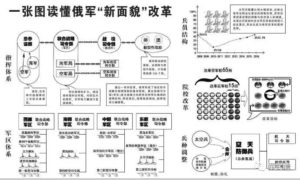
Russian Ministry of Defense set up information operations forces to deal with Western networks – psychological attacks // 俄國防部組建信息作戰部隊 應對西方網絡-心理攻擊
With the Russian and Western cyber space in the game is becoming increasingly fierce, especially in the 2018 Russian presidential election near the background, the Western countries for Russia’s network and information / psychological attacks increasing. To this end, Russia to strengthen the network and information security construction. At the end of 2016, the revision of the new edition of the Russian Federation Information Security Theory. February 27, 2017, Russian Defense Minister Shaoyou announced the formation of information operations forces, accelerate the construction of information combat forces, clear its functional mission.
First, the new theory clearly set up the purpose of information combat forces and their functions
December 6, 2016, Russian President Vladimir Putin approved the new version of “Russian Federation information security theory.” It points out that the main objectives of information security in the field of defense include the implementation of strategic containment and prevention of military conflicts caused by information technology, the improvement of the Russian armed forces information security system, the development of information confrontation forces and equipment, the forecasting, inspection and evaluation of the Russian armed forces Threats in the field of information; elimination of information / psychological effects aimed at destabilizing national history and patriotic traditions.
The formation of information combat forces is one of Russia’s important initiatives to achieve these goals. First of all, the Russian information combat forces is to contain and prevent the field of network information conflict or the main force of war. Second, the formation of information combat forces is the Russian armed forces information security system construction and the Russian new military reform an important step, will take into account the strength of construction and equipment development. Once again, the information warfare forces ensure that Russian armed forces are protected from cyber attacks and information security threats, ensuring wartime command and control and operational capability. Finally, the information warfare forces will also confront and counter the Western countries of the anti-Russian information penetration and psychological impact, to maintain the fighting morale and national stability.
Second, the troops named on the network attack and information penetration of the “two-handedly”
Russian Defense Minister Shao Yigu pointed out that the main functions of the information combatants include: centralized management of network operations; protection of Russian military networks and nodes, military command systems and communications systems from hackers; to ensure reliable access to information; Russian military capacity to expand its ability to act in cyberspace; against the Western anti-Russian information / psychological propaganda and penetration.
Russian military experts believe that the future of military struggle in the information combat objectives not only include the armed forces allegation system, the government administrative system and the financial system and other hard targets, more strategic is the soldiers and public psychology and other soft targets. An attack on the implementation of soft targets such as soldiers and people can lead to dislocation and disintegration. Information combat forces should not only have to protect their own side and attack each other hard targets and other capabilities, but also have to confront and oppose the enemy information / psychological attack and penetration. At present, countries with network dominance use different means to implement information operations against different objectives. For the use of special information weapons, such as computer viruses, information bombs, logic bombs, computer chips that are given special missions, explosive devices that generate electromagnetic pulses, UHF generators, and electronic biological weapons. And for the soldiers and the public psychological and other soft targets, create provocative or intimidating false information and spread through the information media to achieve military and political purposes.
Therefore, Russia will be named the “information combat forces” rather than the network combat forces fully embodies the scope of its combat both soft and hard targets.
Third, the integration of active elite forces and the recruitment of new forces simultaneously
The force will integrate the existing Russian armed forces network operations, electronic reconnaissance and electronic confrontation and other departments and functions, while absorbing the Ministry of Internal Affairs and security system of network information security and related experts, including mathematicians, programmers, engineers, cryptographers , Communications experts, electronic confrontation experts, translators and so on.
Russian military arms and institutions in 2013 has set up a “technology even”, and from college graduates in the recruitment of professionals, which is the key components of the military system / unit reserves and training professionals specializing in technology research and development and information security team. According to statistics, this force mainly includes the Air Force’s second science and technology even the space and defense forces of the third technology even under the Army’s fifth technology even, under the Military Academy of Sciences, the seventh technology even Wait. Each with 2 to 3 rows, each with about 20 people. To the air days of military science and technology, for example, the troops regularly recruit college graduates, give priority to the use of computer security, communications systems, information security, special radio systems, cryptography, electronic optoelectronic special equipment and other professionals, by the Air Force Academy of Military Academy training and education The center is responsible for training new people.
