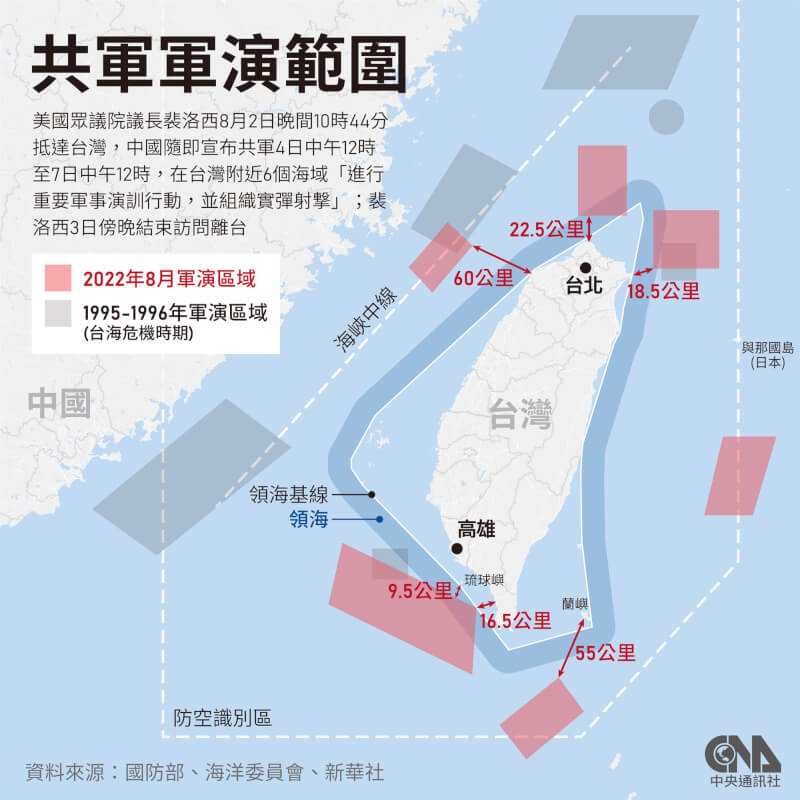
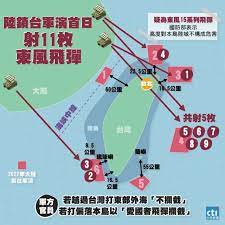
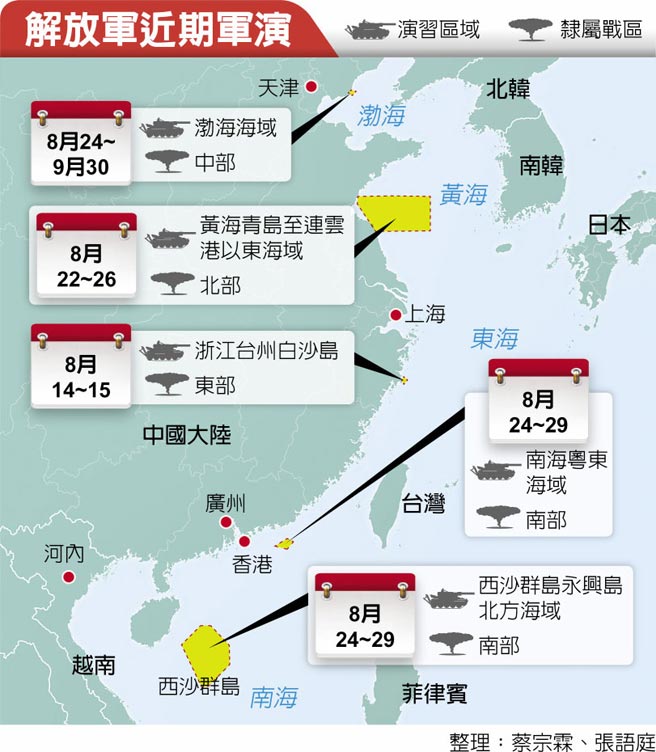
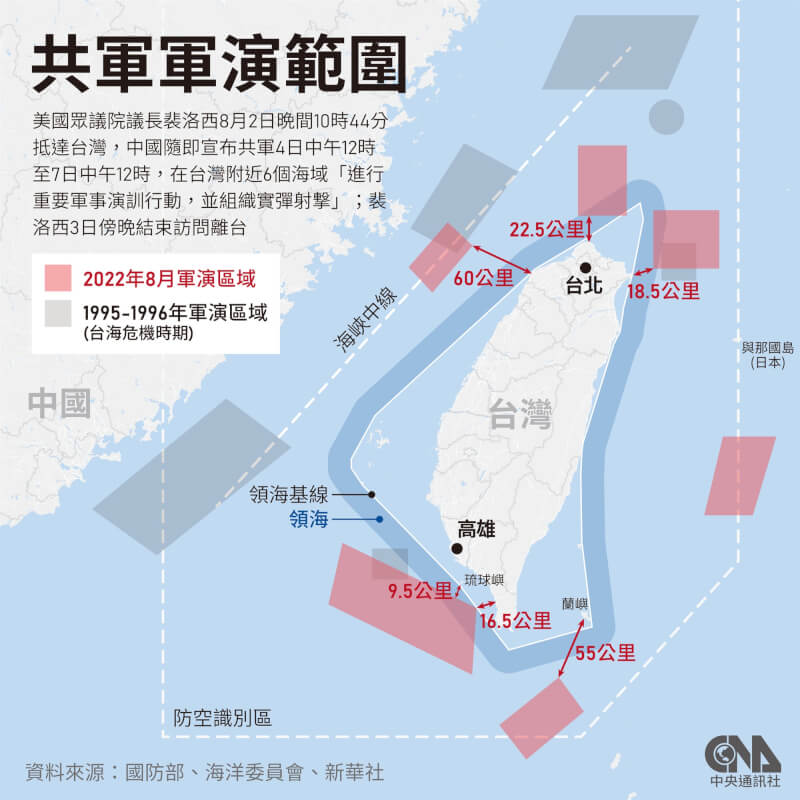
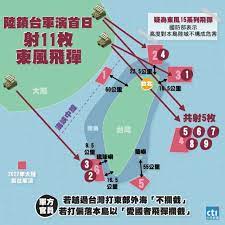
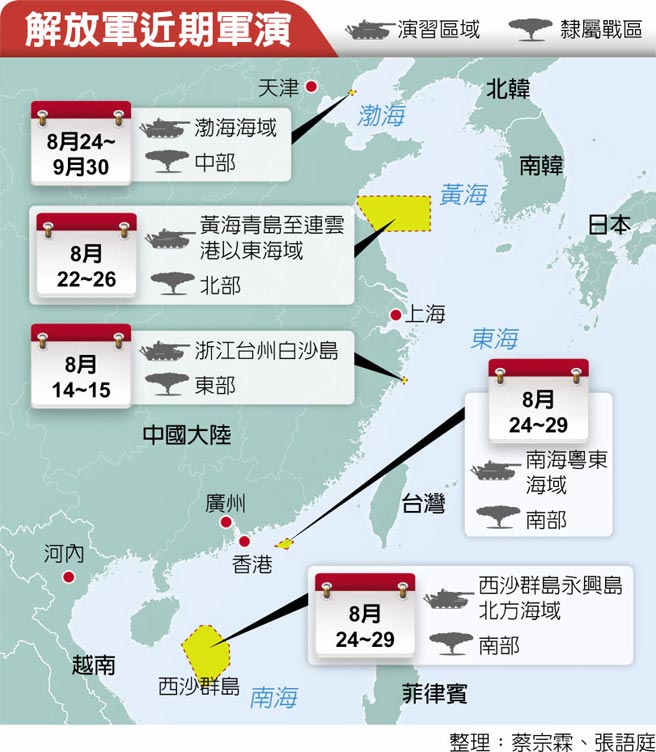
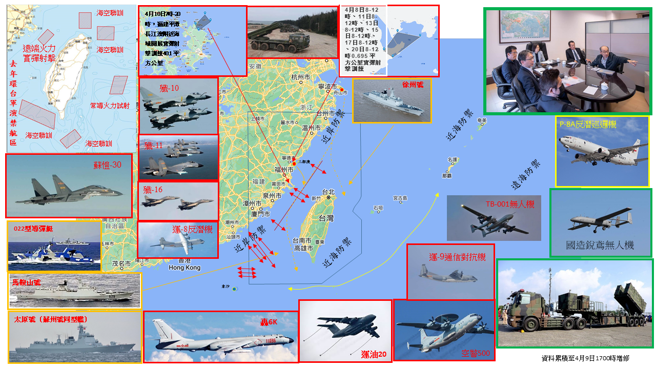
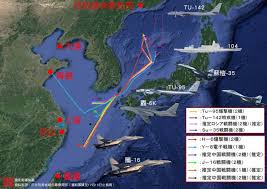
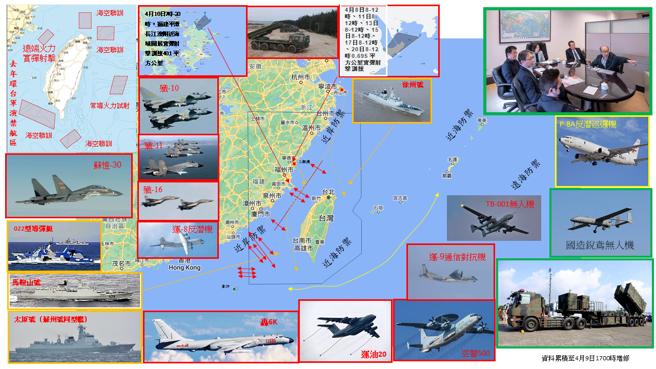
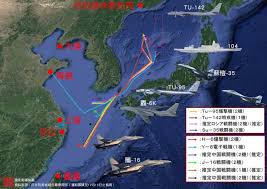
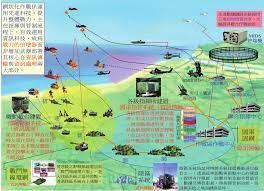
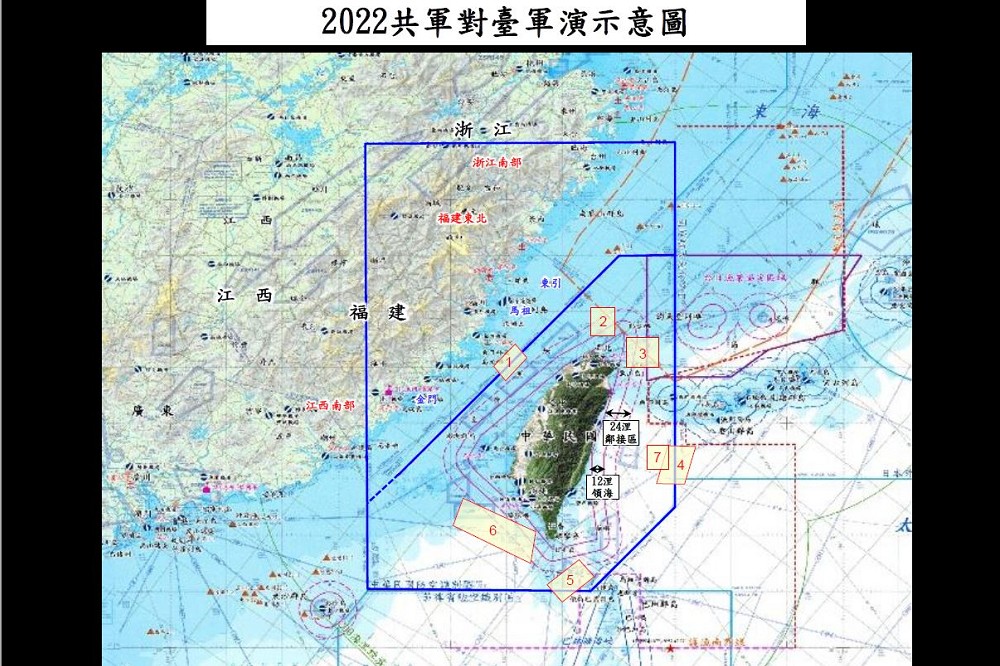
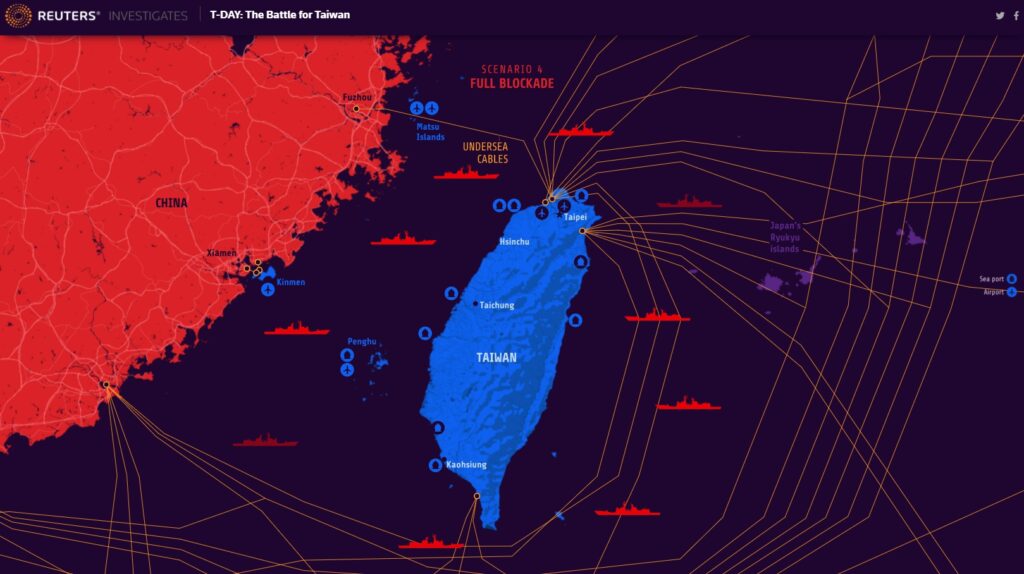
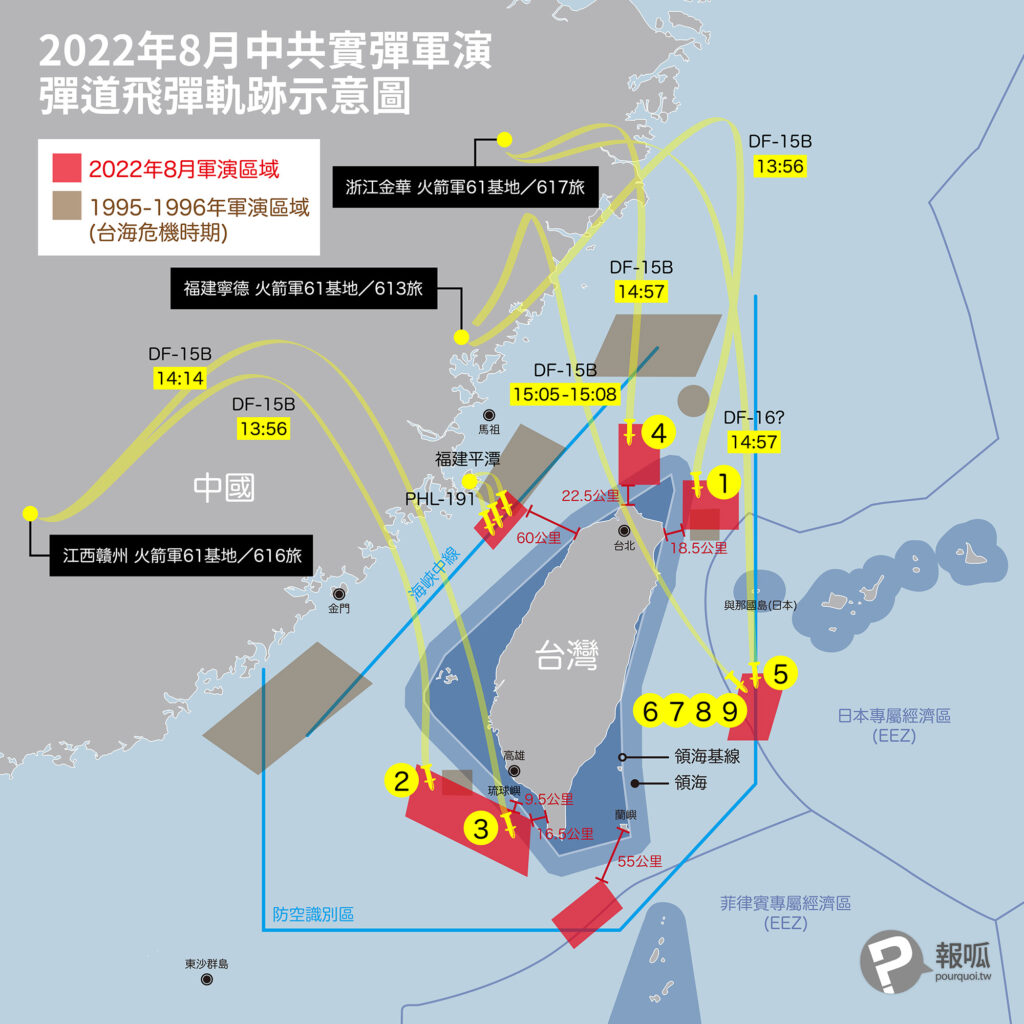
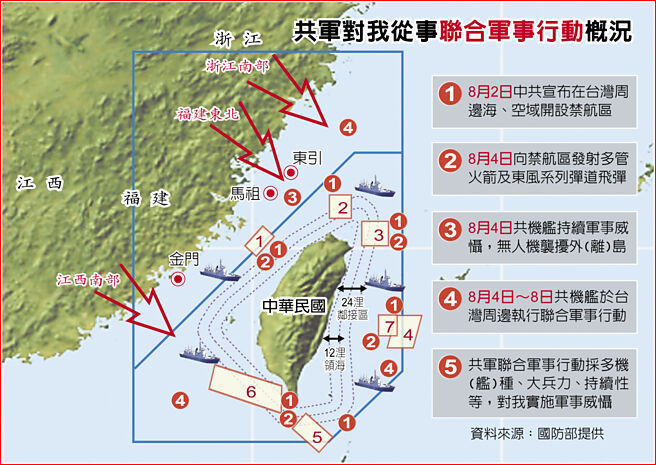
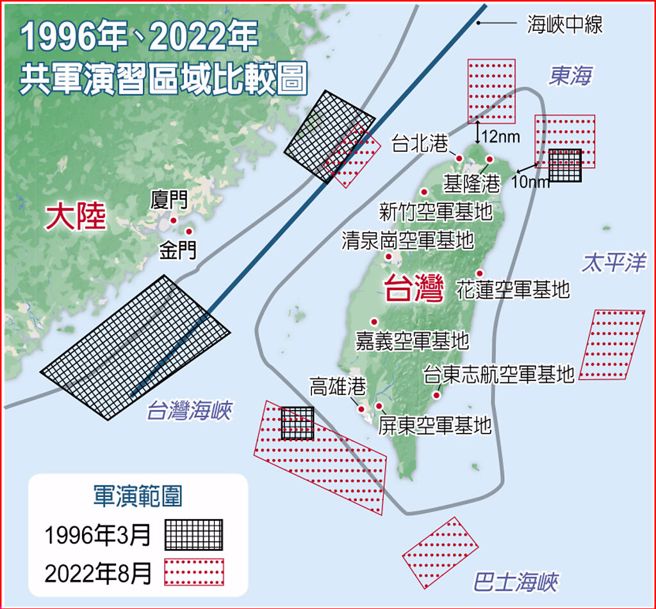
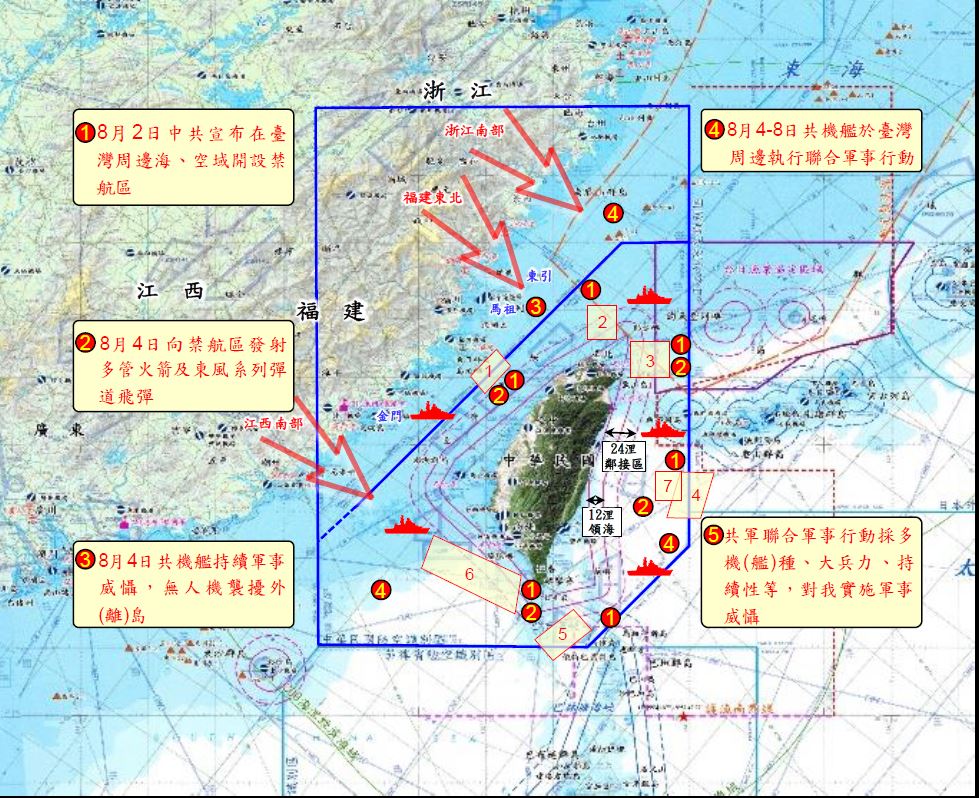
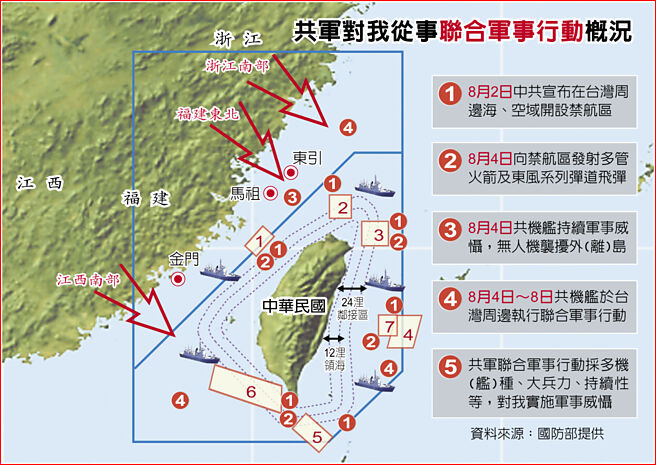
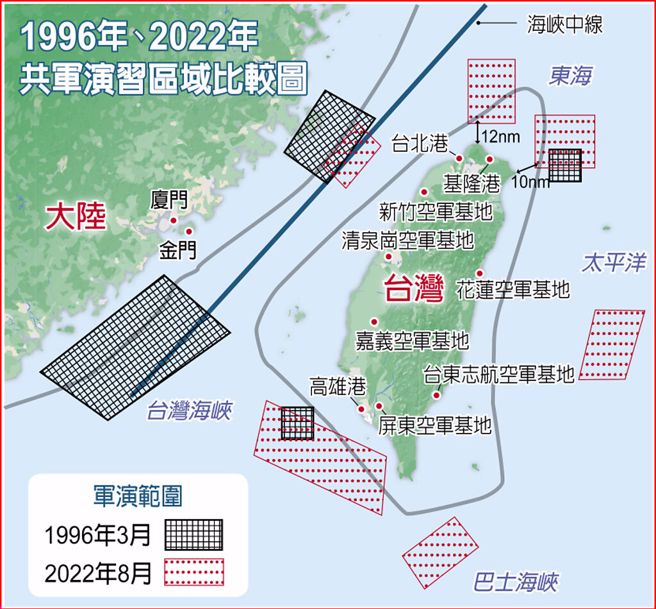
