互聯網”的混沌與網絡空間的迷茫
China’s Internet – creating chaos and confusion in cyberspace
One, chaotic “internet”
1 , from the Apache network to the “Internet”

“Internet” What is the network? China has no “Internet”? The world whether there is no “Internet”? This is not a problem, due to language and cultural expression and understanding of different interests due to the scope and purpose of the different Academic research conditions and the different atmosphere, and so on, these years more and more chaotic. “Internet”, “Internet”, “Internet”, “Mobile Internet”, “Internet Finance”, “Internet +” … … and so on, what are linked to a “Internet”, “Internet” has become a fashion term.
Today’s world has become the “Internet” encompasses the world of the world, in addition to what are “the Internet” that an “Internet”, many people do not know there is no other network, but also can not have other networks, why There are other networks. “Internet” in the end is a network or should be more than one network? Recognize the chaos, chaos awareness, are derived from this.
In 1969, Dr. Xu became the first member of the internetwork at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), and later became the only senior vice president of Chinese lab in the history of Bell Labs, Institute of Engineers (IEEE) academician, has been known as the US network communications industry, “the first Chinese.” In 2004, Mr. Xu told me that people today are keen on the “Internet”, the predecessor of the ARPANET (ARPANET), the US government based on the defense considerations to the university to study the large computer mutual communication of an experimental network, 20 years of innovation and improvement from a network.
In 1970, the American Information Processing Association defined the computer network as “a collection of computer systems with separate functions that could be shared in a way that shared resources (hardware, software, data, etc.).” The definition of this computer network in the United States, perhaps regarded as the earliest from the United States “Internet” definition?
2 , two network architecture
In the 1950s, the United States established a semi-automatic ground air defense system (SAGE, Chinese translation “赛 Qi”), the computer technology and communication technology combined application attempt. In the early 1960s, the American Air Ticket Booking System (SABRE-1) consisted of a central computer and more than 2,000 terminals distributed across the United States to form a computer communication network, enabling the terminals to connect to the central computer via telephone lines on a larger scale Of the typical application. This is a single computer-centric, through the multi-line controller and remote terminal connected to the online system, known as the terminal-based remote online system, that is, early computer network.
At the end of the 20th century, the International Organization for Standardization ISO standardization of computer and information processing technology committee to study and develop network communication standards to achieve the international standardization of network architecture. In 1984, ISO formally promulgated the International Standard ISO 7498, referred to as the “Open System Interconnection Basic Reference Model”, referred to as the OSI RM (Open System Interconnection Basic Reference Model), the famous OSI seven-layer model. OSI RM and standard protocol development and improvement to promote a unified, open network architecture, greatly accelerating the development of computer networks.
However, the United States does not put ISO in the eyes, insist on arbitrary. In 1983, the United States in the Apache network officially launched TCP / IP protocol to replace the original NCP network control protocol, and then the formation of the Internet (Internet). For more than 30 years, the United States has used its technology, economy and military advantages to implement the Internet’s Internet-wide network strategy. The Internet Task Force (ICANN) is naked to put forward the slogan of “the same world, the same Internet”. The Obama administration is also praised “the Internet is unique in the international environment.” As a result, the Internet by the United States and its dormant countries in the iron powder are relish for the “Internet”.
In fact, the Internet is the United States to develop rules, control the exchange, monitoring information of a computer network architecture, does not fully comply with the International Organization for Standardization ISO officially issued OSI RM requirements. In other words, there are two dominant network architectures in the world: one is the OSI RM (open system interconnection reference model) proposed by the ISO, and the other is the use and pushing of the Internet. TCP / IP RM (TCP / IP reference model). The fundamental difference between the two models is that OSI RM to promote the global computer network open system interconnection, TCP / IP forced all the world’s computer terminals are connected to the Internet one network; ISO is committed to all countries, various types of computer network system The interconnection between the United States stressed that the computer between the end of the exchange of information between the end.
3 , “Internet” definition
So far, the scientific and technological circles, academia, education, industry and commerce, there is no uniform, clear, accurate and standardized Internet definition. Here the Chinese Internet, referring to the Internet as early as July 18, 1997 by the State Council authorized by the National Science and Technology Nomenclature Committee clear English internetwork, rather than the Internet.
Some people following the US Internet strategy insist that “the Internet is the Internet,” “China is the Internet translated into the Internet.” This is not a scientific, academic definition, nor is it from the academicians and “authority” of the mouth, more like an unidentified “Ah Q” said.
Or Obama frankly. “Through the Internet connection, the US company’s business can be extended to any place in the world to create countless jobs and opportunities for the American people,” he said in the preface to the International Strategy for cyberspace, published in the White House, “The Internet itself can not open a new era of international cooperation.”
Internet, Internet from English. As a proper noun, it refers to the use of TCP / IP communication protocol of a computer system, and the system provides information, services and users. The Internet requires that the user (the terminal) use the specified domain name and address for information exchange within the defined Internet framework in accordance with its specific rules, which is excluded and closed to the network using other communication protocols, or simply replace it.
Some people say that the definition of the Internet, English should be “a computer network forming of a worldwide network of computer networks that use the TCP / IP network protocols to facilit data transmission and exchange.” Translated into Chinese, is “by a use of TCP / IP Network protocol to promote data transmission and exchange of computer networks composed of a global network. “Please note that this” definition “is very clear:
First, you must use the TCP / IP protocol;
Second, must be the same use of TCP / IP protocol composed of computer networks;
Third, must be in the TCP / IP protocol on the basis of a global network.
Around a long circle around the same circle, or “use TCP / IP protocol computer network”! Can only accept and use TCP / IP with a protocol, the same type of rules, in the same network space for transmission and exchange Of the network, which is not the Internet? How to become the “Internet” in the end is a dull chaos, or chaos led to a dull?
It is said that in the foreign literature, the Internet is described as “no leadership, no law, no political, no army … … incredible social organizational structure.” Dare to ask the US government to the global implementation of such a network structure is what is it? Is to ensure that to induce or force countries, regions, organizations and each use of computers around the world users have succumbed to the Internet, subject to, The United States?
