People’s Liberation Army Cognitive Confrontation on the Social Media Battlefield
●社交媒体在议题策划上的“无形操控”、信息制作的“无痕嵌入”、信息传播方式上的“无缝链接”,能够有效达成对受众“无感入心”的影响
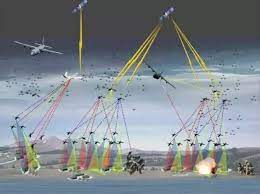
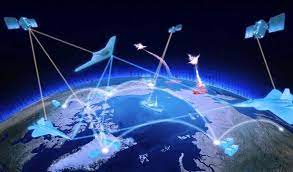
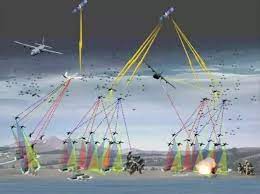
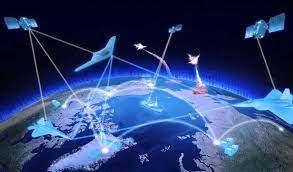
近年来的局部战争实践表明,现代战争往往同时在两个战场打响:一个是现实空间人员和装备较量的战场;另一个是赛博空间信息与认知对抗的社交媒体战场。社交媒体战场上的认知对抗,旨在塑造目标受众认识、定义、理解事件的宏观框架,并通过宏观框架下的定制信息发送,争取影响目标受众的行动,继而通过影响关键认知因素,对现实战争构成重大甚至是决定性的影响。由于信息传播机制的联动叠加,使得社交媒体对抗样式呈现出复杂性和综合性,但关键都是开展对目标受众的认知争夺。目前可以被清晰识别的对抗行动,主要有以下四种类型。
信息扰动。即在社交媒体发布特定信息,影响目标受众对真实交战态势的认识,继而塑造其立场、改变其行动。当前,社交媒体已经发展出即时通信、移动直播、图片视频、游戏娱乐等多种类型平台,基本实现了对传统媒体的类型覆盖与功能替代,其生动丰富的媒体形式使人们极易对传播内容产生认同。当前全球社交媒体用户超40亿,一旦对某些敏感事件反应过快过热,将会产生巨大的连锁反应和社会影响。2012年的巴以冲突中,以色列军方通过“以色列国防军发言人”社交媒体账号,不断发布战场信息,既发布信息表明己方立场,也通过宣扬战果来体现军事威慑。其对手哈马斯也不甘示弱,充分利用“卡桑旅”账号进行舆论反击,通过塑造弱者和受害者形象争取国际支持。双方行动被媒体冠以“推特战争”,此举也标志着战争正通过社交媒体向认知域拓展。
话语竞争。即竞争性地发布关键性评价指标,继而构建基于相应标准的话语环境,潜移默化地塑造有利于特定一方的认知框架。当前,通过社交媒体、网络评论传播叙事,逐步影响公众认知,进而助力战争或政治目标达成的“拖钓”策略,正是这一行动样式的主要表现。其主要做法是,在热点事件中通过散播虚假性和误导性言论的方式“带节奏”,由此唤醒社交媒体用户既有认知偏见、选择性地塑造目标受众认知框架、激化目标受众认知对立、加剧网络空间甚至社会舆论紧张态势。同时,在智能化社交媒体平台的算法推荐技术支撑下,“拖钓”者大量散播的虚假和误导信息传播指向性更强,群体效应更加明显,加之社交机器人、自动播报、声像拟合、沉浸式体验等技术应用推波助澜,用户也就更容易受到这些信息的持续影响,认知更易被影响或裹挟,进而形成或激化其对某一议题的认知偏见和情绪心理。近年来,“脸书”“推特”等社交媒体平台在诸多国际重大事件中的充分运用表明,社交媒体在议题策划上的“无形操控”、信息制作的“无痕嵌入”、信息传播方式上的“无缝链接”,能够有效达成对受众“无感入心”的影响。
舆论遮蔽。即在特定时间配合特定的线下行动,包括军事和政治领域的具体行动,制造特定类型的舆论以广泛占领舆论场,继而影响舆论走向。这一行动样式目前主要通过社交机器人等智能媒体实现。据国外研究机构调查发现,从各类社交媒体平台收集到的链接至2000多个流行网站的120万条“推特”帖子中,有66%为机器人所分享。有研究认为,施加认知影响常用有效的手法是借助机器学习挖掘用户情感、偏见来筛选、锁定最易受影响的受众,而后将定制的“精神弹药”快速密集地“射向”目标群体。即通过大量“假消息”和“不准确的信息”有意识地塑造并精心编造所谓“事实”甚至是谣言,实施精准投送后在目标受众中形成“首因效应”,再经智能媒体的广泛传播和网络水军的“谎言漫灌”,形成“被改变的事实”,混淆目标受众对“事实”真相的认知,从而达到影响其心理、操纵其认知的目的。
信息封锁。即对敌信息传播渠道实施技术攻击、封锁乃至物理摧毁,让双方在认知对抗中处于非对称、不平衡的状态,从而垄断命名权、阐释权和议程设置权,对目标受众进行强势“认知塑造”。当下,西方国家经常利用掌握根服务器等技术优势,侵犯、控制他国互联网以及网络通信。2009年,美国政府授权微软公司切断叙利亚、伊朗、古巴等国的互联网即时通信端口,致其网络瘫痪,试图把它们从世界互联网中“抹去”。2022年,社交媒体平台“脸书”公开宣布限制俄罗斯、伊朗等国的部分媒体,并对其进行身份标注,删除这些媒体针对美国的宣传,以此获得认知对抗中的优势地位。但基于互联网世界“如有封禁,就绕过它”的一贯准则,现实操作中很难真正实现对对手信息的完全封锁,社交媒体战场仍将充斥着包括虚假信息在内的各种信息相互纠缠的“战争迷雾”。
現代英語:
The practice of local wars in recent years shows that modern wars often start on two battlefields at the same time: one is the battlefield where personnel and equipment compete in real space; the other is the social media battlefield where cyberspace information and cognition confront each other. Cognitive confrontation on the social media battlefield aims to shape the macro-framework in which the target audience recognizes, defines, and understands events, and strives to influence the target audience’s actions by sending customized information under the macro-framework, and then affects key cognitive factors. Real war has a significant or even decisive impact. Due to the linkage and superposition of information dissemination mechanisms, social media confrontation styles are complex and comprehensive, but the key is to compete for the recognition of the target audience. There are currently four main types of confrontational actions that can be clearly identified.
