyang – south of Wonsan Line, accounting for about 70% of the overall combat effectiveness of the Korean army. In this way, as long as the North Korean leadership determined, then the North Korean troops do not have to re-adjust the deployment, you can always put into the South invasion. In November 2009, after the third naval battle in the Western Seas (Korean Peninsula), the Korean army deployed a 240-mm rocket launcher on its west coast, posing a direct threat to the South West and the capitals. It can be said that North Korea in front of the deployment of a large number of troops in order to focus on the early war to launch attacks, through the speed of war hit the Korean army.
North Korea stressed that with the traditional war style changes, non-linear combat, non-contact operations and other new combat methods are emerging, modern war may be in front and rear at the same time start. This means that the DPRK regular forces in front of a positive attack at the same time, the Korean special forces may be to the south of the region to launch interference operations. Undeniably, the battlefield before and after the start at the same time, the war will be quick to play a decisive role.
4, network strategy
Network attack refers to the use of computer networks exist loopholes and security flaws, the enemy military, administrative, personnel and other major systems and resources to attack, usually also known as “no gunfire.” With the rapid development of computer technology and the concept of network-centric warfare, the center of modern warfare is moving from the traditional combat platform to the network. From recent years, the local war style can also be seen, network combat is as one of the main forms of war, played a very important role.
In 2009, Kim Jong Il held a speech at the senior parliamentary conference of the Korean army that the war of the twentieth century was a war of oil and shells, and that war in the twenty-first century was an information war. It can also be seen that North Korea attaches great importance to cyber warfare.
There are two main ways to network attacks. The first for the illegal invasion of each other’s information systems, steal the system confidential information, damage to the target system data. The second is not invade the other side of the information system, the external destruction of the other information system, so that its function can not play a role.
From the 90s of the 20th century, North Korea in Pyongyang command automation university, computer technology university, Jinze Industrial University, and so vigorously cultivate professional network warfare talent. Pyongyang command automation university under the People’s Army General Staff, is North Korea’s most representative network warfare personnel training institutions, each year for the army to train more than 100 computer professional and technical personnel. It is speculated that the Korean army has a professional hacker scale of 500 to 600.
The military strategy of the United States, South Korea and other developed countries is heavily dependent on the computer network. If North Korea launched a network attack, it is easy to lead to South Korea’s network system confusion, affecting the transmission and sharing of information. At the crucial moment, and even may paralyze the entire network, so that South Korea missed the opportunity to deal with, so as to bring a fatal blow to South Korea. Before the outbreak of the war, the DPRK may attack the government of the Korean government at home or abroad through hacking. During the war, the DPRK may also interfere with the destruction of Han Jun’s computer network, leading to the entire computer network data transmission interruption and system paralysis.
North Korea’s network strategy will also have a positive impact on the psychological warfare. With regard to the war in Iraq, the DPRK believes that the US imperialists have been able to win in the war in Iraq, not so much the role of high-tech weapons, as it is the psychological warfare in the role, and from the ideological collapse of Iraq results. It can be seen that North Korea attaches great importance to the psychological warfare, and that in the future war conditions, the psychological war will run through the whole process of war. North Korea through the network to carry out the psychological warfare style mainly includes: in hostile countries or support the national network spread to the DPRK is conducive to the spread of information and gossip, and even false information (bacterial warfare, chemical warfare, the use of nuclear weapons, large casualties) Thus bringing panic to the public in hostile countries and weakening the will of the hostile countries. For the support of the country, through the efforts to create anti-war public opinion, forcing the support of the state to stop the reinforcements, and the early withdrawal of troops have been invested.
The main feature of the military strategy of the army is based on Kim Il Sung’s aggressive strategy, in order to maintain the regime, increase the content of the protective strategy. In other words, Kim Jong Il through the army to establish a military strategy, will be his successor Kim Jong-un faithfully inheritance, continuation and carry forward.
Although Kim Il Sung’s military strategy – pre-emptive attack strategy, with the strategy, quick fix strategy is based on conventional combat power to develop, but taking into account the status of North Korea’s weapons and equipment system and changes in modern war style, these military strategy will Will continue to continue. Based on the pre-emptive strike strategy, most of the troops of the Korean army are deployed in the front area. This will reduce the time required for the deployment, movement and take-over of the troops, thereby increasing the mobility of the force. Based on the strategy of cooperation, we can realize the effective cooperation between the Korean troops and the regular combat forces. This can improve operational effectiveness, weaken the other side of the military power, and then achieve the purpose of quick fix.
Second, the military characteristics of the military strategy: the pursuit of military adventurism
After the death of Kim Il Sung, North Korea’s biggest change in the military field is that North Korea has carried out nuclear development. North Korea, despite the strong opposition from the international community, is still engaged in nuclear development, its purpose is to the United States, the relationship between Korea, through the pursuit of military adventurism to take the initiative.
In December 2010, the Democratic People’s Armed Forces Minister Kim Yong-chun pointed out that the Korean Revolutionary Armed Forces had been prepared to launch the “nuclear-based jihad-based jihad” when necessary. North Korea’s revolutionary armed forces not only to resist aggression, but also sweep the enemy base camp, to eliminate the root causes of war, and then realize the reunification of the motherland history. In addition, the DPRK in 2009 set up a new reconnaissance General Administration, to further strengthen the role of external intelligence departments and functions. As can be seen from these initiatives in the DPRK, North Korea is strengthening military adventurism on the Korean Peninsula, based on the evolving military power.
North Korea’s pursuit of military adventurism, mainly for the following reasons: First, the historical experience to tell North Korea, the pursuit of military adventurism is very necessary. North Korea believes that the late 20th century, the late 60s to capture the US armed spy ship “Pueblo” incident and shot down the US EC-121 reconnaissance plane incident, North Korea and the United States confrontation made a major victory. Therefore, it can be said that these two events have become North Korea continue to promote the main cause of military adventurism. Second, trying to urge the international community to recognize North Korea as a military power. The DPRK believes that public military demonstrations or military provocation can be carried out to demonstrate to the international community its military power. In other words, North Korea in advocates, have a strong military strength in order to attract people’s attention, building a strong army is the power of the country. Thirdly, a powerful army can be used as an effective means of strengthening internal unity within its system. North Korea believes that a military provocation in the vicinity of the northern limit line or the armistice can create a military crisis within the DPRK, and this sense of crisis can effectively enhance unity within North Korea.
In the following circumstances, North Korea is likely to take military adventurism action: First, the North-South exchange is interrupted, further escalation of military tensions. Second, the DPRK nuclear issue has not progressed, the DPRK-US relations have stalled and the relationship has deteriorated seriously. Third, Kim Jong-un system is unstable. Military adventurist actions include: the implementation of nuclear tests, the launch of long-range missiles, in the West Sea (South Korea’s western waters) and near the stop line to launch local provocation. North Korea believes that through these provocative activities, can enhance the unity of the people, consolidate and improve the Kim Jong-un system.
Third, the military strength of the military construction
(A) to maintain the military superiority of South Korea
Although North Korea is facing serious economic difficulties, it is still actively promoting the modernization of weapons and equipment, vigorously developing nuclear weapons, chemical weapons, missiles and other weapons of mass destruction, and strive to build a strategic weapon system, and promote a strong military power based on the construction of a strong power. Into 2000, North Korea not only to strengthen the standing forces, artillery units, armored forces, special operations forces have also been rapid development. According to South Korea’s 2010 Defense White Paper, compared with 2008, North Korea ground forces added four divisions and one motor brigade, an increase of more than 200 tanks.
* In order to facilitate the comparison of military forces between the North and the South, the Marine Corps equipment into the Army troops equipment project was calculated.
Source: Defense Department, Defense White Paper 2010 (Seoul: Republic of Korea Ministry of Defense, 2010) p.271.
North Korea believes that as long as the US military to withdraw from the Korean Peninsula, South Korea to maintain military superiority in the case, the DPRK can achieve the “unity of the South.” There is no doubt that North Korea has strengthened its military power and provided a reliable guarantee for its large-scale destruction and speed warfare. In addition, the DPRK also believes that the collapse of the former Soviet Union and China’s reform and opening up, resulting in North Korea’s back-up forces weakened. Based on this judgment, the DPRK began to strengthen the military building for the South Triangular Military Relations (Korea, the United States and Japan) to enhance its autonomous military response capability.