It was argued that, from a general point of view, the definition of the Internet should include three aspects, namely:
– is a TCP / IP protocol based on the network;
– is a computer users of the network group, the user in the use of network resources at the same time, but also for the development and expansion of the network contribute;
– is a collection of all the information resources that can be accessed and used.
The question is whether or not the other computer networks that do not use or do not apply the TCP / IP protocol exist. Is it allowed to exist? Should it exist? Use different protocols The interconnection, convergence, exchange between networks is not the Internet, is it interconnected? Even if the same from the TCP / IP protocol network, IPV6 and IPV4 network is the relationship between the interconnection, or the upgrading of the relationship between China’s national intellectual property rights of IPV9 and the United States have intellectual property IPV6, IPV4 network, is the sovereign equality of network interconnection, or technology-compatible coverage of the alternative relationship? If the realization of IPV9, V6, V4 technology system network of mutual integration and sharing co-governance, which is the Internet? It is only the Internet To the future of the network of technological progress?
According to the above Internet, the definition and statement of the Internet, China only has a network within the Internet framework, there is no consistent with the national sovereignty, consistent with the public network, there is no interconnection with non-sovereign public Internet (internetwork).
The concept of “the Internet is the Internet” that the Americans themselves can not say clearly define, in recent years, have appeared in China’s strategic, planned, decision-making documents and media coverage. Some “authorities” who take the opportunity to hustle and dust, constantly extending, expanding, distorting, fabricating its connotation and extension, it is chilling. If only by the United States 忽悠, but also not detained our independent innovation thinking, and will not be able to reverse and adjust the decision-making mistakes and mistakes strategy. If we themselves fool yourself, self-deception, does not mean that we know the chaos has been deep mud, it is difficult to extricate themselves?
Second, the confusion and confusion of cyberspace

1 , the Internet constitutes the network space
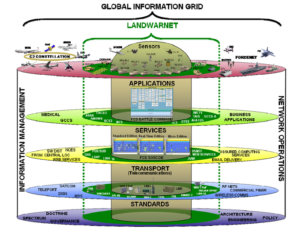
With the approval of the Central Network Security and Information Leading Group, the National Internet Information Office published the “National Network Space Security Strategy”, which was first published by “Internet, Communication Network, Computer System, Automated Control System, Digital Equipment and Its Bearer Which is “a new area of human activity that is important to land, sea, sky and space. National sovereignty extension extends to cyberspace, and cyberspace sovereignty becomes An important part of national sovereignty.
What is the “Internet” mentioned above? Refers to the network of Internet coverage of a global network of space or the world’s multiple sovereign network interconnection of the network space formed? This problem is not clear, people’s cyberspace awareness, Recognize and identify the ability to distinguish still deep chaos, confusion and confusion.
The Internet is the Internet, in order to achieve the exchange of information between the terminal and the terminal in a network within the framework of the formation of a joint network of space; the Internet is the Internet, is a number of different types of networks in order to share the purpose of mutual benefit Interconnected network space. The Internet and the Internet constitute the integration of the network space, inclusive of common, but also the existence of their own specific and specific rules, categories, ecological and other characteristics. Different cyberspace can not be generalized, confused. Our knowledge should not be disturbed more and more chaos.
Different network space is the most fundamental, the most typical characteristic difference is that countries in the Internet (internetwork) under the framework of sovereignty can not be changed, can not cover up, irreversible, can only be between the sovereignty of the handshake, shake hands, In contrast, bullying. The sovereignty of the Internet is only one, that is, the United States a unique sovereignty, or hegemony. Within the framework of the Internet, any country’s sovereignty has been unilaterally formulated and closely governed by the United States, the scope and the shackles and shackles of ecology, and have to let the United States and its allies (such as Japan) violate, penetrate, , To play, to play in the applause.
In particular, the need for deep and clear, highly important is the dissemination of information, economic development, prosperity, culture, governance, cooperation and exchanges, not the Internet patent, the national sovereign network can also be implemented and implemented, based on national sovereign cyberspace Internet interconnection may do better. The use of the Internet in the United States a network of technical systems and means to bypass the national network of sovereignty, governance and legal rights, is leading to the sovereign cyberspace security is the biggest source of security, is the sovereign state of the greatest threat to security, The most destabilizing factors that endanger the peace, stability and national unity of the sovereign states. In the Internet, there is no country with the country’s diplomacy, there is no equal and mutual respect for international cooperation, only the United States a dominance, a strong, one dominate, one of the words have the final say. In the framework of such a network, with the United States to talk about the rules, stresses the principle of governance, on the Pratt & Whitney, not with the tiger skin, dance with the wolf? How can the United States take their own national interests to share with other countries, to sell their own network sovereignty To allow other countries to rival the country’s cyberspace “sovereignty in me, not subject to people”, if subject to the people, will be subject to chaos, will suffer! The truth, Iran understand, Germany understand that Russia understands that many countries understand. Over the years, from Asia, the Americas, the Middle East to the EU lessons one by one, we have no reason not to understand, do not accept the lesson?
2 , cyber space sovereignty belongs to the United States

Some people say that cyberspace is cyberspace, that the English Cyberspace is internetwork. If the two English words is entirely a meaning, pointing to the same category of words, why have to be divided into how to see, how to read, how to write can not stand on the two words, speak English foreigners tired tired!
It is said that Cyberspace translated into Chinese cyberspace is more meaningful. Some people say that the US Presidential Decree on Cyberspace’s definition shows that “the Internet is an important infrastructure for cyberspace,” “Internet computers are the most basic elements of Cyberspace,” “Internet + is the Internet’s most important move to cyberspace ”
Here the “Internet”, obviously refers to the Internet that Internet, “Internet +” is the Internet +. There is also a dizzy chaos: the Internet or “Internet” does not constitute cyberspace, the Internet or “Internet” is only Cyberspace this cyberspace infrastructure? “Internet +” is only the Internet to Cyberspace this Network space expansion of an important action, but also does not belong to the network space?