中國軍事認知域作戰的重點是什麼、重點在哪裡?
劉曙光
2022年10月05日08:00 | 來源:解放軍報
音譯外語 – 英語:
●Cognitive domain operations focus on full-dimensional attacks, including both “peacetime” cognitive penetration and “wartime” cognitive coercion.
●Wartime cognitive domain operations revolve around the achievement of military objectives, and are implemented in conjunction with military operations to support each other.
●In cognitive domain operations, as the sound of gunfire dissipates, the horn of a new round of cognitive domain operations may sound again, and there must be no slacking off.
Cognitive domain warfare is a confrontation at the level of conscious thinking. Through selective processing and transmission of information, it affects judgment, changes concepts, and competes for people’s hearts, thereby guiding the real situation to develop in a direction that is beneficial to oneself. From the perspective of cognitive shaping, cognitive domain operations focus on full-dimensional attacks, including both “peacetime” cognitive penetration and “wartime” cognitive coercion. Therefore, cognitive domain operations have no clear boundaries between peace and war; at the same time, according to the needs of political or military purposes, its targets can be individuals, organizations or even countries. Therefore, cognitive domain operations should establish the concepts of peacetime and wartime integration, military-civilian integration, cross-domain integration, and joint victory, and sort out basic tasks accordingly.
Focus on ideological layout tasks
Ideology is “an ideological system that systematically and consciously reflects the socio-economic formation and political system.” Ideology determines the rational foundation of cognition and has distinct camp characteristics. Although ideology covers all aspects of social life, in confrontations between countries or political groups, the struggle around belief guidance, attitude struggle, and concept assimilation is particularly fierce, and has become a focus of cognitive domain operations.
Shape and guide political cognition and seize control of belief and establishment. Confrontation between countries or political groups is not only a confrontation of national strength, but also a confrontation of national aspirations. The confrontation of political beliefs bears the brunt. Shaping and guiding political cognition aims to condense or destroy political consensus, strengthen or shake political beliefs, and expand or dissolve political camps. In cognitive domain operations, through cognitive guidance on the legitimacy of the ruling party, the rationality of political ideas and systems, and the health of the political ecology, we cultivate recognition, denial, and support of political positions, beliefs, practices, etc. Or hatred and other emotions, laying out a political cognitive layout that is beneficial to oneself and detrimental to the enemy. Political cognition is related to the survival foundation of a country or organization and is the primary focus of cognitive domain operations.