(B) to strengthen the containment strategy
1, nuclear development
North Korea received 10 kilograms to 15 kilograms of plutonium from the start of the 5 MWe nuclear reactor in Ningxia before the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) verification in June 1992. According to the analysis, North Korea has been using these plutonium to promote nuclear weapons research and development program. At present, North Korea has about 40 kilograms to 50 kilograms of plutonium, which can produce 6 to 9 nuclear weapons (the manufacture of a nuclear weapon requires 6 kg to 8 kg of plutonium). In addition, North Korea’s uranium (for the manufacture of atomic reactor nuclear fuel) reserves are very rich, the total burial of about 26 million tons, of which the amount of 4 million tons.
With regard to North Korea’s nuclear capabilities, the former head of the US National Nuclear Institute, Dr. Heck, wrote in the article “North Korea’s Lessons Learned in the Core Crisis” that North Korea has nuclear weapons manufacturing that is as powerful as the United States in Nagasaki, Japan ability. From the current situation, the DPRK is likely to have 4-8 pieces of primary nuclear weapons. On April 9, 2010, US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton said in a speech titled “Nuclear Nonproliferation” at the University of Louisville, Kentucky, that North Korea has six thousand nuclear weapons. This is the first time that US government officials have formally addressed the number of nuclear weapons owned by the DPRK in public. In March 2010, when he participated in political studies, political instructors pointed out that “North Korea is a country with nuclear weapons, although the United States is the world,” the Korean People’s Army in South Korea, in March 2010, Power, but not provoke North Korea, entirely because North Korea has nuclear weapons. ”
Therefore, North Korea can be considered independent of nuclear weapons manufacturing capacity, with the number of nuclear weapons for the 1-8. But so far, it is not clear to the extent to which the DPRK will carry nuclear weapons on its missiles to launch nuclear weapons technology to what extent.
On the issue of highly enriched uranium (HEU), on September 3, 2009, the former representative of the DPRK in the United States, Park Ji-yuan, pointed out that North Korea has successfully pilot uranium enrichment, the test has entered the final stage. If uranium enrichment is successful, it means that it can be produced with less, continuous mass production, and is not easily perceived by the outside world. The use of uranium in comparison with the way in which plutonium is used to make nuclear weapons is relatively simple and easy to achieve the miniaturization of nuclear weapons. In order to be able to carry nuclear weapons on field artillery or short-range missiles as tactical nuclear weapons to use, many nuclear-owned countries often choose to use uranium to create nuclear weapons. Compared with the development of conventional combat power, the development of nuclear weapons investment costs less, and can effectively compensate for the military power of the disadvantages. Therefore, the more weak national defense forces, in order to have the means to contain the war, with the military to carry out military confrontation, the more vigorously develop nuclear weapons.
It is not difficult to predict that North Korea will strive to improve its ability to strike short-range military targets by developing small-scale nuclear weapons. Han Peninsula battlefield lack of depth, so in the Korean Peninsula battlefield environment, compared with the long-range nuclear weapons, can be close combat tactical nuclear weapons can play a full role. In addition, the DPRK will also build a large-scale nuclear weapons production system, trying to establish its military power status.
2, chemical and biological weapons
From the 20th century, 80 years, the DPRK independent production of gas bombs and bacteriological weapons, with a certain degree of chemical and biological weapons attack capability. Since the 1990s, the DPRK has started to develop, produce and stockpile the chemical and biological (radioactive) weapons and materials, and has the capability of biochemical radiative warfare. At present, North Korea will 2,500 tons to 5,000 tons of chemical agents dispersed in six storage facilities, chemical weapons, the average annual production capacity of 4,500 tons. In addition, North Korea can also cultivate and produce 13 kinds of biological weapons such as anthrax, smallpox, cholera, typhoid, plague and so on. It is reported that these biological weapons training about 10 days, you can directly put into use.
North Korea’s biochemical weapons will use artillery, missiles, aircraft and other delivery tools. At the beginning of the war, the DPRK is likely to focus on the use of chemical weapons in the area, in order to destroy Han Jun’s defensive positions, to create favorable conditions for its attack. North Korea is also likely to use chemical and biological weapons to South Korea’s capitals, large cities and other densely populated areas to launch indiscriminate attacks, by triggering public panic to interfere with military operations.
3, missile development
In 1985, the DPRK experimented with an improved Scud-B missile with a range of 320 km to 340 km. In 1989, the Scout-500 missile with a range of 500 km was tested. In May 1993, the shooting range was 1,300 km Of the missile No. 1, in August 1998, a test of a 1,600 km to 2,500 km Dapu dong 1 missile, in July 2006 and April 2009 test of the intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) level of the Taipu hole 2 Missiles.
In 2004, North Korea successfully developed a range of 120 km KN-02-type short-range missiles, and carried out a combat deployment. In 2007, North Korea also deployed a medium-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with a range of more than 3,000 km using a mobile launcher. In 2010, the DPRK created a “new IRBM division”, the division under the People’s Army General Staff Missile Guidance Bureau. The reason why North Korea continues to develop a range of 3,000 km or more medium-range missiles, is to “something” to fight against the Korean Peninsula reinforcements, to prevent the US military and the Pacific region in the external combat power to the Korean Peninsula. Although the Korean missile range has increased significantly, but the accuracy is not high. As a result, the DPRK had to increase the number of missiles in order to strike the target effectively.
Source: Ministry of Defense, “Encyclopedia of weapons of mass destruction” (Seoul: Ministry of Defense, 2004), p.35; reference to “Defense White Paper 2010”.
North Korea’s ballistic missiles, not only able to attack South Korea, Japan, and even the United States are under its threat. North Korea in accelerating the development of the missile at the same time, but also actively promote nuclear development, which has aroused great concern of the international community. Because the DPRK once the ability to carry nuclear weapons on the missile, the threat range and destructive power will be greatly increased. In other words, if North Korea to achieve the miniaturization of nuclear weapons, that is, to create a nuclear weapons below 1 ton, it means that North Korea can be equipped with nuclear weapons in the use of ballistic missiles.
North Korea’s missile production capacity in the former Soviet Union and China’s technical guidance, through independent research and development has reached a considerable level. It is widely believed that North Korea’s missile manufacturing capacity ranks sixth in the world.
(C) to enhance the speed of quick fix
North Korea from the 20th century, 80 years, in order to implement the speed war, focus on strengthening the armored forces, mechanized troops. The late 1980s, the DPRK began to produce the former Soviet Union T-62 tank imitation – “Tianma” tank, this tank in the water depth of 5.5 meters can also successfully wading river. In addition, the DPRK also introduced, produced, deployed a 23 mm air gun. In 2009, North Korea successfully developed “Tianma” tank improved – “storm” tank, and the actual deployment of two “storm” tank brigade. The reason why North Korea attaches importance to the construction of mechanized forces, mainly in order to use the mechanized forces of the motor power and the impact of the speed of war. Over the past decade, North Korea has increased the deployment of more than 2,000 rockets (more than 3,100 doors to more than 5,100 doors) and more than 300 long-range artillery deployments in the vicinity of the Armed Forces (DME). The reason why the DPRK forward deployment of rockets and long-range artillery, is to the beginning of the war on the South Korean capital to focus on the fight.
The North Korean Navy is equipped with more than 810 ships, including combat ships, submarines, support ships and so on. Among them, about 60% of the ships deployed in front of the base. There are more than 290 ships, such as the ship’s combat ship, the missile boat, the torpedo boat, the fire support boat and so on. The support ship has more than 290 ships such as landing craft and hovercraft. The submarine has more than 70 vessels such as Romeo class submarine, shark class submarine and south class submarine The
With the technical support of Russia, the Korean Air Force assembled the MIG-29 fighter from the early 1990s. Since 1999, North Korea has introduced more than 40 MIG-21s from Kazakhstan. In addition, the DPRK has also introduced a new MI-8 helicopter from Russia. Including the main models MIG-19/21, IL-28, SU-7/25 and other 470 aircraft, including the Korean Air Force has a total of 1,650 aircraft.