English Cyberspace Chinese literal translation, is cyberspace. 2008 President of the United States President Bush issued the Presidential Decree No. 8 (NSPD) / 23 Homeland Security Presidential Decree, the Chinese translation of cyberspace definition is: “a global domain in the information environment, by independent and interdependent information Technology infrastructure network, including the Internet, telecommunications networks, computer systems and embedded processors and controllers, etc. “This seemingly rigorous definition defines cyberspace as a global information environment, encompassing all of the world’s” information technology Infrastructure network “. US Air Force Chief of Staff said the cyber space encompasses everything from “direct current to visible light”. To say that, or the Internet a network of the world that the concept of a replica, for a noun, changed the argument only, not the right.
This definition can be seen almost as an American imperial edict to declare war on all sovereignty over the world. The definition does not recognize the resources, conditions and foundations of countries to build and develop sovereign cyberspace, and first incorporate all kinds of network infrastructures into the category of cyber cyberspace. The definition is preemptively bundled with political, economic, military and cultural Hands and feet of the “certain rules”, thrown out of the national scientists, strategists in the future development of the field of network innovation voyage cable; the definition of only state officials set fire to the people not allowed to light, domineering, ambition, aggressive.
3 , Internet sovereignty and power confused
Although the OSI RM (Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model) proposed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is one of the two dominant network architectures in the world, these years have not resulted in large-scale market applications. Some people think that the model exists level and content is not the best, the session layer and presentation layer is almost empty, the corresponding service definition and protocol complexity and other technical shortcomings.
And the obvious and unsafe problems caused by the inherent lack of Internet technology have been widely concerned by countries and international organizations. Fundamentally change the Internet’s single control center framework, TCP / IP protocol, identity and security authentication mechanism, has become a major global key core technology innovation research topics.
Perhaps because of this, the current countries have not yet formed in the sovereign cyberspace based on the construction of the global Internet (internetwork) conditions, resources and support, not the ability and the Internet “zhongjiang governance”, “equally”, “shared peace” Can only “send people”, in access to the Internet, rent Internet services, to prevent excessive penetration of the Internet and so on, put huge costs and bargaining with the United States to try to minimize harm and loss. Countries are equally involved in Internet governance, equitable distribution of Internet infrastructure resources, common management of Internet root servers and other key information infrastructure, to strengthen the representation and voice of developing countries, like slogans, and like a mirage, shouting fills, and can not reach.
In the framework of the United States Internet within a network, in the United States cyberspace sovereignty and security under the serious deterrence, the peaceful development of the theme of cyberspace international cooperation strategy is likely to only wishful thinking, the premise and the foundation is wrong, direction and route Biased The United States and the rest of the world continue to lag behind the United States in the network space, subject to the United States, the United States, the United States, the United States, the United States, the United States, the United States, Succumbed to the United States, and will actually lose cyberspace sovereignty, loss of development opportunities and strategic opportunities, more harm than good, regret not the beginning.
4 , cyberspace international cooperation trade-offs

Corresponding to the Chinese cyberspace English is Net Space, the scientific definition is: information infrastructure to connect, cover and carry information processing space-time domain.
This definition specifies the most common commonality of the Internet, the Internet, cyberspace, and any other cyberspace, not to the will of a particular country or interest, not limited to a particular network, Country to build the network space.
With this definition as a prerequisite to support countries to strengthen the construction and development of sovereign cyberspace, to promote the international community in a spirit of mutual respect for dialogue and cooperation, have the resources to protect the public in the cyberspace of the right to know, participation, expression, supervision Rights and conditions to build a multilateral, democratic and transparent global network space management system, it is possible to achieve scientific and rational, fair and orderly, equal and reciprocal, security checks and balances of international cooperation in cyberspace.
China in the supercomputer development, aerospace computer system applications, etc. has been rushed in the forefront of the world, can be compatible with IPV6 and IPV4 IPV9 technical system test run test is satisfactory. Russia in the domestic network information control and prevention of foreign network invasion and so has accumulated a good experience, the establishment of a good system. The EU has embarked on a potential threat to the Internet and is committed to building an autonomous cyberspace system. More and more countries put forward cyber space sovereignty demands, in favor of Xi Jinping President “jointly build cyberspace fate community” claims.
In the current limited conditions, the basis and the expected prospects, China’s international cooperation in cyberspace initiatives should be able to assess the situation, do what, careful operation, not rushed into the routines of other countries. Should be single-handedly with the United States and other countries to negotiate international Internet space governance diplomacy, a rainy day, one hand to build the power of the United States enough to balance the US Internet and cyberspace of China’s sovereign public network system. At the same time, take decisive and resolute measures to resolutely deal with domestic and foreign network security risks and threats, and resolutely punish the network of criminal activities, and resolutely crack down on China’s cyberspace sovereignty, betrayal of national and national interests, resolutely correct long passive Cyberspace following strategy and strategy.
Third, the world cyberspace security situation

The US Internet-dominated world cyberspace security situation is increasingly grim. Wearing the “Internet” caps of the Internet security problems riddled with more and more countries to become difficult to save the network of ills and long-lasting “heart disease.”
According to the “China cyberspace security report (2016)” Blue Book, since 2015, based on the Internet and cyber space network conflict and attack, become the main form of confrontation between countries. Russia Kaspersky accused the United States “Formula Group” through the implantation of spyware, infected Iran, Russia, China, more than 30 countries such as military, financial, energy and other key sectors of the tens of thousands of computers. Iran says it has thwarted the United States’ cyber attacks on its oil sector. Italy “Hacking Team” more than 400G of the company’s data was open and found that the United States, Morocco, Ethiopia and other institutions in more than 20 countries to buy a network of spy and vulnerability tools. The company blames Russia’s “APT28” organization for exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities to attack NATO and US defense agencies.
Blue Book Disclosure, the United States set up “Network Threat Intelligence Integration Center”, and expand the State Council “Anti-Terrorism Strategy Information Center” scale, the CIA set up “Digital Innovation Department” to strengthen the network intelligence gathering capacity. The US Department of Defense launched a network security incubator program, the British government to expand its network security research capabilities, the US Navy prepared offensive network action, NATO announced the preparation of mixed network warfare, countries focus on network attack and defense and hard and soft strength, and strive to security and attack Ability to enhance the two-way. Media disclosure, the world has more than 50 countries set up a network warfare forces, the global cyberspace “military race” escalating.