Fourth, the force commander has not yet determined, Gracimov is the most likely candidate
Russian Defense Minister Shaoyou clear, information warfare force commander will be general rank. Western countries believe that the Russian armed forces, the current chief of staff, Mr. Grazimov served as the commander of the information operations the possibility of the largest. He has proposed the Russian version of the “mixed war” concept, and received the approval of President Putin. He pointed out that “the current principle of war itself has undergone substantial changes, the realization of political and strategic objectives of the non-military means of the status of a series of events show that the effect of non-military means sometimes more than the use of weapons.” In his description of the “civil war in Ukraine” and “the spring of Arabia”, he pointed out that the information / psychological warfare could “turn a peaceful and prosperous country into a brutal armed struggle in months or even days”. March 4, 2017, Grazimov in military academy, asked the Russian Academy of Military Sciences to intensify the study of the new model of confrontation between countries and effective counter-measures. In addition, the West speculated that Gerasimov’s another reason is that he has served as the Russian armed forces network information warfare the highest commander. In 2010, the Russian Armed Forces commanded a powerful message / psychological offensive, and it was Gracimov who had recaptured the Crimea.
Five, conclusion
At present, the Russian Defense Ministry official website has not yet put information warfare troops, and the existing army, air force, navy and strategic missile soldiers, airborne soldiers of these five arms tied. The forces become separate forces or scattered in the existing five arms and key sectors are not yet known. However, the formation of information combat forces is not only a key step in the construction of Russian network information security forces, but also an important step in the reform of the Russian army in the context of the increasingly fierce network security of information security and the increasingly complex environment of security. Information operations forces will defend Russia’s cyberspace and information in the field of soft and hard targets, to achieve their own attack and defense functions, maintaining national network security and political and military security.