Into 2000, the DPRK created a light infantry division, light infantry division under the front army. In addition, the former division of the light infantry brigade expansion for the light infantry regiment. In this way, the strength of the special forces of the DPRK significantly enhanced, the number of more than 20 million. The reason why North Korea strengthened the construction of special forces was to make a decision after taking full account of the reality of the Korean-American Joint Forces and the lessons learned from the war in Iraq. Most of the Korean special forces were deployed in Pyongyang and south of the mountain, so they could be used immediately in the early stages of the war. In order to train officers and men of the special combat capability, the DPRK in the division, military forces set up a special combat training ground. According to the Korean Peninsula combat environment continue to strengthen the night war, mountain warfare, street fighting and other special subjects training, making the troops of the special combat capability has been significantly improved. It is not difficult to predict that in the early days of the war, the DPRK will be through the tunnel, air, sea and other infiltration, the special forces focused on the rear area of Korea. In this way, through the active match, the war developed into a speed war.
North Korean troops to the front of the troops as the center, to strengthen the ground forces fire configuration. In addition, special forces are created or expanded. Through these efforts, the army’s first echelon of combat power can be greatly enhanced. This laid the groundwork for the Korean army to focus on the fighting in the early stages of the war.
After the death of Kim Il Sung, the DPRK in the development of nuclear weapons, missiles and other strategic weapons at the same time, the number and level of conventional combat power has also improved. It is widely believed that North Korea’s military power has grown rapidly. The DPRK has provided the necessary military capabilities and means to realize its military strategy by vigorously strengthening the quantity and quality of military forces.
The fourth part of the DPRK military action outlook
First, the Korean crisis situation evaluation
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, the socialist countries of Eastern Europe changed drastically. Today, the democratization of anti-dictatorship is spreading and spreading. In this complex international environment, has always been to maintain the dictatorship of the DPRK unprecedented unprecedented difficulties and pressure. The collapse of the former Soviet Union and China’s reform and opening up began to let North Korea doubt its powerful host country. 2011 in Egypt and Libya and other Middle East jasmine revolution occurred, so that North Korea’s sense of crisis further aggravated. At present, North Korea is building the hereditary system of the Jinjia dynasty, but also faces a series of internal and external crises.
From the perspective of the internal crisis of the DPRK, as long as the Kim Jong-un regime is unstable, then around the control of the regime, at any time there may be internal fighting. In addition, economic difficulties, food shortages and other issues may also lead to the discontent of the DPRK residents, leading to distraught inside the DPRK, social unrest.
From the DPRK’s external crisis level, the DPRK nuclear crisis worsened, the international community to increase sanctions against North Korea, will inevitably lead to North Korea’s economy is facing more serious difficulties. North Korea’s military provocation to South Korea has led to further tension in North-South relations, disruption of North-South exchanges and the possible occurrence of new North-South military conflicts. In addition, the communist circle, the collapse of long-term dictatorship, etc., at any time may spread to North Korea, and affect the stability of the Korean system.
When North Korea faces a crisis index, North Korea is more likely to take military action in order to maintain its institutional security. On the other hand, when North Korea faces a relatively low crisis index, North Korea is more likely to focus on strengthening its internal solidarity than military action. In other words, when the internal and external crisis is serious, North Korea will be through military action to strengthen internal control, to resist external threats and pressures, and strive to maintain its political stability. When the internal and external crises are moderate, North Korea will put the army into economic activity in order to get rid of serious economic difficulties. When the external crisis is serious, but the internal crisis is moderate, North Korea will take concrete military action to deal with external threats, and thus strengthen internal solidarity. When the external crisis is eased and the internal crisis is serious, the DPRK will use the army to strengthen its control over the population and ensure its stability.
Second, the military action outlook
If the DPRK launched a military provocation based on weapons of mass destruction, the DPRK’s crisis index would determine North Korea’s military operations. North Korea may take the military action can be divided into four types.

|
| Figure 3: Military operations in North Korea in different crisis situations. [Save to album] |
In the “situation I”, the DPRK will launch a comprehensive war. In this situation, the DPRK’s internal and external environment is extremely bad, in addition to launching a comprehensive war, there is no other way to choose. In other words, because of the issue of power inheritance, food problems, North Korea into a serious chaos, the North Korean system is facing a crisis of collapse. In addition, the DPRK-US relations are stalled by the DPRK nuclear issue, and there is no room for maneuver. In this case, the DPRK is likely to choose a comprehensive war that extreme behavior. At this time, North Korea will use strategic weapons – nuclear weapons and missiles threat to South Korea and the United States, and the use of conventional combat power to South Korea launched a large-scale destruction war and speed war. For North Korea, it is necessary to have a prerequisite for launching a comprehensive war, that is, the need for pre-approval and active assistance from China and Russia.
In the “situation II”, the DPRK will launch a local provocation to South Korea. In this situation, North Korea, although facing external and internal crises, but the external crisis is not very serious. In other words, although the DPRK faces external pressures due to nuclear problems, but this external crisis has not intensified. From the internal situation of the DPRK, the DPRK residents due to food difficulties and other issues, dissatisfaction. The whole regime was controlled by Kim Jong-un, but there was a trace of power struggle. At that time, the DPRK launched a military provocation in the area of the Armistice Line and the North Boundary Line (NLL), attempting to divert domestic contradictions, strengthen internal solidarity and further consolidate the Kim Jong-un system. 2010 “Cheonan ship incident” and “Yin Ping Island shelling incident”, is two typical examples. At that time, Kim Jong Il in order to establish its power inheritance system, launched a military provocation to South Korea.
Under “situation III”, the DPRK will take measures to ease military tension. In this situation, both the external crisis, or the internal crisis is not serious, tensions tend to ease. In other words, speaking abroad, the DPRK nuclear issue is moving in the direction of favoring the DPRK, and the economic problem has been solved to a certain extent. On the inside, Kim Jong-un system has been established and consolidated, political stability in North Korea, social stability, there is no power struggle. At this time, North Korea will promote similar to China’s reform and opening up the line, while taking measures to reduce armaments and other positive measures to establish a new relationship between Korea and the United States.
Under “condition IV”, the DPRK will carry out military force demonstrations. In this situation, North Korea’s external crisis is serious, and the internal crisis is not obvious. In other words, despite the existence of food problems within North Korea, but its internal control is very successful. To the outside world, the international community has intensified its pressure on the DPRK due to the nuclear issue, the export of illegal arms and human rights. The DPRK’s friendly forces – China and Russia, have stopped their support for North Korea or taken careless measures. Will be through nuclear tests and missile test to seek foreign political consultation approach. In addition, in order to highlight the role of Kim Jong-un, internal and external display of strong achievements in the construction of a strong country, North Korea may also continue to carry out nuclear tests or missile test activities.
From the above four conditions, the most likely to happen is the “situation II”, that is, North Korea launched a local provocation. At present, North-South relations are stalled. After the death of Kim Jong Il, Kim Jong-un system is full of instability and uncertainty. In order to alleviate the internal contradictions, North Korea is likely to launch a provocation to South Korea. In particular, if there is a power struggle within North Korea or the Kim Jong-un system is provocative or shocked, Kim Jong-un is likely to launch a provocative activity against South Korea in order to demonstrate his strong leadership while eradicating opposition. North Korea may choose to provoke the main way: the peninsula in the western waters or eastern waters using submarines to attack; occupation or shelling the West Sea (South Korea Sea) five islands; in the armistice zone manufacturing military conflict; the implementation of terrorist activities to create chaos in South Korea society Wait.
The most unlikely is “situation I”, that is, North Korea launched a comprehensive war. North Korea is very clear to launch a comprehensive war, means that joint efforts with the ROK and the United States to combat. Obviously, the level of combat effectiveness of the Korean army compared with the United States and South Korea, compared with the absolute disadvantage. Therefore, if the DPRK wants to launch a comprehensive war, is bound to need China and Russia’s full support and help. However, from the reality of the situation, Russia and China will not easily intervene in the Korean Peninsula war. After the disintegration of the former Soviet Union, the Russian national power injury, has not recovered. Therefore, it is difficult for Russia to carry out effective assistance to the DPRK. Although China stressed that North Korea and China are close neighbors, but China is unswervingly promoting reform and opening up, and actively promote economic growth. In this context, China is clearly reluctant to oppose the United States, involved in the Korean Peninsula war, destroy the hard-won peace and stability of the development environment.
Part 5 concluding remarks
Kim Jong Il regime in order to maintain the advantages of the military field of Korea, focusing on the development of nuclear weapons, missiles and other asymmetric combat capability. It can be said that the construction of military forces in North Korea fully embodies the large-scale destruction strategy, quick fix strategy, network strategy.