According to the disclosure, relying on the United States Internet technology, agreements and infrastructure development developed “China Internet”, government, banking, energy and other vital departments of the network information system generally can not achieve safe and controllable, the domestic industrial control system is ” Security loopholes. ” 2015 appears Alipay, Ctrip data loss, Netease e-mail leakage and other troubles, in recent years through SMS, WeChat implementation of financial fraud every day in a large number of occur. Minister of Industry and Trade Miao Wei told reporters that now an average of one month to search for 173 million telecommunications fraud information.
According to the “National Internet Information Center”, “Network Security Information and Dynamic Weekly”, February 13, 20-19, the number of domestic infected network virus host 400,000 units, up 6.6% over last week; territory was implanted back door Of the government website rose 47.1%; for the domestic website of the number of counterfeit pages increased by 165.2%; new information security high-risk loopholes rose 26.2%. Monitoring found that the source of network virus transmission to the site of the horse, involving 68 domain names in 30.9% for overseas registration, and the top domain for the .com about 83.8%, most of the horse site through the domain name to visit the implementation of the virus spread.
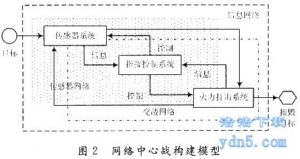
National Defense University professor Dai Xu pointed out that today’s world has been in a “network”. Changes in the military field have taken place. From the sensor as the core, to electromagnetic space as the boundary of the electronic information warfare (which can be called “telecommunications war”), to the network as the core, to the psychological space for the characteristics of the network, psychological warfare (can be called “network Heart war “),” network “into the basic characteristics of the seventh generation of war, is becoming the main battle of the big country game. China’s traditional strategic advantage is becoming the focus of opponents crack, China once again in a natural barrier can rely on the dangerous situation, the face of being blackmail the state of the network. The traditional cognitive system of war and anti-war requires urgent upgrading. In the new era of mixed warfare of the network, China must also have the ability to hold the “bull nose” of the times.
Fourth, the history of sovereign cyberspace
1 , “cyber space” alert the world
The United States carefully thrown out the “cyberspace” theory, self-righteous, and then without hesitation in its delineation of the “cyber space that cyberspace” large-scale global information monitoring, network war deployment and network information intelligence collection And plunder, etc., alert the world’s scientists, economists, military scientists, socialists and businessmen, politicians, people and so on. People suddenly realized that “the Internet is the Internet” and “cyber space is cyberspace” exactly the same. In the final analysis, the superpower capitalist hegemony of the United States regarded himself as the head of the “global village” and regarded “economic globalization” as “selfish”. “I am my, you or my, this earth on the land and sea sky all everything is my” – this is the real United States, which is all the interests of the United States. The United States, is so arrogant unreasonable.
However, reality and science have repeatedly verified that cyberspace is only a type of network that exists in a variety of independent runs, and is part of a space for different types of networks that are different in technology, different in purpose, and for different purposes. Cyberspace is not equal to cyberspace, cyberspace covers cyberspace, cyberspace is a subset of cyberspace.
Since the performance of the United States sovereignty and interests of cyber space, indicating that all constitute a subset of cyberspace, all countries and areas of the network space, have their sovereignty and interests of the demands. Iran, Russia, Germany, China and so on the EU and so on, should have, there must be, otherwise there is no construction of “cyberspace fate community,” the basic conditions and the necessary basis for peace, sharing, co-governance, win-win International cyberspace is out of the question.
In this way, to strengthen the national sovereignty network construction and development, build and maintain their own security and stability, national unity, and promote the prosperity of the domestic community of sovereign cyberspace, become a sovereign state important event. This is the common responsibility of the United Nations, the United States and the world’s sovereign States. “Cyber space” deter the world, is the United States contempt for the world’s cyberspace strategy of the major errors; any follow the US Internet, cyber space strategy decisions and initiatives, will be lost in the direction of major mistakes.
2 , Internet space strategy has been put on the agenda

Network space (Net Space), is the space-time system created by mankind, is the generic name of the concept, is the information processing and exchange of bearing space. It summarizes the three elements that make up the cyberspace: attributes, connection coverage, and the ability to carry processing information. Regardless of the financial network, enterprise network, government network, regardless of the Internet, Internet, Internet, regardless of land-based network, aviation network, space network, regardless of cable network, wireless network, quantum network, regardless of public or private network related services Providers and operators of private access networks, and so on, there are independent connections to cover the space-time domain and bearer processing exchange of different information on the network space.
The cyberspace has not been able to rigorously, regulate and accurately reflect and embrace all of its inherent characteristics, and extend the scope of the cyber space in the new network space. The conditions and the basis for the development of the law of change. This network and the network between the super network space, inspired the “Internet space” (Nets Space) doctrine. Internet space is an integrated domain of cyberspace.
Standing in the Internet space height, depth and breadth of the full dimension, full view of cyberspace, our vision will be wider and farther and clearer, our thinking will be easier to jump out yesterday and today, looking to tomorrow, we will from the Internet , “Internet”, cyber space caused by chaos in the liberation of ideas, out of a computer network era beyond the new path of the human information society.
A network space, wireless networks, quantum communication, space networks and other interconnected, interactive, interdependent constitute the era of Internet space, has come and is entering a more advanced stage. The rise of China’s cyberspace strategy will inevitably lead to the rise of revolutionary thought, the rise of science and technology, the rise of economy, the rise of the nation, the rise of the country, the benefit of future generations, the impact and drive the global human society by leaps and bounds.
Internet space strategy and technical preparation has been put on the agenda, the best time may be in front of and in the next few years. China can not seize the opportunity to seize the opportunity to go beyond the United States to lead the new super cyberspace – Internet space era, to seize the day and night, to now move from scratch, to the number of romantic figures, but also to see the current.
3 , the development of Internet space to be the power of the whole country
The United States to push the country to push the Internet, push IPV6, push the Bo space, leading to chaos in the country and confused at the same time, but also indeed created a remarkable network technology, network economy and network military glory.
China has become the world’s second largest economy. China is fully capable, conditional and confident to develop the international space strategy and technology with the power of the whole country.