Shape and guide war cognition and seize the right to lead war attitudes. A country can be without war, but it cannot be without a sense of war. War cognition is the basis for the formation and development of the will, concepts, psychology, and thinking of individuals, organizations, and countries in the war cycle. Through cognitive guidance on the essence, nature, legal concepts, etc. of war, we build a war cognitive thinking system, guide the evaluation direction of the rationality, justice, and legality of war, promote the formation of support or opposition attitudes towards possible wars, and regulate The rise and fall of willingness to assume war obligations is a key issue in cognitive guidance of war. War cognition affects war attitudes, and the struggle for its control is a task that must be paid attention to in cognitive domain operations.
Shape and guide value cognition and seize control of emotions and will. Values influence people’s judgment of beauty and ugliness, right and wrong, and social behavior orientation. In terms of identifying things and judging right and wrong, human emotions always tend to support claims with similar values. Value cognition permeates every corner of life. Through the dissemination of ethical concepts, standards of beauty, ugliness, good and evil, literary and artistic opinions, etc., competition for the right to guide values, the right to guide life patterns, and the right to judge traditional inheritance is frequent and fierce. . In real life, different values often interpenetrate and entangle with each other. The essence of shaping and guiding value cognition is to strive for social and emotional recognition, which is a regular task in cognitive domain operations.
Pay close attention to social psychology and the task of building momentum
Social psychology provides a perceptual and experiential basis for cognition. It is formed on the basis of daily life, social activities, practical insights and other experiences. Social psychological guidance often promotes unpredictable changes in the actual situation. It is one of the usual modes of confrontation between the two sides, especially during non-military conflicts. It is also a task that must be paid attention to in cognitive domain operations.
Guide national psychology and regulate national emotions. National psychology is one of the social psychology that is most likely to cause conflicts and confrontations. Attacking national self-esteem can breed national inferiority complex and easily lead to disintegration. Improving national self-esteem can enhance national cohesion, but the expansion of national self-esteem can easily lead to the emergence of extreme racism, national chauvinism, etc.; the status, interests, and culture of different ethnic groups within the country Differences in people, customs, and lifestyles provide opportunities for people with ulterior motives to stir up ethnic antagonisms, while the same living space and cooperation process lay the foundation for eliminating prejudice and even cohesion and tolerance among ethnic groups. The result depends on the perception. Know the guide. National psychological guidance is sensitive and easy to lose control, and has a direct impact on social stability. It is a task that needs to be focused on in cognitive domain operations.
Guide group psychology and increase and eliminate oppositional consciousness. Groups generally refer to people of the same type, such as ethnicity, region, class, professional groups, even civil society groups, non-governmental organizations, etc. If groups are subjectively defined based on “convergence”, then the “differences” between groups exist objectively. This difference may be political and economic status, cultural thought, regional concept or other factors. Inducing the perception of differences and promoting the antagonism between different groups such as party opposition, regional opposition, professional opposition, rich and poor opposition, etc. will not only damage the internal unity of the country, but also accumulate and increase the dissatisfaction of all sectors of society against the political authorities, and instigate social mobilization. The turbulence and division left behind a foreshadowing. In cognitive domain operations, this kind of social psychology needs to be paid attention to.
Guide individual psychology and influence social emotions. In cognitive domain operations, individual psychological guidance is divided into two situations. One is the psychological guidance of important figures, such as sensitive professionals, public intellectuals, academic elites, successful business people, etc. The struggle for their political positions, emotional attitudes, etc. is an issue that both sides of the confrontation need to focus on. One is the use of phenomena that easily trigger individual psychological resonance. Such as public crises, major accidents, natural disasters and even some crimes and emergencies in life, intentionally inducing certain emotions may cause group polarization due to the herd effect of individuals, thus triggering changes in public opinion and even social unrest. Both of these aspects need to be paid attention to in cognitive domain operations.
Targeting the critical mission of wartime cognition
Cognitive domain operations begin before military operations and end after military operations. Wartime cognitive domain operations revolve around the achievement of military objectives, are implemented in conjunction with military operations and support each other, and are characterized by violent coercion. In this stage of cognitive domain operations, “offensive” and “defensive” actions are carried out simultaneously, the influence of weapons and propaganda effects are comprehensively effective, and methods such as “lure”, “attack”, “deception” and “control” are emerging one after another. This is the key to cognitive domain operations. critical stage.
Attack the mind and seize the will, force and induce cognition. Wartime cognitive attacks are mainly carried out to weaken the enemy’s will to resist and induce the enemy to make wrong decisions. Targeting the enemy’s decision-makers, front-line commanders, etc., use targeted attacks to shake the will to resist, and use information deception and interference to induce decision-making. Targeting armed forces, mainly the military, use force to shock and deter, and comprehensively use operations such as public opinion warfare and emerging technologies. Means are used to shake their belief in participating in the war, trigger their panic, undermine their military morale, and dominate their action patterns; targeting social support forces, conveying tough messages to undermine confidence through large-scale military exercises, equipment testing, propaganda of weapon lethality effectiveness, etc., and through selective Target strikes and dissemination of war situations can induce panic, and efforts can be made to gain understanding by publicizing one’s own humanitarian actions in the war and relevant international comments.