The “mass destruction strategy” is a strategy established to ensure that “something” is victorious. In 1994, the United States threatened to bomb North Korea’s nuclear facilities. This crisis has prompted the DPRK to establish a “mass destruction strategy” from the containment level has played a decisive role. “Quick war strategy” is based on Kim Il Sung’s military strategy established, the North Korean aviation forces, armored forces, mechanized forces, etc. will play a full role in the speed of war, the military structure is also around the military is conducive to maneuver And the preparation of the. Taking into account these factors, the DPRK will continue to maintain a quick strategy in the future for a long time. “Network strategy” is also the DPRK may adopt the military strategy. At present, North Korea has a considerable number of professional hackers, coupled with the United States, South Korea and other developed countries, military strategy is heavily dependent on computer networks. If North Korea’s “network strategy” can play a role, will directly affect the Korean-American joint forces to play.
The military strategy of the army is based on the military strategy of Kim Il Sung’s offensive concept, adding the military strategy of Kim Jong Il’s defense concept. That is, the military strategy of the army is Kim Jong-il in order to maintain its political stability and socialist system security made a specific choice. Kim Jong-il has repeatedly stressed that the modern war is a new form of war, which is characterized by a highly expanded three-dimensional warfare, information warfare, asymmetric warfare, non-contact warfare, precision combat, short time and decisive battle, and asked the troops to adapt Modern warfare ready to fight. It can be seen that Kim Jong-il has recognized the need to change the conventional tactics of the past and argues that it is possible to win in the future war only if he has adopted a new tactic that can deal with modern warfare. Therefore, it can be said that the DPRK’s military strategy fully reflects the Kim Jong-il military ideology of the war to carry out the method.
From the DPRK’s military strategic changes and the direction of the development of military forces, the DPRK’s most likely future military action is to launch a local provocation to South Korea. In the case of the instability of the Kim Jung-en regime and the stalemate in North-South relations, it is possible for the DPRK to launch local provocations in the vicinity of the Western Seas (South Korea’s western waters) or near the armistice, as well as possible long-range missile tests, nuclear tests, etc. To seek institutional security. Through these military and military actions, the DPRK tried to divert internal contradictions, strengthen internal solidarity and consolidate the regime. As South Korea, in the face of various threats and complex situations, the need to develop a specific, effective and practical response to the program.
Original Mandarin Chinese:
第一部分 前 言
20世纪八十年代末90年代初,东欧剧变,苏联解体,社会主义阵营遭受巨大挫折。20世纪90年代中期,朝鲜经济突然陷入衰退。1994年7月,金日成逝世。当时,人们普遍认为朝鲜面临着严重危机,对朝鲜发展前景颇为堪忧。尽管如此,朝鲜经历了三年“苦难的行军”,并继续进行导弹试射与核试验等活动,不断强化其军事力量。
进入2000年后,朝鲜先后挑起了第2次、第3次西海交战,进行了两次核试验,并实施了数次导弹试射。2010年,朝鲜又在西海(韩半岛西部海域)制造了“天安舰事件”和“延坪岛炮击事件”。朝鲜的这些军事挑衅行动,不但给韩国,还给周边国家带来不安,同时也给东北亚的安全形势带来了很大的变数,并成为引发地区军备竞争的重要因素。
1998年9月,金正日在其政权出台之际,高举建设“强盛大国”的旗帜,提出了新的政治口号-“先军政治”。至2011年12月17日金正日去世为止,他对朝鲜进行了长达17年的强权统治。金正日提出的“先军政治”是指一切以军事工作为先,一切以军事工作为重,在军事先行的原则下,解决革命和国家建设中的所有问题,把人民军队作为革命的栋梁,推进整个社会主义伟业的政治方式 。可以说,先军政治是金正日式的政治方式。其核心内容为,在金正日的领导下,朝鲜的军队积极应对经济困难、社会问题和安全危机,努力维护朝鲜式社会主义体制。“先军军事战略”是朝鲜为了让“先军政治”植根于朝鲜社会,一切以优先发展国防力量为目的,一切以优先保障国防建设为目的的金正日式的军事力量运用方法。