Ideological emancipation, institutional reform is China’s reform and opening up since the two initiatives complement each other. From this start, it is recommended:
⑴ the establishment of the CPC Central Committee, the National People’s Congress, the State Council and the CPPCC under the leadership and under the constraints of a highly authoritative, rule of law and error correction mechanism and error correction mechanism, and resolutely put an end to the confusion and decision-making road.
A small number of follow the United States, “experts”, “authority” long-term impact and intervention in the national network of information authorities who also a number of “one speech” strange thing, no longer allow, exist and continue, and must be resolutely reversed and broken.
Should immediately resolutely correct the “comprehensive introduction, upgrading, the deployment of IPV6” major strategic decision-making and planning mistakes, abolished with the United States signed all the hazards and endanger China’s cyberspace sovereignty and security of the unequal agreement; cyberspace field investment projects one by one The implementation of the audit and post-evaluation, obviously “for others to marry clothes,” all shut down and turn.
(2) The State encourages and supports the construction, development and maintenance of a sovereign public network on the basis of the premise and national ownership of intellectual property rights.
Should be clearly in the United States based on the current “Internet”, the construction of independent development of the Chinese public network and other sovereign public network and provide services, the people have the right to use the sovereign public network and non-sovereign public network rights. The state should introduce the tendency of the incentive policies and measures to allow the sovereign public network using IPV9, Zheng code, Tao Chen code, CFL safety certification, MISC, and so on with national independent intellectual property rights technology. Actively build, develop and maintain the domestic independent operation of the multi-network constitute the Internet, can build a global network space fate community to explore the model, the accumulation of experience and create the conditions.
(3) to seize the opportunity to create a national-led, social participation, private operation of the “Internet Space Research Institute”, all-round, multi-dimensional, deep-level research and development of Internet space technology and development of development strategies and strategies to create a world-class training of Internet space talent base , Build the sovereign network / future network / Internet space experiment, test the system application environment, explore and solve the sovereign network, cyberspace and the development of Internet space in various problems, strides in the lead in the forefront of the development of Internet space.
(4) First of all, with Russia, Iran, Germany, the European Union and other countries committed to the development, development and maintenance of their own sovereign cyberspace and actively organize the construction of cyberspace destiny community communication, exchange, negotiation and cooperation, joint multi- The United States is the main negotiator.
Clear the chaos, swing confused, we will no longer be subject to the people, let the mercy, we will be firmly into the era of cyberspace, we will be far-sighted toward the future of Internet space.