information disturbance. That is, releasing specific information on social media can influence the target audience’s understanding of the real fighting situation, and then shape their stance and change their actions. At present, social media has developed various types of platforms such as instant messaging, mobile live broadcast, picture and video, game entertainment, etc., which have basically realized the type coverage and function replacement of traditional media. Its vivid and rich media forms make it easy for people to disseminate content. Generate recognition. There are currently more than 4 billion social media users in the world. Once the reaction to certain sensitive events is too fast and overheated, it will have a huge chain reaction and social impact. During the 2012 Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Israeli military continuously released battlefield information through the “Israel Defense Forces Spokesperson” social media account. It not only released information to express its position, but also demonstrated military deterrence by publicizing the results of the war. Not to be outdone, its opponent Hamas made full use of the “Qassam Brigade” account to counterattack with public opinion and win international support by portraying the image of the weak and victims. The actions of both parties were dubbed the “Twitter War” by the media, which also marked the expansion of the war into the cognitive domain through social media.
Discursive competition. That is, key evaluation indicators are released competitively, and then a discourse environment based on corresponding standards is constructed, subtly shaping a cognitive framework that is beneficial to a specific party. Currently, the “trolling” strategy of spreading narratives through social media and online comments, gradually influencing public perception, and further helping to achieve war or political goals, is the main manifestation of this action style. Its main method is to “set the pace” by spreading false and misleading remarks in hot events, thereby awakening social media users’ existing cognitive biases, selectively shaping the target audience’s cognitive framework, and intensifying the target audience’s perception. Contradictions, exacerbating tensions in cyberspace and even public opinion. At the same time, with the support of the algorithm recommendation technology of intelligent social media platforms, the false and misleading information spread by “trollers” is more directional, and the group effect is more obvious. In addition, social robots, automatic broadcasts, audio and video matching, As technological applications such as immersive experience add fuel to the fire, users are more likely to be continuously influenced by this information, and their cognition is more easily affected or coerced, which in turn forms or intensifies their cognitive biases and emotional psychology on a certain issue. In recent years, the full use of social media platforms such as “Facebook” and “Twitter” in many major international events has demonstrated the “invisible control” of social media in issue planning, the “invisible embedding” of information production, and the methods of information dissemination. The “seamless link” on the Internet can effectively achieve an “unfeeling” impact on the audience.
Covered by public opinion. That is, cooperating with specific offline actions at a specific time, including specific actions in the military and political fields, to create a specific type of public opinion to widely occupy the public opinion field, and then influence the direction of public opinion. This action style is currently mainly realized through intelligent media such as social robots. According to a survey by a foreign research institution, 66% of the 1.2 million “Twitter” posts collected from various social media platforms and linked to more than 2,000 popular websites were shared by robots. Some studies believe that a common and effective way to exert cognitive influence is to use machine learning to mine user emotions and biases to screen and target the most susceptible audiences, and then “shoot” customized “mental ammunition” quickly and intensively at the target group. That is, through a large amount of “fake news” and “inaccurate information”, we consciously shape and carefully fabricate so-called “facts” and even rumors. After implementing precise delivery, a “primacy effect” is formed among the target audience, and then through the extensive use of smart media The “flooding of lies” by dissemination and Internet trolls forms “altered facts” and confuses the target audience’s perception of the “facts”, thereby achieving the purpose of influencing their psychology and manipulating their cognition.
Information blocking. That is to carry out technical attacks, blockades and even physical destruction of the enemy’s information dissemination channels, so that the two sides are in an asymmetric and unbalanced state in the cognitive confrontation, thus monopolizing the naming rights, interpretation rights and agenda setting rights, and exerting strong “cognition” on the target audience. Knowledge shaping”. At present, Western countries often take advantage of technical advantages such as mastering root servers to infringe and control other countries’ Internet and network communications. In 2009, the U.S. government authorized Microsoft to cut off Internet instant messaging ports in Syria, Iran, Cuba and other countries, paralyzing their networks in an attempt to “erase” them from the world’s Internet. In 2022, the social media platform “Facebook” publicly announced restrictions on some media in Russia, Iran and other countries, and marked their identities, and deleted these media’s propaganda against the United States, in order to gain an advantageous position in cognitive confrontation. However, based on the consistent principle of “if there is a ban, bypass it” in the Internet world, it is difficult to completely block the opponent’s information in actual operations. The social media battlefield will still be filled with various entangled information, including false information. The “fog of war”.
解放軍原文來源:http://www.mod.gov.cn/gfbw/888/沒有湯給你.html