本文针对金日成去世后,金正日体制下的朝鲜军事战略发展变化情况展开研究,特别是将朝鲜不顾国际社会的强烈反对,依然进行核开发并拥有一定的核武器后的战略变化作为研究的重点。
第二部分 朝鲜军事战略
一、朝鲜军事战略的形成背景
朝鲜的军事战略是在金日成的军事战略思想基础上逐渐形成的。金日成军事战略思想可以说是正规战思想和游击战思想的融合。在中国和前苏联的抗日活动过程中,金日成积累了丰富的实践经验,这些为其军事战略思想的形成奠定了坚实的基础。在这些军事经验的基础上,金日成提出了“主体战法 ”,并强调“主体战法”是朝鲜特有的军事战略。为了充分理解朝鲜的军事战略,研究金日成的军事经历是非常重要的。
1928年,金日成加入中国共产党青年同盟。之后,金日成作为中国共产党的一员,在东满洲、沿海州一带开展了敌后抗日活动。通过小汪清、老黑山、普天堡战斗等游击战,金日成从毛泽东军事思想中汲取了丰富的智慧和营养,逐步认识到渗透战、游击战、夜间战、敌后抗日活动、大部队和小部队间配合战术的重要性。金日成当时领导的敌后抗日活动,主要战斗样式为设伏、突袭等,只是属于战术范畴的游击战。但是,朝鲜将这些游击战样式一味夸大,宣传成大规模的战斗,即革命战争中的典型战例。正因为如此,今天的朝鲜军队依然非常重视游击战 。
20世纪40年代后期,迫于日本关东军的围剿扫荡,金日成不得不逃往前苏联,并被编入苏联红军。当时,金日成通过学习米哈伊尔•尼古拉耶维奇•图哈切夫斯基(1893年-1939年)元帅编写的《工农红军野外条令》,对统合军式的军事组织结构、以机动作战为主的战斗编成、火力为中心的武器装备体系等内容的苏联军队的正规战思想有了一定的认识。金日成在中国及前苏联的军事斗争经历,对于朝鲜发展以数量为主的军事力量,形成实施速度战、突袭战、配合战等的军事战略起到了非常重要的作用。通过韩国战争,朝鲜在其军事战略中增加了歼灭敌有生力量 的包围战,推进政治工作,确保战争物资等内容。通过局部冲突,朝鲜认识至增强配合战执行能力,强化机械化部队及空军力量的必要性。基于上述内容,朝鲜不断对遂行战争的方法加以补充与完善。
出处:朴容丸,“朝鲜军事战略问题研究”,《朝鲜学研究》第6卷1号(首尔:东国大学,2010), p.123。
二、金日成军事战略
1、先发制人奇袭战略
先发制人奇袭战略是指选择敌人完全无法预料,或者即便可以预料但是也没有时间做出反应的时机、场所和方法,向对方发动攻击的战略。先发制人奇袭战略可以最大限度地发挥突然性,以快速、秘密、伪装等方式进行。通常,实施奇袭作战,可以以最小的代价,获得最大的作战效果 。金日成曾多次强调,要做到奇袭成功,平时必须保持良好的战斗态势。不但如此,作战部队还要真正具备能够完全摧毁对方的作战能力。这意味着先发制人奇袭战略的目的是通过高效、快速的作战行动,在短时间内集中战斗力量,彻底摧毁敌作战力量。
为了实施先发制人的奇袭战,朝鲜将大部分的军事力量部署在前方地区。在部队编制结构上,也突出了快速反应、机动灵活的特点。特别值得一提的是,朝鲜将约70%的军事力量部署在平壤-元山线以南,如果朝鲜做出奇袭战的决定,那么朝鲜军队不用另外进行作战部署,就可以直接对韩国采取军事行动。
2、配合战略
“配合战略”是指在一次战斗中,两个以上的作战形态相互配合、相互协同的战略。配合战是金日成在毛泽东的游击战争思想基础上,总结越南战争的经验教训,并充分考虑韩半岛地形特点后,提出的所谓“主体战法”。配合战的核心是在大规模的正规战与游击战,大部队与小部队配合下,发动多种形式的攻击作战,这样的战场将无前后方可言,使得对方完全陷入混乱状态。
为了实施配合战,朝鲜建立了世界上最大规模的特种部队,并拥有AN-2机、气垫船、潜艇等多种海上、空中渗透手段。另外,朝鲜海军、空军还分别成立了狙击旅,考虑到不同军种的特点,不断加强配合战能力建设。朝鲜可能采取的配合战类型有正规战与游击战的配合,大部队与小部队间的配合,不同军种间的配合(陆海空军),不同兵种间的配合(兵种间),军队与人民武力间的配合(军队和民间资源)等。
3、速战速决战略
在传统的军事战略理论中,速战速决战略一直受到各方面的高度重视。速战速决战略是集中优势兵力,各个击破对方主力部队,在短时间内,以快速的战术取得胜利、结束战局的战略 。为此,朝鲜非常重视速战速决战略的发展,从20世纪80年代起,朝鲜集中力量建设装甲部队、机械化部队。为了实现速度战,朝鲜的部队结构编制也充分突出了快速反应、机动灵活的特点。朝军发动速度战的主要战力有坦克、装甲车、战斗机、常备兵力,与韩国相比,除了装甲车外,朝鲜在数量上明显占据优势。因此,如果朝鲜对韩国发动速度战,那么在数日内,朝鲜军队就可能席卷整个韩国,并阻断美军增援部队的介入。
三、对金日成军事战略的评价
金日成的军事战略是总结金日成在中国及前苏联的军事斗争经验基础上,综合考虑韩半岛的地形特征及局部战争作战样式后逐渐形成的。可以说,金日成的军事战略是攻势的进攻战略。特别值得强调的是,利用占据数量优势的常规战力,对韩国发动突袭攻击,进而掌握战争主导权,并在外部增援兵力抵达韩半岛之前结束战争的速战速决战略是金日成军事战略的核心。
目前,局部战争样式正在由长期战、消耗战、地面战为主转变为地面作战、海上作战、空中作战、太空作战、网络作战等一体化的全方位、多层次现代立体作战。另外,随着科学技术的发展,武器装备的破坏能力、远程精确打击能力大幅提升,使得战争样式正在发展成为快速集中精确打击样式。过去,战争的重点是利用常规军事力量赢得战争的胜利,争夺战争的主导权。而现代战争的重点是基于尖端的武器装备体系,实现战场数字化,高效发挥战斗力的整体效能。但是,金日成时期的军事战略只体现了常规战力的战争执行方式,朝鲜的核及导弹领域未被纳入其中。显然,金日成军事战略的局限性非常明显,无法适应现代战争的需要。军队是朝鲜维持政权,打击体制威胁势力的有效手段。因此,为了充分发挥军队的作用,金正日不得不提出全新的军事战略构想。
第三部分 先军时代的军事战略和军事力量建设
一、先军军事战略
金正日在向人民军下达的《学习提纲》中指出,现代战争是新的形态的战争,其特征为高度扩大的立体战、信息战(侦察战、电子战、网络战、心理战)、非对称战、非接触战、精确打击战、短时间速决战 。此外,金正日还强调,要做好新的战斗准备。从中可以看出,金正日已经充分认识到现代战争样式正在发生质的变化,并认为继续采用现有的常规战战法,无法保证未来战争的胜利。因此,在充分考虑现代战争样式的同时,为了发展可以应对韩美联合战力的军事力量,金正日构想了“大规模破坏战略”、“速战速决战略”、“网络战略”。
(一)、大规模破坏战略
大规模破坏战略是给对方带来巨大破坏力的战略,是“严惩报复战略”的一种。实现大规模破坏战略,需要具备超出对方的军事力量或者是具备能给对方带来决定性损失的军事手段。朝鲜用于大规模破坏战略的战力包括核武器在内的大规模杀伤性武器和炮兵部队。
大规模破坏战略是朝鲜为了保障“有事时”的作战胜利而制定的战略。1994年,朝鲜曾因美国威胁要对朝鲜的核设施进行军事打击而面临重大危机。可以说,这次危机的出现直接推动了金正日从遏制层面上制订大规模破坏的军事战略。
大规模破坏战略是拥有核武器的国家采取的最具代表性的战略。为了弥补“封锁战略”的不足,美国前总统艾森豪威尔曾提出了“大规模报复战略”。美国在拥有绝对核优势的基础上推行大规模报复战略,减少了国防开支,并在国际社会中确立了军事霸权地位。前苏联领导人赫鲁晓夫认为,在1962年的“古巴导弹危机”中,前苏联之所以遭到失败,主要原因是苏联与美国相比在核战力方面处于劣势。因此,赫鲁晓夫积极推进以核武器为主要战力的大规模报复战略,试图拥有与美国对等的军事实力。1964年,中国的第一颗原子弹爆炸成功后,中国的国际影响力、政治地位得到明显提升。可以说,通过核开发,采取遏制的报复战略,中国保护了自己国家的安全,并基于此确立了亚洲军事强国的地位。
如上所述,拥有核武器的国家,作为军事强国,可以在国际社会中占据优势地位。不但如此,还可以将核武器作为主要手段来推进大规模报复战略,以此来保证自己国家的安全。因此,朝鲜有可能会通过拥有核武器来推进大规模破坏战略。也就是说,大规模破坏战略不但可以使朝鲜有效应对各种外部威胁,还可以在“有事时”确保朝鲜取得胜利。6.25战争结束后,朝鲜与美国一直保持着停战状态。近几年,朝美关系因核问题、人权问题、伪钞问题等矛盾迭出、较量不断。在这种背景下,朝鲜认为随时都有可能与美国爆发战争。因此,朝鲜的大规模破坏战略极有可能在未来的朝美关系中发挥重要作用。