Original Mandarin Chinese:
一、混沌的“互聯網”
1、從阿帕網到“互聯網”
“互聯網”究竟是什麼網?中國究竟有沒有“互聯網”?世界究竟有沒有“互聯網”?這本不是問題的問題,由於語言文化表達和理解的不同,由於利益追求範圍和目的的不同,由於學術研究條件和氛圍的不同,等等,這些年越來越顯得混沌不清。 “互聯網”、“中國互聯網”,“國際互聯網”、“移動互聯網”、“互聯網金融”、“互聯網+”……等等,什麼都掛上個“互聯網”,“互聯網”竟成為時尚用語。
今天的世界儼然成了“互聯網”囊括天下的世界,除了什麼都是“the Internet”那一張“互聯網”,許多人都不知道還有沒有其它網,還能不能有其它網,為什麼還會有其它網?。 “互聯網”到底是一張網?還是應該不止一張網?認識的混沌,混沌的認識,皆源於此。
1969年,許浚博士成為在美國加州大學洛杉磯分校(UCLA)實驗室誕生的第一個互聯網絡(internetwork)的研究成員,他後來成為貝爾實驗室歷史上唯一的華裔高級副總裁,美國電子電氣工程師學會(IEEE)院士,曾被譽為美國網絡通信界“第一華人”。 2004年,許先生告訴我,人們今天熱衷的“互聯網”,前身是阿帕網(ARPANET),是美國政府基於國防上的考量出錢給高校研究的大型計算機互相通信的一個實驗網,又經過20多年的創新和改進而來的一張網。
1970年,美國信息處理協會將計算機網絡定義為“以能夠共享資源(硬件、軟件和數據等)的方式連接起來,並且各自具備獨立功能的計算機系統之集合”。這個計算機網絡的美國定義,也許算是最早來自美國的“互聯網”定義?
2、兩張網絡體系結構
20世紀50年代,美國建立了一個半自動的地面防空系統(SAGE,中文譯作“賽琪”),進行了計算機技術與通信技術相結合的應用嘗試。 60年代初,美國航空訂票系統(SABRE-1)由一台中心計算機和分佈在全美範圍內的2000多個終端組成計算機通信網絡,更大規模地實現了各終端通過電話線連接到中心計算機的典型應用。這種以單個計算機為中心、通過多重線路控制器與遠程終端相連接的聯機系統,被稱做面向終端的遠程聯機系統,即早期的計算機網絡。
20世紀70年代末,國際標準化組織ISO的計算機與信息處理標準化技術委員會著手研究和製定網絡通信標準,以實現網絡體系結構的國際標準化。 1984年,ISO正式頒布了稱為“開放系統互連基本參考模型”的國際標準ISO 7498,簡稱OSI RM(Open System Interconnection Basic Reference Model),即著名的OSI七層模型。 OSI RM及標準協議的製定和完善推動了統一、開放的網絡體系結構,大大加速了計算機網絡的發展。
但是,美國並不把ISO放在眼裡,堅持獨斷專行。 1983年,美國在阿帕網中正式推出TCP/IP協議取代原有的NCP網絡控制協議,進而形成因特網(Internet)。 30多年來,美國利用其科技、經濟和軍事優勢,以舉國之力推行因特網一張網連接覆蓋全球的戰略。美國因特網任務工作組(ICANN)赤裸裸地提出“同一個世界,同一個因特網”的蠱惑人心口號。奧巴馬政府更是讚譽“因特網在國際環境中獨樹一幟”。由此,因特網被美國及其蟄伏在各國的鐵粉們津津樂道為“互聯網”。
實際上,因特網就是美國製定規則、控制交換、監控信息的一種計算機網絡體系結構,並不完全符合國際標準組織ISO正式頒布的OSI RM的要求。也就是說,目前世界上存在著兩種占主導地位的網絡體系結構:一種是國際標準化組織ISO提出的OSI RM(開放式系統互連參考模型);另一種是因特網使用和力推的TCP/IP RM(TCP/IP參考模型)。兩種模型的根本區別在於,OSI RM推動全球計算機網絡開放式系統互連,TCP/IP迫使世界所有計算機終端都接入因特網一張網之中;ISO致力於各國、各種類型的計算機網絡系統之間的相互連接,美國強調的是計算機端對端之間的信息互通。
3、“互聯網”的定義
迄今,各國科技界、學術界、教育界、工商界,沒有統一、清晰、準確、規範的互聯網定義。這裡的中文互聯網,指的是早在1997年7月18日就經我國國務院授權的全國科學技術名詞審定委員會明確的英文internetwork,而不是Internet。
追隨美國因特網一張網戰略的某些人堅持說,“因特網就是互聯網”,“中國就是將因特網翻譯成互聯網”。這不是科學的、學術的定義,也不像是出自院士和“權威”之口,更像是不明事理的“阿Q”之說。
還是奧巴馬坦誠。他在白宮發表的《網絡空間國際戰略》的序言裡說,“通過因特網連接,美國公司的業務可以延伸至全球任何一個地方,為美國民眾創造無以計數的就業崗位和機會”,他承認, “因特網本身無法開啟國際合作的新紀元。”
因特網,源自英文的Internet。作為專有名詞,它所指的是使用TCP/IP通訊協議的一種計算機系統,以及這個系統所提供的信息、服務與用戶。因特網要求用戶(終端)按照其特定的規則在限定的因特網框架內使用指定的域名和地址進行信息交換,它對採用其它通訊協議的網絡是排斥和封閉的,或者乾脆越俎代庖、取而代之。
有人說,因特網的定義,英文應該是“a computer network consisting of a worldwide network of computer networks that use the TCP/IP network protocols to facilitate data transmission and exchange.”翻譯成中文,就是“一個由使用TCP / IP網絡協議促進數據傳輸和交換的計算機網絡組成的全球網絡。”請注意,這個“定義”說得很明確:
第一,必須使用TCP/IP協議;
第二,必須是同樣使用TCP/IP協議的計算機網絡組成;
第三,必須是在TCP/IP協議基礎上構成的全球一張網絡。
繞了這麼長一個繞口令一般的圈子,歸齊還是“使用TCP/IP協議的計算機網絡”!只能接受和使用TCP/IP同一種協議、同一類規則、在同一個網絡空間內進行傳輸與交換的網絡,這不還是因特網嗎?怎麼就成了“互聯網”了?到底是愚鈍產生了混沌,還是混沌導致了愚鈍?
有人說,在國外的文獻中,因特網被描述成“沒有領導、沒有法律、沒有政治、沒有軍隊……的不可思議的社會組織結構”。敢問,美國政府向全球推行這樣的網絡結構是何居心呢?是確保、誘導或迫使各國、各地區、各組織以及每個使用計算機的世界各地用戶都通過因特網屈從於、受制於、聽命於美國嗎?
有人說,從一般的角度認為,因特網的定義應包括三個方面內容,即:
——是一個基於TCP/IP協議的網絡;
——是一個計算機用戶的網絡集團,用戶在使用網絡資源的同時,也為網絡的發展壯大貢獻力量;
——是所有可被訪問和利用的信息資源的集合。
問題在於,不使用或者不適用TCP/IP協議的其它計算機網絡是否存在?是否允許存在?是否應該存在?使用不同協議網絡之間相互連接、融合、交換構成的是不是互聯網、是不是互連互通的網絡空間?即便同樣源於TCP/IP協議的網絡,IPV6與IPV4網絡之間是互連互通的關係,還是升級換代的關係?具有我國民族自主知識產權的IPV9與美國擁有知識產權的IPV6、 IPV4網絡之間,是主權平等的網絡互連關係,還是技術兼容的覆蓋替代關係?如果實現IPV9、V6、V4技術體系網絡的相互融通與共享共管共治,這是互聯網呢?還僅僅是因特網走向未來網絡的技術進步?
按照以上的因特網、“互聯網”定義和說法,中國祇有因特網框架內的一張網,沒有與國家主權相吻合、相一致的公眾網絡,沒有與非主權公眾網絡互聯互通的互聯網(internetwork)。
一個連美國人自己都說不清定義的“因特網就是互聯網”的概念,近些年來,接二連三地出現在我國戰略性、規劃性、決策性的文件和媒體連篇累牘地報導渲染之中。某些“權威”人士藉機喧囂塵上,不斷延伸、膨脹、曲解、編造其內涵和外延,實在令人不寒而栗。如果僅僅被美國忽悠,還不至於禁錮我們的自主創新思維,不至於不能扭轉和調整決策的失誤和失誤的策略。如果我們自己一個勁地忽悠自己,自欺欺人,難道不是意味著我們認識的混沌已經深陷泥沼、難以自拔了嗎?