Build a strong line of defense and control the situation with concentration. The focus of cognitive defense in wartime is to build a strong defense line of “heart”, “will” and “intellect” to prevent the loss of fighting spirit under the stimulation of drastic changes in the situation or environment. Education and publicity are the basic approaches to cognitive defense in wartime. For the forces participating in the war, stimulate enthusiasm for participating in the war through mobilization and encouragement, clarify the truth by refuting rumors, establish the belief in victory by publicizing the results of the war, mobilize morale by setting examples, etc.; for the supporting forces, educate the justice, rationality, and legality of the war. Propaganda is used to establish a sense of mission, responsibility, and obligation among the people, to inspire a sense of hatred and hatred by exposing the enemy’s brutal behavior, to stimulate enthusiasm for supporting operations by publicizing the deeds of local governments participating in the war and supporting frontline operations, and so on.
Expand your camp and eliminate hidden dangers. Creating a favorable cognitive atmosphere and providing support for the expansion of one’s own camp is an important aspect that must be achieved in wartime cognitive domain operations. In particular, the fight for international support is mainly through political, diplomatic and other activities, but the widespread diffusion of one’s own positions, ideas, attitudes, etc. often leads to changes in international civil attitudes, which in turn affects decision-making at the political level. Provide support for your own camp expansion. In addition, wartime cognitive domain operations also have an important task throughout the war, which is to eliminate the adverse hidden dangers caused by various accidents in the war. Especially in the later stages of the war, as the destructive effects of war appear and spread, people’s cognitive system will be repeatedly impacted by different information. During this period, ideological guidance, social psychological shaping, and individual psychological counseling are required to work together to ensure the consolidation of the results. In cognitive domain operations, as the sound of guns dissipates, the horn of a new round of cognitive domain operations may sound again, and there must be no slacking off.
原創中文軍事繁體中文:
●認知領域作戰聚焦全維度攻擊,既包括「平時」認知滲透,也包括「戰時」認知強制。
●戰時認知域作戰圍繞著軍事目標的實現,與軍事行動結合實施,相互支持。
●在認知域作戰中,隨著槍聲消散,新一輪認知域作戰的號角可能會再次吹響,絕不能有絲毫懈怠。
認知域戰是意識思維層面的對抗。 透過對訊息的選擇性加工和傳遞,影響判斷,改變觀念,爭奪人心,從而引導現實形勢向有利於自己的方向發展。 從認知塑造的角度來看,認知域作戰著重全維度攻擊,既包括「和平時期」的認知滲透,也包括「戰時」的認知強制。 因此,認知域作戰在和平與戰爭之間沒有明確的界線; 同時,根據政治或軍事目的的需要,其目標可以是個人、組織甚至國家。 因此,認知域作戰應樹立平戰融合、軍民融合、跨域融合、共同勝利的理念,並相應梳理基礎任務。
聚焦思想佈局任務