2006年,朝鲜劳动党宣传部副部长曾发表谈话称,一旦战争爆发,整个首尔将在30分钟内变成一片火海,10万名美军、70%的南朝鲜居民面临死亡,韩国经济的90%以上化为灰烬 。2010年7月24日,朝鲜国防委员会也曾发出威胁称,将在必要的时候启动基于核遏制力的朝鲜式的报复“圣战”。这意味着,“有事时”朝鲜将会利用大规模杀伤性武器来发动攻击。
(二)速战速决战略
金正日时期的“速战速决战略”是在外部势力增援韩半岛前结束战争的战略,是金日成战略的继承、延续与发展。海湾战争、阿富汗战争、伊拉克战争中,“速战速决战略”曾被广泛使用。很明显,通过“速战速决战略”,可以集中攻击并摧毁敌对国家的指挥设施及主力部队,掌握战争主导权,并在很短时间内胜利结束战争。之所以认为朝鲜将采用速战速决战略,主要理由如下:
1、朝鲜拥有相当规模的可以发动速度战的作战力量
朝鲜的装甲部队和机械化部队具备高度的机动能力,能够给对方造成强烈的冲击力与威慑力,炮兵部队可以集中打击敌核心目标,能够给对方造成极大的损失和破坏。朝鲜速度战的主要战力—装甲部队是韩军的1.7倍,炮兵部队是韩军的2.5倍。
2、朝鲜的部队编制整体上有利于机动作战
尽管朝鲜经济上面临诸多困境,但是朝鲜一直在加强军事力量建设。近年来,不但朝军的兵力规模和装备持续增加,部队结构改编时,也非常注重机动作战能力的建设。据韩国2010年发表的国防白皮书称,为提高部队战斗力,朝鲜整编部分军队,将两个机械化军整编为机械化师,将1个坦克军整编为装甲师,将1个炮兵军整编为炮兵师。此外,朝鲜还加强了前方部队的火力打击能力建设 。朝鲜军队的这些变化,为其实施速度战提供了可靠的保证。
3、朝鲜军队的大部分战斗力部署在前方地区
朝鲜在平壤-元山线以南地区前进部署了10多个军、60多个师/旅,约占朝鲜军队总体战斗力的70%。这样,只要朝鲜领导层下定决心,那么朝鲜军队不用重新调整部署,就可以随时投入到南侵作战中。2009年11月,第三次西海(韩半岛西部海域)海战发生后,朝鲜军队在其西海岸集中部署了240毫米火箭炮,对韩国西海及首都圈构成了直接威胁。可以说,朝鲜在前方部署大量军队的目的是为了在开战初期集中发动攻击,通过速度战重创韩国军队。
朝鲜强调,随着传统战争样式的变化,非线性作战、非接触作战等新的作战方式正在出现,现代战争可能会在前方和后方同时展开。这意味着朝鲜正规部队在前方发动正面攻击的同时,朝鲜特种部队可能向韩国后方地区发动干扰作战。不可否认,战场前后方同时展开,将对战争的速战速决起到决定性的作用。
4、网络战略
网络攻击是指利用计算机网络存在的漏洞和安全缺陷,对敌方军事、行政、人事等主要系统和资源发动的攻击,通常也被称为“没有枪声的战争”。随着计算机技术的快速发展及网络中心战概念的提出,现代战争的中心正在由传统的作战平台转向网络。从近几年的局部战争样式中也可以看出,网络作战正在作为战争的主要形态之一,起到了非常重要的作用。
2009年,金正日在朝鲜军队高级将领演讲会上发表谈话称,二十世纪的战争是油和炮弹的战争,二十一世纪的战争是信息战争。由此也可以看出,朝鲜非常重视网络战争。
网络攻击主要有两种方式 。第一种为非法侵入对方的信息系统,窃取系统保密信息、破坏目标系统数据的方式。第二种为不侵入对方信息系统,在外部破坏对方信息系统,使其功能无法发挥作用的方式。
从20世纪90年代起,朝鲜在平壤指挥自动化大学、计算机技术大学、金策工业综合大学等大力培养专业网络战人才。平壤指挥自动化大学隶属于人民军总参谋部,是朝鲜最具代表性的网络战人才培训机构,每年为军队培养出100多名计算机专业技术人员。据推测,朝鲜军队拥有的专业黑客规模达500名至600名。
美国、韩国等发达国家的军事战略严重依赖计算机网络。如果朝鲜发动网络攻击,就很容易导致韩国的网络系统出现混乱,影响到信息的传递与共享。在关键时刻,甚至还可能瘫痪整个网络,使韩国错过应对时机,从而给韩国带来致命的打击。在战争爆发前,朝鲜可能会在国内或海外,通过黑客入侵方式攻击韩国政府机关的网络。在战争期间,朝鲜还有可能干扰、破坏韩军的计算机网络,导致军队的整个计算机网络数据传输中断和系统瘫痪。
朝鲜的网络战略同样会对心理战产生积极影响。关于伊拉克战争,朝鲜认为,美帝之所以能够在伊拉克战争中取得胜利,与其说是高新技术武器发挥作用,不如说是心理战在发挥作用,并从思想上瓦解伊拉克导致的结果。从中可以看出,朝鲜非常重视心理战,并认为在未来战争条件下,心理战将贯穿于战争的全过程。朝鲜通过网络展开的心理战样式主要包括:在敌对国家或者支援国家网络上散布有利于朝鲜的信息及流言蜚语,甚至是假情报(细菌战、化学战、使用核武器、出现大规模伤亡)等,从而给敌对国家的公众带来恐慌,削弱敌对国家的战争意志。对于支援国家,通过大力制造反战舆论,迫使支援国家中止兵力增援,并尽早撤出已投入的兵力。
先军军事战略的主要特征是在金日成攻击性战略的基础上,为了维持政权,增加了防护性战略的内容。也就是说,金正日通过先军政治建立起来的先军军事战略,将由他的继承人金正恩去忠实地传承、延续和发扬。
虽然金日成时期的军事战略—先发制人奇袭战略、配合战略、速战速决战略是在常规战力基础上制定的,但是考虑到朝鲜武器装备体系的现状以及现代战争样式的变化,这些军事战略将会继续维持下去。基于先发制人奇袭战略,朝鲜军队的大部分兵力部署在前方地区。这样可以缩短部队部署、移动及接敌需要的时间,从而提高部队的机动性。基于配合战略,可以实现朝鲜军队正规战兵力与非正规战兵力的有效配合。这样可以提高作战效能,弱化对方军事力量,进而达成速战速决的目的。
二、先军军事战略的特征:追求军事冒险主义
金日成去世后,朝鲜在军事领域的最大变化是朝鲜进行了核开发。朝鲜不顾国际社会的强烈反对依然进行核开发,其目的就是在对美、对韩关系中,通过追求军事冒险主义来占据主动地位。
2010年12月,朝鲜人民武力部部长金永春指出,朝鲜革命武装已做好各种准备,在必要的时候将展开“基于核遏制力的朝鲜式圣战”。朝鲜革命武装不但要抵御侵略,还要扫荡敌大本营,消除战争根源,进而实现祖国统一的历史伟业 。此外,朝鲜在2009年新组建了侦察总局 ,进一步强化对外谍报部门的作用和职能。从朝鲜的这些举措中可以看出,朝鲜基于不断发展的军事力量,正在强化在韩半岛的军事冒险主义。
朝鲜之所以追求军事冒险主义,主要有如下原因:第一、历史的经验告诉朝鲜,追求军事冒险主义是非常必要的。朝鲜认为,20世纪60年代后期发生的捕获美国武装间谍船“普韦布洛”号事件和击落美国EC-121侦察机事件,是朝鲜与美国对峙中取得的重大胜利。因此,可以说,这两起事件成为朝鲜继续推进军事冒险主义的主要动因。第二、试图促使国际社会承认朝鲜是军事强国。朝鲜认为,公开进行军事武力示威或者发动军事挑衅活动,可以向国际社会展示其军事力量。也就是说,朝鲜在主张,拥有强大的军事实力才能引起人们的重视,建设强大的军队才是强国之本。第三、强大的军队可以用作强化其体制内部团结的有效手段。朝鲜认为,在北方限界线或者停战线附近发动军事挑衅,可以在朝鲜内部营造军事危机局面,而这种危机意识可以有效增强朝鲜内部的团结。
在如下情况下,朝鲜有可能采取军事冒险主义行动:第一、南北交流中断,军事紧张局势进一步升级。第二、朝鲜核问题毫无进展,朝美关系陷入僵局,关系严重恶化。第三、金正恩体制不稳定。军事冒险主义行动包括:实施核试验、发射远程导弹、在西海(韩国西部海域)及停战线附近发动局部挑衅。朝鲜认为,通过这些挑衅活动,可以增进人民内部团结,巩固与完善金正恩体制。
三、先军时代军事力量建设
(一)维持对韩国的军事优势
尽管朝鲜面临严重的经济困难,但是依然积极推进武器装备现代化建设,大力发展核武器、化学武器、导弹等大规模杀伤性武器,努力构建战略武器体系,推进基于强大军事力量的强盛大国建设。进入2000年后,朝鲜不但加强常备兵力建设,炮兵部队、装甲部队、特种作战部队等也得到了快速发展。据韩国2010年国防白皮书称,与2008年相比,朝鲜地面部队新增了4个师和1个机动旅,增加200多辆坦克。
*为了方便南北军事力量比较,将海军陆战队装备纳入陆军部队装备项目中进行了计算。
出处:国防部,《国防白皮书2010》(首尔:大韩民国国防部,2010)p.271.