二、網絡空間的迷茫與錯亂

1、因特網構成的網絡空間
經中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組批准,國家互聯網信息辦公室首次發布的《國家網絡空間安全戰略》中表述,網絡空間是由“互聯網、通信網、計算機系統、自動化控制系統、數字設備及其承載的應用、服務和數據等組成的”,是“國家主權的新疆域”,是“與陸地、海洋、天空、太空同等重要的人類活動新領域,國家主權拓展延伸到網絡空間,網絡空間主權成為國家主權的重要組成部分。”
以上述及的“互聯網”是指什麼?是指因特網一張網覆蓋全球構成的網絡空間?還是世界多張主權網互連互通構成的網絡空間?這個問題不搞清楚,人們的網絡空間意識、認識和識別辨析能力仍然深陷混沌、迷茫和錯亂之中。
因特網就是因特網,是為了實現終端與終端之間的信息交換而在一張網框架之內形成聯合的網絡空間;互聯網就是互聯網,是多個不同類型的網絡為了共享共治共贏的目的構成互連互通的網絡空間。因特網與互聯網各自構成的網絡空間存在融合、包容的共性,更存在各自專有與特定的規則、範疇、生態等特性。不同的網絡空間不能一概而論、混為一談。我們的認識不應該被攪和得越來越混沌不清。
不同的網絡空間最根本、最典型的特性區別在於,各國在互聯網絡(internetwork)框架下的主權不可改變,不可掩蓋,不可逆襲,只能是主權之間的握手言歡、握手言和,不可刀槍相向、恃強凌弱。因特網的主權只有一個,即美國一家獨有的主權,或者說是霸權。在因特網一張網的框架內,任何國家的主權都被美國單方面製定和嚴密掌控的規則、範疇和生態束縛、捆綁、桎梏,不得不任憑美國及其盟國(例如日本)侵犯、滲透、改變、驅使,把玩於鼓掌之中。
特別需要深度明晰、高度重視的是,傳播信息、發展經濟、繁榮文化、治理社會、合作交流等,不是因特網的專利,各國的主權網絡同樣可以實施和實現,建立在各國主權網絡空間基礎上的網絡互聯可能會做得更好。美國利用因特網的一張網技術體系和手段,繞開各國網絡空間的主權、治權和法權,是導致各主權網絡空間不安全的最大根源,是對各主權國家安全最大的威脅,是長期危害各主權國家和平穩定、民族團結的最不安定因素。在因特網內,沒有國與國的外交,沒有平等與相互尊重的國際合作,只有美國一家獨大,一家獨強,一家獨霸,一家之言說了算。在這樣的一張網框架內,同美國談規則、講原則、說治理、論普惠,豈非與虎謀皮、與狼共舞?美國怎麼可能拿自己的國家利益讓其他國家分享,出讓自己的網絡主權允許其他國家分庭抗禮呢?各國的網絡空間“主權在我、不受制於人”,倘若受制於人,必受其亂、必受其害!這個道理,伊朗明白、德國明白、俄羅斯明白,許多國家都明白。這些年來,從亞洲、美洲、中東到歐盟的教訓一個接一個,我們有什麼理由不明白、不接受教訓嗎?
3、“互聯網”的定義
迄今,各國科技界、學術界、教育界、工商界,沒有統一、清晰、準確、規範的互聯網定義。這裡的中文互聯網,指的是早在1997年7月18日就經我國國務院授權的全國科學技術名詞審定委員會明確的英文internetwork,而不是Internet。
追隨美國因特網一張網戰略的某些人堅持說,“因特網就是互聯網”,“中國就是將因特網翻譯成互聯網”。這不是科學的、學術的定義,也不像是出自院士和“權威”之口,更像是不明事理的“阿Q”之說。
還是奧巴馬坦誠。他在白宮發表的《網絡空間國際戰略》的序言裡說,“通過因特網連接,美國公司的業務可以延伸至全球任何一個地方,為美國民眾創造無以計數的就業崗位和機會”,他承認, “因特網本身無法開啟國際合作的新紀元。”
因特網,源自英文的Internet。作為專有名詞,它所指的是使用TCP/IP通訊協議的一種計算機系統,以及這個系統所提供的信息、服務與用戶。因特網要求用戶(終端)按照其特定的規則在限定的因特網框架內使用指定的域名和地址進行信息交換,它對採用其它通訊協議的網絡是排斥和封閉的,或者乾脆越俎代庖、取而代之。
有人說,因特網的定義,英文應該是“a computer network consisting of a worldwide network of computer networks that use the TCP/IP network protocols to facilitate data transmission and exchange.”翻譯成中文,就是“一個由使用TCP / IP網絡協議促進數據傳輸和交換的計算機網絡組成的全球網絡。”請注意,這個“定義”說得很明確:
第一,必須使用TCP/IP協議;
第二,必須是同樣使用TCP/IP協議的計算機網絡組成;
第三,必須是在TCP/IP協議基礎上構成的全球一張網絡。
繞了這麼長一個繞口令一般的圈子,歸齊還是“使用TCP/IP協議的計算機網絡”!只能接受和使用TCP/IP同一種協議、同一類規則、在同一個網絡空間內進行傳輸與交換的網絡,這不還是因特網嗎?怎麼就成了“互聯網”了?到底是愚鈍產生了混沌,還是混沌導致了愚鈍?
有人說,在國外的文獻中,因特網被描述成“沒有領導、沒有法律、沒有政治、沒有軍隊……的不可思議的社會組織結構”。敢問,美國政府向全球推行這樣的網絡結構是何居心呢?是確保、誘導或迫使各國、各地區、各組織以及每個使用計算機的世界各地用戶都通過因特網屈從於、受制於、聽命於美國嗎?
有人說,從一般的角度認為,因特網的定義應包括三個方面內容,即:
——是一個基於TCP/IP協議的網絡;
——是一個計算機用戶的網絡集團,用戶在使用網絡資源的同時,也為網絡的發展壯大貢獻力量;
——是所有可被訪問和利用的信息資源的集合。
問題在於,不使用或者不適用TCP/IP協議的其它計算機網絡是否存在?是否允許存在?是否應該存在?使用不同協議網絡之間相互連接、融合、交換構成的是不是互聯網、是不是互連互通的網絡空間?即便同樣源於TCP/IP協議的網絡,IPV6與IPV4網絡之間是互連互通的關係,還是升級換代的關係?具有我國民族自主知識產權的IPV9與美國擁有知識產權的IPV6、 IPV4網絡之間,是主權平等的網絡互連關係,還是技術兼容的覆蓋替代關係?如果實現IPV9、V6、V4技術體系網絡的相互融通與共享共管共治,這是互聯網呢?還僅僅是因特網走向未來網絡的技術進步?
按照以上的因特網、“互聯網”定義和說法,中國祇有因特網框架內的一張網,沒有與國家主權相吻合、相一致的公眾網絡,沒有與非主權公眾網絡互聯互通的互聯網(internetwork)。
一個連美國人自己都說不清定義的“因特網就是互聯網”的概念,近些年來,接二連三地出現在我國戰略性、規劃性、決策性的文件和媒體連篇累牘地報導渲染之中。某些“權威”人士藉機喧囂塵上,不斷延伸、膨脹、曲解、編造其內涵和外延,實在令人不寒而栗。如果僅僅被美國忽悠,還不至於禁錮我們的自主創新思維,不至於不能扭轉和調整決策的失誤和失誤的策略。如果我們自己一個勁地忽悠自己,自欺欺人,難道不是意味著我們認識的混沌已經深陷泥沼、難以自拔了嗎?