Original Mandarin Chinese:
隨著俄羅斯與西方在網絡空間的博弈日趨激烈,特別在2018年俄總統大選臨近的大背景下,西方國家針對俄羅斯的網絡和信息/心理攻擊日益增多。為此,俄羅斯加強網絡和信息安全建設。 2016年底,修訂頒布新版《俄羅斯聯邦信息安全學說》。 2017年2月27日,俄國防部長紹伊古宣布組建信息作戰部隊,加快推進信息作戰力量建設,明確其職能使命。
一、新版學說明確組建信息作戰部隊的目的及其職能
2016年12月6日,俄總統普京批准新版《俄羅斯聯邦信息安全學說》。其中指出,國防領域信息安全保障的主要目標包括:對利用信息技術導致的軍事衝突實施戰略遏制和預防;完善俄武裝力量信息保障體系,發展信息對抗力量和裝備;預測、檢查和評估俄武裝力量在信息領域的威脅;消除旨在動搖國家歷史觀念和愛國傳統的信息/心理影響等。
組建信息作戰部隊是俄實現上述目標的重要舉措之一。首先,俄羅斯信息作戰部隊是遏制和預防網絡信息領域衝突或戰爭的主要力量。其次,組建信息作戰部隊是俄武裝力量信息保障體系建設和俄羅斯新軍事改革的重要步驟,將兼顧力量建設和裝備發展。再次,信息作戰部隊確保俄武裝力量免受網絡攻擊和信息安全威脅,保證戰時指揮控制和作戰行動能力。最後,信息作戰部隊還將對抗和反制西方國家的反俄信息滲透和心理影響,保持士兵鬥志和國民思想穩定。
二、部隊命名體現對網絡攻擊和信息滲透的“兩手抓”
俄國防部長紹伊古指出,信息作戰部隊主要職能包括:對網絡作戰行動進行集中統一管理;保護俄羅斯軍用網絡和節點、軍事指揮系統和通信系統免受黑客攻擊;確保實現可靠的信息傳遞通道;檢驗俄軍的網絡能力,拓展其在網絡空間的行動能力;對抗西方的反俄信息/心理宣傳和滲透等。
俄軍事專家認為,未來軍事鬥爭中的信息作戰目標不僅包括武裝力量指控系統、政府行政管理系統和金融系統等硬目標,更具戰略意義的是士兵和民眾心理等軟目標。對士兵和民眾等軟目標實施的信息攻擊,可導致人心渙散和瓦解。信息作戰部隊不僅要具備保護己方和攻擊對方硬目標等能力,還要具備對抗和反制敵方信息/心理的攻擊與滲透。當前,擁有網絡主導權的國家針對不同目標運用不同手段實施信息作戰。針對硬目標使用特殊的信息武器,如計算機病毒、信息炸彈、邏輯炸彈、被賦予特殊使命的計算機芯片、能產生電磁脈衝的爆炸裝置、超高頻發生器、電子生物武器等。而針對士兵和民眾心理等軟目標,製造煽動性或恐嚇性的虛假消息並通過信息媒介傳播,以達到軍事政治目的。
因此,俄將該部隊命名為“信息作戰部隊”而非網絡作戰部隊充分體現了其作戰範圍兼顧軟硬兩類目標。
三、整合現役精銳力量和招募高校新生力量並舉
該部隊將整合現有俄羅斯武裝力量網絡作戰、電子偵察和電子對抗等部門人員和職能,同時吸收內務部和安全系統的網絡信息安全及相關專家,包括數學家、程序員、工程師、密碼學家、通信專家、電子對抗專家、翻譯人員等。
俄各軍兵種和機關在2013年先後組建“科技連”,並從高校畢業生中招募專業人才,這是軍隊系統各關鍵部門/單位儲備和培養的專門從事技術研發和信息安全保障的隊伍。據資料顯示,這支力量主要包括隸屬於空天軍的空軍第二科技連和空天防禦部隊的第三科技連、隸屬於陸軍的第五科技連、隸屬於軍事通訊科學院的第七科技連等。每個連有2~3個排,每個排約20人。以空天軍“科技連”為例,部隊定期招收高校畢業生,優先錄用計算機安全、通訊系統信息安全、特種無線電系統、密碼學、電子光電特種設備等專業人員,並由空軍軍事科學院培訓教育中心負責培養新人。
四、部隊司令尚未確定,格拉西莫夫是最大可能人選
俄國防部長紹伊古明確,信息作戰部隊司令將是大將軍銜。西方國家認為,俄武裝力量現任總參謀長格拉西莫夫大出任信息作戰部隊司令的可能性最大。他曾提出俄版“混合戰爭”概念,並得到普京總統的認同。他指出,“目前的戰爭原則本身已發生實質性改變,實現政治和戰略目標的非軍事手段的地位在上升。一系列事件表明,非軍事手段的效果有時超過了使用武器”。他在對“烏克蘭內戰”和“阿拉伯之春”等事件的描述中指出,信息/心理戰能夠將“一個祥和繁榮的國家在幾個月甚至幾天之內變成殘酷武裝鬥爭的戰場”。 2017年3月4日,格拉西莫夫在參加軍事學術會議時,要求俄軍事科學院加緊研究國家間對抗的新模式及有效反製手段。此外,西方推測格拉西莫夫的另一原因是,他此前一直擔任俄武裝力量網絡信息作戰的最高指揮官。 2014年指揮俄武裝力量發動強大信息/心理攻勢,兵不血刃收復克里米亞的正是格拉西莫夫。
五、結語
目前,俄國防部官方網站還沒有將信息作戰部隊,與現有的陸軍、空天軍、海軍和戰略導彈兵、空降兵這五大軍兵種並列放置。該部隊成為單列軍兵種亦或散佈於現有五大軍兵種和關鍵部門還未可知。但信息作戰部隊的組建不僅是俄羅斯網絡信息安全力量建設的關鍵舉措,更是在大國網絡信息安全博弈日益激烈和安全環境日益複雜的大背景下俄軍改革的重要步驟。信息作戰部隊將保衛俄羅斯網絡空間和信息領域的軟、硬目標,實現自身的攻、防職能,維護國家網絡信息安全和政治軍事安全。
作者:易鑫磊 來源:中國日報網
http://world.chinadaily.com.cn/2017-06/19/content_29801583.htm