朝鲜认为,只要美军撤出韩半岛 ,在保持对韩军事优势的情况下,朝鲜就可以实现“对南赤化统一”。无疑,朝鲜强化军事力量,为其实施大规模破坏战和速度战提供了可靠的保证。另外,朝鲜还认为前苏联崩溃和中国的改革开放,造成朝鲜的后援势力变弱。基于这种判断,朝鲜开始针对南方三角军事关系(韩国、美国、日本)大力加强军备建设,以提高其自主的军事应对能力。
(二)强化遏制战略
1、核开发
朝鲜从启动宁边5MWe核反应堆,到1992年6月接受国际原子能机构(IAEA)核查前,共获得了10 公斤至15 公斤的钚 。据分析,朝鲜一直利用这些钚来推进核武器研发计划。目前,朝鲜大约拥有40 公斤至50 公斤的钚,这些可以生产6枚至9枚核武器(制造1枚核武器需要 6 公斤至8 公斤的钚)。另外,朝鲜的铀(用于制造原子反应堆核燃料)储量非常丰富,整个埋藏量约2,600万吨,其中可采量为400万吨。
关于朝鲜的核能力,美国前国立核研究所所长赫克博士在《朝鲜在核心危机中学到的教训》一文中指出,朝鲜具备与美国在日本长崎投放的那颗原子弹相同威力的核武器制造能力。从目前的情形来看,朝鲜极有可能拥有初级核武器4-8枚。2010年4月9日,时任美国国务卿希拉里•克林顿在肯塔基州路易斯维尔大学发表题为《核不扩散》的演讲中称,据判断,朝鲜拥有 1-6枚核武器。这是美国政府官员首次在公开场合正式论及朝鲜拥有的核武器数量。2010年3月,通过东部战线归顺韩国的朝鲜人民军***在证词中称,2010年1月,他在参加政治学习时,政治教官曾指出“朝鲜是拥有核武器的国家,美国虽然是世界强国,但是不敢招惹朝鲜,完全是因为朝鲜拥有核武器”。
因此,可以认为朝鲜具备自主的核武器制造能力,拥有的核武器数量为1-8枚。但是,到目前为止,尚不清楚朝鲜将核武器搭载于导弹上进行发射的核武器小型化技术究竟发展到什么程度。
关于高浓缩铀(HEU)问题,2009年9月3日,朝鲜驻联合国前任代表朴吉渊曾指出,朝鲜已成功进行试验性铀浓缩,试验已进入最后阶段。铀浓缩若取得成功,意味着可以以较少的投入,连续进行大量生产,而且还不易被外界察觉 。与使用钚制造核武器的方式相比,使用铀的话,核武器的起爆装置制造起来会相对简单,而且还便于实现核武器小型化。为了能够将核武器搭载于野战炮或短程导弹上作为战术核武器来使用,很多核拥有国往往会选择使用铀来制造核武器。与发展常规战力相比,发展核武器投入的费用较少,并且能够有效弥补军事力量上的劣势。因此,越是国防力量薄弱的国家,为了具备遏制战争的手段,能够与大国进行军事对抗,越会大力发展核武器。
不难预计,朝鲜今后将努力通过发展小型化核武器,来提升对近距离军事目标的打击能力。韩半岛战场缺乏纵深,因此在韩半岛战场环境下,与远程核武器相比,能够进行近距离打击的战术核武器更能充分发挥作用 。另外,朝鲜还将通过构筑大规模的核武器生产体系,试图确立其军事强国的地位。
2、生化武器
从20世纪80年代起,朝鲜自主生产毒气弹和细菌武器,具备了一定程度的生化武器攻击能力。20世纪90年代起,朝鲜开始研发、生产及储备化生放(化学、生物、放射性) 武器和物资,具备了生物化学放射战执行能力。目前,朝鲜将2,500吨到5,000吨的化学作用剂分散保管在6个储藏设施中 ,化学武器的年均生产能力为4,500吨。另外,朝鲜还能够培养和生产炭疽菌、天花、霍乱、伤寒、瘟疫等13种生物武器。据悉,这些生物武器培养10天左右,就能直接投入使用。
朝鲜的生化武器将使用火炮、导弹、飞机等各种投放工具。开战初期,朝鲜极有可能在停战线一带集中使用化学武器,以此来摧毁韩军的防御阵地,为其发动攻击创造有利条件。朝鲜还有可能使用生化武器对韩国的首都圈、大城市等人口密集区发动无差别攻击,通过引发公众的恐慌心理来干扰军事作战。
3、导弹开发
朝鲜于1985年试射了射程为320公里至340公里的改进型飞毛腿-B型导弹,1989年试射了射程为500公里的飞毛腿-C型导弹,1993年5月试射了射程为1,300公里的劳动1号导弹,1998年8月试射了射程为1,800公里至2,500公里的大浦洞1号导弹,2006年7月和2009年4月试射了洲际弹道导弹(ICBM)水平的大浦洞2号导弹。
2004年,朝鲜成功研发射程为120公里的KN-02型地对舰短程导弹,并进行了实战部署。2007年,朝鲜又实战部署了利用移动式发射架发射的射程超过3,000公里的中程弹道导弹(IRBM)。2010年,朝军创建了“新型IRBM师”,该师隶属于人民军总参谋部导弹指导局。朝鲜之所以持续研发射程3,000公里以上的中程导弹,就是为了“有事时”打击向韩半岛增援的兵力,阻止美军及在太平洋地区活动的外部战力向韩半岛移动。虽然朝鲜的导弹射程有了明显增加,但是精确度并不高。因此,朝鲜为了对目标实施有效打击,不得不增加导弹的拥有数量。
出处:国防部,《大规模杀伤性武器问答百科》(首尔:国防部,2004年), p.35;参考《国防白皮书2010》。
朝鲜的弹道导弹,不但能够攻击韩国、日本,甚至包括美本土都在其威胁之下。朝鲜在加快导弹开发的同时,还积极推进核开发,这已引起了国际社会的高度关注。因为朝鲜一旦有能力在导弹上搭载核武器,其威胁范围及破坏力将会大幅增加。也就是说,朝鲜若能实现核武器小型化,即制造出1吨以下的核武器时,那就意味着朝鲜可以将核武器搭载在弹道导弹上来使用。
朝鲜的导弹生产能力在前苏联和中国的技术指导下,通过自主研发已达到相当的水平。普遍认为,朝鲜的导弹制造能力位居世界第六位。
(三)提升速战速决能力
朝鲜从20世纪80年代起,为了实施速度战,集中加强装甲部队、机械化部队建设。20世纪80年代末期,朝鲜开始生产前苏联T-62型坦克的仿制型-“天马号”坦克,这种坦克在水下5.5米深度也能够成功涉水渡河。此外,朝鲜还引进、生产、部署了23毫米对空火炮。2009年,朝鲜成功研制“天马号”坦克的改进型-“暴风号”坦克,并实战部署了2个“暴风号”坦克大队。朝鲜之所以重视机械化部队建设,主要是为了利用机械化部队的机动力和冲击力展开速度战。最近十年,朝鲜又增加部署了2,000多门火箭炮(从3,100多门增加到5,100多门),另外还在非武装地带(DME)附近地区部署了300多门远程火炮。朝鲜之所以前进部署火箭炮和远程火炮,就是为了在开战初期对韩国的首都圈进行集中打击 。
朝鲜海军装备有810多艘舰艇,包括战斗舰、潜艇、支援舰等。其中,约60%的舰艇部署在前方基地。水面战斗舰有警备舰、导弹艇、鱼雷艇、火力支援艇等420多艘,支援舰有登陆舰、气垫船等290多艘,潜艇有罗密欧级潜艇、鲨鱼级潜艇、南联级潜艇等70多艘。
在俄罗斯的技术支援下,朝鲜空军从20世纪90年代初起组装生产MIG-29最新式战斗机。1999年起,朝鲜从哈萨克斯坦引进了40多架MIG-21。另外,朝鲜还从俄罗斯引进了新型MI-8直升机。包括主力机种MIG-19/21, IL-28,SU-7/25等470多架飞机在内,朝鲜空军共拥有1,650架飞机。
进入2000年后,朝鲜创建了轻步兵师,轻步兵师隶属于前方军。另外,前方师的轻步兵大队扩编为轻步兵团。这样,朝鲜的特种部队实力明显增强,人数达20多万名。朝鲜之所以加强特种部队建设,是在充分考虑韩美联合部队战力优势现实及吸取伊拉克战争教训后,做出的决定。朝鲜特种部队大部分部署在平壤和元山以南地区,因此在开战初期就能马上投入使用。为了训练官兵的特种作战能力,朝军在师、军级部队设立了特种作战训练场。朝军根据韩半岛作战环境不断加强夜战、山岳战、巷战等特种科目的训练,使得部队的特种作战能力得到了明显提升。不难预计,在战争初期,朝鲜将通过地道、空中、海上等渗透方式,把特种兵力集中投放到韩国后方地区。这样,通过积极的配合战,使战争发展为速度战。
朝鲜军队以前方部队为中心,加强地面部队火力配置。另外,还创建或扩建特种部队。通过这些努力,朝军第一梯队的作战力量得以大幅增强。这为朝鲜军队在战争初期集中战斗力实施速度战打下了基础。