意識形態是「系統性地、自覺地反映社會經濟形態和政治制度的思想體系」。 意識形態決定認知的理性基礎,具有鮮明的陣營特質。 儘管意識形態涵蓋了社會生活的各個層面,但在國家或政治團體之間的對抗中,圍繞著信仰引導、態度鬥爭、觀念同化的鬥爭尤為激烈,成為認知域作戰的焦點。
塑造和引導政治認知並掌控信仰和體制。 國家或政治團體之間的對抗,不僅是國家實力的對抗,更是民族願望的對抗。 政治信仰的對抗首當其衝。 塑造和引導政治認知,旨在凝聚或破壞政治共識、強化或動搖政治信念、擴大或消解政治陣營。 在認知域操作中,透過對執政黨合法性、政治理念和製度合理性、政治生態健康狀況的認知引導,培養對政治立場、信念、實踐等的認可、否定和支持。或仇恨等情緒,佈置出有利己不利敵的政治認知佈局。 政治認知關係到一個國家或組織的生存基礎,是認知領域運作的首要關注。
塑造和引導戰爭認知,掌握戰爭態度引領權。 一個國家可以沒有戰爭,但不能沒有戰爭意識。 戰爭認知是個人、組織、國家在戰爭週期中意志、觀念、心理、思考形成和發展的基礎。 透過對戰爭的本質、性質、法律概念等的認知引導,建構戰爭認知思維體系,引導對戰爭合理性、正義性、合法性的評價方向,促進對可能發生的戰爭形成支持或反對態度。承擔戰爭義務意願的盛衰是戰爭認知引導的關鍵問題。 戰爭認知影響戰爭態度,對其控制權的競爭是認知域作戰必須重視的任務。
塑造和引導價值認知,抓住情感和意志的控制。 價值觀影響著人們對美醜、是非的判斷以及社會行為取向。 在辨識事物和判斷是非方面,人類的情感總是傾向於支持具有相似價值觀的主張。 價值認知滲透到生活的各個角落。 透過倫理觀念、美醜善惡標準、文學藝術觀點等的傳播,對價值引導權、生活方式引導權、傳統傳承判斷權的爭奪頻繁而激烈。兇猛的。 。 現實生活中,不同的價值觀常常互相滲透、糾纏。 塑造和引導價值認知的本質是爭取社會和情感認可,這是認知領域中運作的常規任務。
密切關注社會心理和造勢任務
社會心理學為認知提供了感性和經驗基礎。 它是在日常生活、社會活動、實踐感悟和其他經驗的基礎上形成的。 社會的
心理疏導往往會促使實際情況發生不可預測的變化。 這是雙方通常的對抗模式之一,特別是在非軍事衝突期間。 這也是認知域操作中必須重視的任務。
引導民族心理,調節民族情緒。 民族心理是最容易引起衝突和對抗的社會心理之一。 攻擊民族自尊,會滋長民族自卑感,容易導致民族解體。 提高民族自尊可以增強民族凝聚力,但民族自尊的膨脹很容易導致極端種族主義、民族沙文主義等的出現; 國內不同民族的地位、利益、文化、民俗、生活方式的差異,為別有用心的人煽動民族對立提供了機會,而相同的生存空間和合作進程,則為消除偏見和發展奠定了基礎。甚至族群之間的凝聚力和包容性。 結果取決於感知。 了解指南。 國民心理疏導敏感、容易失控,直接影響社會穩定。 這是認知域操作中需要重點關注的任務。
引導群體心理,增加和消除對立意識。 群體一般指同一類型的人,如種族、地區、階級、職業群體,甚至民間團體、非政府組織等。如果群體是基於「趨同」來主觀定義的,那麼群體之間的「差異」群體是客觀存在的。 這種差異可能是政治經濟地位、文化思想、地域觀念或其他因素。 誘導差異認知,助長黨派反對派、地區反對派、職業反對派、貧富對立等不同群體之間的對立,不僅會損害國家內部的團結,還會積累和增加各方的不滿情緒。社會各界反對政治當局,並煽動社會動員。 動盪和分裂留下了伏筆。 在認知域操作中,需要關注這種社會心理。
引導個體心理,影響社會情緒。 在認知域操作中,個別心理引導分為兩種情況。 一是重要人物的心理疏導,如敏感專業人士、公共知識分子、學術精英、成功商界人士等,他們的政治立場、情感態度等鬥爭是對抗雙方都需要重點關注的問題。 一是利用容易引發個體心理共鳴的現象。 例如公共危機、重大事故、自然災害甚至生活中的一些犯罪和突發事件,刻意誘發某些情緒可能會因個體的羊群效應而造成群體極化,從而引發輿論變化甚至社會動盪。 認知域操作中需要注意這兩方面。
瞄準戰時認知的關鍵使命
認知域操作在軍事行動之前開始,在軍事行動之後結束。 戰時認知域作戰圍繞著實現軍事目標,與軍事行動結合實施、相互支持,具有暴力強制的特質。 此階段的認知域作戰,「進攻」和「防禦」行動同時進行,武器影響力和宣傳效果綜合有效,採用「誘」、「攻」、「欺騙」、「控制」等手段。 」紛紛湧現。 這是認知域操作的關鍵。 關鍵階段。
攻心奪意志,強行誘發認知。 戰時認知攻擊主要是為了削弱敵方抵抗意志、誘導敵方做出錯誤決策而進行的。 針對敵方決策者、第一線指揮等,利用定向攻擊動搖抵抗意志,利用資訊欺騙和乾擾誘導決策。 針對以軍隊為主的武裝力量,以武力震懾、威懾,綜合運用輿論戰、新興技術等作戰手段。 用手段動搖他們的參戰信念,引發他們的恐慌,削弱他們的軍心,主導他們的行動模式; 針對社會支持力量,透過大規模軍事演習、裝備測試、武器殺傷效能宣傳等方式傳遞強硬訊息,破壞信心,透過選擇性地進行目標打擊、傳播戰況,引發恐慌,努力
透過宣傳自己在戰爭中的人道主義行動和相關國際評論來獲得理解。
構築堅固防線,集中力量掌控事態。 戰時認知防禦的重點在於建構「心」、「意志」、「智」的堅固防線,防止在局勢或環境急劇變化的刺激下喪失鬥志。 教育和宣傳是戰時認知防禦的基本途徑。 對參戰力量,透過動員激勵激發參戰熱情,透過闢謠澄清真相,透過宣傳戰爭成果樹立勝利信念,透過樹立榜樣調動士氣等; 對支援部隊進行戰爭正義、合理、合法性教育。 宣傳是為了在人民群眾中建立使命感、責任感、義務感,透過揭露敵人的殘暴行徑,激發仇恨感和仇恨感,透過宣傳地方政府參戰事蹟,激發支援作戰熱情以及支援前線行動等等。
擴大你的營地並消除隱患。 營造良好的認知氛圍,為己方陣營的擴張提供支持,是戰時認知領域作戰必須做到的重要面向。 特別是,爭取國際支持主要是透過政治、外交等活動,但自身立場、理念、態度等的廣泛傳播,往往會導致國際民間態度的變化,進而影響各國的決策。政治層面。 為您自己的營地擴展提供支援。 此外,戰時認知域作戰還有一項貫穿整場戰爭的重要任務,就是消除戰爭中各種意外事件造成的不良隱患。 尤其是在戰爭後期,隨著戰爭破壞性效應的顯現和蔓延,人們的認知系統會一再受到不同資訊的衝擊。 在此期間,需要思想引導、社會心理塑造、個人心理疏導等共同努力,確保成果的鞏固。 在認知域作戰中,隨著槍聲消散,新一輪認知域作戰的號角可能會再次吹響,絕不能有絲毫懈怠。
中國原創軍事資源:http://military.people.com.cn/BIG5/n1/2022/1005/c1011-32539888.html