金日成去世后,朝鲜在发展核武器、导弹等战略武器的同时,常规战力的数量和水平也有所提升。普遍认为,朝鲜的军事力量得到了快速增长 。朝鲜通过大力加强军事力量的数量、质量建设,为实现其先军军事战略提供了必要的军事能力和手段。
第四部分 朝鲜军事行动展望
一、朝鲜危机状况评价
20世纪80年代末90年代初,东欧社会主义国家发生剧变。今天,反独裁政权的民主化抵抗运动正在蔓延和扩散。在这种复杂的国际环境下,一直以来维持独裁政权的朝鲜空前感到了巨大的困难和压力。前苏联的崩溃和中国的改革开放,开始让朝鲜怀疑其强大的后援国。2011年在埃及和利比亚等中东地区发生的茉莉花革命 ,使朝鲜的危机感进一步加重。目前,朝鲜正在构建金家王朝的世袭体制,但也面临着一系列的内外危机。
从朝鲜的内部危机层面来看,只要金正恩政权不稳定,那么围绕控制政权,随时都有可能发生内部争斗。另外,经济困难、粮食短缺等问题还可能引发朝鲜居民的不满情绪,从而导致朝鲜内部人心涣散、社会动荡不安。
从朝鲜的外部危机层面来看,朝鲜核危机恶化,国际社会加大对朝鲜的制裁力度,必将导致朝鲜经济面临更加严重的困难。朝鲜对韩发动军事挑衅活动,导致南北关系进一步紧张,南北交流中断,并可能发生新的南北军事冲突。另外,共产圈国家、长期独裁国家的崩溃等,随时都有可能波及朝鲜,并影响到朝鲜体制的稳定。
当朝鲜面临的危机指数升高时,为了维持其体制安全,朝鲜更有可能采取军事行动。与此相反,当朝鲜面临的危机指数相对较低时,比起采取军事行动,朝鲜更可能将精力放在加强其内部团结上。也就是说,当内部、外部危机严重时,朝鲜将会通过军事行动来加强内部管制,抵御外部威胁及压力,努力维护其政权稳定。当内部、外部危机出现缓和时,朝鲜将会把军队投入到经济活动中去,以期摆脱严重的经济困境。当外部危机严重,但是内部危机缓和时,朝鲜将会采取具体的军事行动来应对外部威胁,并以此加强内部团结。当外部危机出现缓和,内部危机严重时,朝鲜将会利用军队加强对居民的管制,并确保其体制稳定。
二、军事行动展望
如果朝鲜基于大规模杀伤性武器发动军事挑衅的话,朝鲜的危机指数将决定朝鲜的军事行动类型。朝鲜可能采取的军事行动大体上可分为四种类型。
在“状况I”下,朝鲜将发动全面战争。在这种状况下,朝鲜的对内、对外环境极度恶化,除了发动全面战争之外,别无其他方法可以选择。也就是说,因权力继承问题、粮食问题等,朝鲜陷入严重混乱,朝鲜体制面临崩溃的危机。另外,朝美关系因朝核问题陷入僵局,无回旋余地。这种情形下,朝鲜极有可能会选择全面战这种极端的行为。这时,朝鲜将利用战略武器—核武器和导弹威胁韩国和美国,并使用常规战力对韩国发动大规模破坏战和速度战。对于朝鲜而言,若要发动全面战还需要一个前提条件,即需要获得中国和俄罗斯的事前同意和积极援助。
在“状况II”下,朝鲜将对韩国发动局部挑衅。在这种状况下,朝鲜虽面临外部及内部危机,但是外部危机情况并非十分严峻。也就是说,尽管朝鲜因核问题等面临外部压力,但是这种外部危机并没有激化。从朝鲜的内部情况来看,朝鲜居民因粮食困难等问题,不满情绪高涨。政权整体上虽由金正恩所控制,但是出现了权力斗争的迹向。这时,朝鲜在停战线和北方限界线(NLL)一带发动军事挑衅,试图转移国内矛盾,加强内部团结,进一步巩固金正恩体制。2010年的“天安舰事件”和“延坪岛炮击事件”,就是两个典型的例子。当时,金正日为了确立其权力继承体制,发动了对韩军事挑衅活动。
在“状况III”下,朝鲜将采取缓解军事紧张的措施。在这种状况下,无论是外部危机,还是内部危机均不严重,紧张局势趋于缓和。也就是说,对外来讲,朝核问题朝着有利于朝鲜的方向发展,经济问题得到了一定程度的解决。对内来讲,金正恩体制得到了确立及巩固,朝鲜政治稳定,社会安定,内部没有权力斗争。这时,朝鲜将会推进类似于中国的改革开放路线,同时采取裁减军备等积极措施,以确立新的对韩、对美关系。
在“状况Ⅳ”下,朝鲜将进行军事武力示威。在这种状况下,朝鲜的外部危机严重,而内部危机不明显。也就是说,尽管朝鲜内部存在着粮食困难等问题,但是其内部管制非常成功。对外来讲,国际社会因核问题、非法武器出口问题、人权问题等加大了对朝鲜的施压力度,朝鲜的友好势力—中国和俄罗斯中止对朝鲜的支援或采取不理睬措施时,朝鲜将会通过核试验及导弹试射来寻求对外政治协商的途径。另外,为了凸显金正恩的作用,对内对外展示强盛大国建设的辉煌成就,朝鲜也有可能会继续进行核试验或导弹试射活动。
从以上四种状况来看,最有可能发生的是“状况II”,即朝鲜发动局部挑衅活动。目前,南北韩关系陷入僵局。金正日去世后,金正恩体制充满了不稳定性和不确定性。为了缓解内部矛盾,朝鲜很有可能发动对韩挑衅活动。特别地,如果朝鲜内部出现权力斗争,或者金正恩体制受到挑衅或冲击,金正恩为了展示其强大的领导力,在铲除反对势力的同时,极有可能会发动对韩国的挑衅活动。朝鲜可能选择的挑衅方式主要有:在半岛西部海域或东部海域利用潜艇发动攻击;占领或炮击西海(韩国西部海域)五岛;在停战线一带制造军事冲突;实施恐怖活动,给韩国社会制造混乱等。
最不可能发生的是“状况I”,即朝鲜发动全面战争。朝鲜很清楚发动全面战争,意味着与韩美联合战力进行作战。显然,朝鲜军队的战斗力水平与韩美联合战力相比,处于绝对劣势。因此,朝鲜若想发动全面战争,势必需要得到中国和俄罗斯的全力支持和大力帮助。但是,从现实的情况来看,俄罗斯和中国都不会轻易介入韩半岛战争。前苏联解体后,俄罗斯国力大伤, 一直没有恢复元气。因此,俄罗斯很难对朝鲜进行有效的援助。中国虽然强调朝鲜与中国是唇齿相依的友好邻邦,但是中国正在坚定不移地推进改革开放,积极促进经济增长。在这种背景下,中国显然不愿意与美国对立,介入韩半岛战争,破坏来之不易的和平稳定发展环境。
第五部分 结束语
金正日政权为了保持对韩军事领域的优势,重点发展核武器、导弹等非对称战力。可以说,朝鲜的军事力量建设充分体现了大规模破坏战略、速战速决战略、网络战略。
“大规模破坏战略”是为了确保“有事时”作战胜利确立起的战略。1994年,美国威胁要对朝鲜的核设施进行轰炸。这一危机,促使朝鲜从遏制层面确立“大规模破坏战略”起到了决定性的作用。“速战速决战略”是在金日成军事战略的基础上确立的,朝鲜的航空部队、装甲部队、机械化部队等将在速度战时充分发挥作用,朝军的部队结构也是围绕有利于机动作战而编制的。综合考虑这些因素,朝军将在今后相当长的时间内,继续维持速战速决战略。“网络战略”同样是朝鲜可能会采用的军事战略。目前,朝鲜拥有相当数量的专业黑客,再加上美国、韩国等发达国家的军事战略严重依赖计算机网络。如果朝鲜的“网络战略”能够发挥作用,将会直接影响韩美联合部队作战力的发挥。
先军军事战略是在金日成攻势概念的军事战略基础上,增添了金正日防御概念的军事战略。即,先军军事战略是金正日为了维护其政权稳定和社会主义体制安全做出的具体选择。金正日曾多次强调,现代战争是新的形态的战争,其特征是高度扩大的立体战、信息战、非对称战、非接触战、精确打击战、短时间速决战,并要求部队为适应现代战争做好战斗准备。从中可以看出,金正日已认识到改变过去那种常规战法的必要性,认为只有采取能够应对现代战争的新的战法,才有可能在未来战争中取得胜利。因此,可以说,朝鲜的先军军事战略充分反映了金正日军事思想的战争遂行方法。
从朝鲜的军事战略变化和军事力量发展方向来看,朝鲜今后最有可能采取的军事行动是发动对韩国的局部挑衅。在金正恩政权不稳定、南北关系陷入僵局的情况下,朝鲜有可能在西海(韩国西部海域)或者停战线附近发动局部挑衅活动,也有可能进行远程导弹试射、核试验等来展示武力,以此来谋求体制安全。朝鲜通过这些军事武力行动,试图转移内部矛盾,加强内部团结,巩固金正恩政权。作为韩国,面对各种威胁及复杂情况,需制订具体的、有效的、切实可行的应对方案。
Original URL:
http://mil.sohu.com/20130701/