二、網絡空間的迷茫與錯亂

1、因特網構成的網絡空間
經中央網絡安全和信息化領導小組批准,國家互聯網信息辦公室首次發布的《國家網絡空間安全戰略》中表述,網絡空間是由“互聯網、通信網、計算機系統、自動化控制系統、數字設備及其承載的應用、服務和數據等組成的”,是“國家主權的新疆域”,是“與陸地、海洋、天空、太空同等重要的人類活動新領域,國家主權拓展延伸到網絡空間,網絡空間主權成為國家主權的重要組成部分。”
以上述及的“互聯網”是指什麼?是指因特網一張網覆蓋全球構成的網絡空間?還是世界多張主權網互連互通構成的網絡空間?這個問題不搞清楚,人們的網絡空間意識、認識和識別辨析能力仍然深陷混沌、迷茫和錯亂之中。
因特網就是因特網,是為了實現終端與終端之間的信息交換而在一張網框架之內形成聯合的網絡空間;互聯網就是互聯網,是多個不同類型的網絡為了共享共治共贏的目的構成互連互通的網絡空間。因特網與互聯網各自構成的網絡空間存在融合、包容的共性,更存在各自專有與特定的規則、範疇、生態等特性。不同的網絡空間不能一概而論、混為一談。我們的認識不應該被攪和得越來越混沌不清。
不同的網絡空間最根本、最典型的特性區別在於,各國在互聯網絡(internetwork)框架下的主權不可改變,不可掩蓋,不可逆襲,只能是主權之間的握手言歡、握手言和,不可刀槍相向、恃強凌弱。因特網的主權只有一個,即美國一家獨有的主權,或者說是霸權。在因特網一張網的框架內,任何國家的主權都被美國單方面製定和嚴密掌控的規則、範疇和生態束縛、捆綁、桎梏,不得不任憑美國及其盟國(例如日本)侵犯、滲透、改變、驅使,把玩於鼓掌之中。
特別需要深度明晰、高度重視的是,傳播信息、發展經濟、繁榮文化、治理社會、合作交流等,不是因特網的專利,各國的主權網絡同樣可以實施和實現,建立在各國主權網絡空間基礎上的網絡互聯可能會做得更好。美國利用因特網的一張網技術體系和手段,繞開各國網絡空間的主權、治權和法權,是導致各主權網絡空間不安全的最大根源,是對各主權國家安全最大的威脅,是長期危害各主權國家和平穩定、民族團結的最不安定因素。在因特網內,沒有國與國的外交,沒有平等與相互尊重的國際合作,只有美國一家獨大,一家獨強,一家獨霸,一家之言說了算。在這樣的一張網框架內,同美國談規則、講原則、說治理、論普惠,豈非與虎謀皮、與狼共舞?美國怎麼可能拿自己的國家利益讓其他國家分享,出讓自己的網絡主權允許其他國家分庭抗禮呢?各國的網絡空間“主權在我、不受制於人”,倘若受制於人,必受其亂、必受其害!這個道理,伊朗明白、德國明白、俄羅斯明白,許多國家都明白。這些年來,從亞洲、美洲、中東到歐盟的教訓一個接一個,我們有什麼理由不明白、不接受教訓嗎?
2、賽博空間主權屬於美國
有些人硬說賽博空間就是網絡空間,說英文的Cyberspace就是internetwork。如果這兩個英文單詞完全是一個意思、指向同一個詞語範疇,為什麼非要分成怎麼看、怎麼讀、怎麼寫也挨不上的兩個單詞呢,說英語的外國人累不累呀!
有人說,Cyberspace翻譯成中文的網絡空間意義更寬。有人說,美國的總統令關於Cyberspace的定義表明,“互聯網是網絡空間重要的基礎設施”,“互聯網計算機是Cyberspace最基本的元素”,“互聯網+才是互聯網向網絡空間擴展最重要的一個動作”。
此處的“互聯網”,明顯指的是因特網即Internet,“互聯網+”也就是Internet+。這裡又出現了令人頭暈眼花的混沌:因特網亦或“互聯網”不構成網絡空間,因特網亦或“互聯網”只不過是Cyberspace這個網絡空間的基礎設施?“因特網+”只不過是因特網向Cyberspace這個網絡空間擴展的一個重要動作,也並不歸屬於網絡空間?
英文Cyberspace的中文直譯,就是賽博空間。 2008年美國總統布什發布的54號國家安全總統令(NSPD)/23號國土安全總統令,對賽博空間定義的中文翻譯是:“信息環境中的一個全球域,由獨立且相互依存的信息技術基礎設施網絡組成,包括因特網、電信網、計算機系統以及嵌入的處理器和控制器等。”這個看上去嚴謹的定義,將賽博空間圈定為全球信息環境域,囊括世界所有的“信息技術基礎設施網絡”。美國空軍參謀長說,賽博空間囊括了從“直流電到可見光波”的一切東西。說來說去,還是因特網一張網網羅天下的那一套概念的翻版,換了個名詞、換了個說法而已,不出其右。
這個定義,幾乎可以被看作是向世界所有網絡空間主權宣戰的美國總統詔書。該定義不承認各國建設和發展主權網絡空間的資源、條件和基礎,先入為主地將各國各種網絡基礎設施統統納入美國賽博空間的範疇;該定義搶先拋出捆綁他國政治、經濟、軍事、文化手腳的“一定之規”,甩出了束縛各國科學家、戰略家在未來網絡發展領域創新遠航的纜繩;該定義只許州官放火,不許百姓點燈,霸氣十足、野心昭彰、咄咄逼人。
3、互聯網主權與治權迷茫
儘管國際標準化組織ISO提出的OSI RM(開放式系統互連參考模型)是目前世界上兩種占主導地位的網絡體系結構之一,但這些年並沒有形成規模化的市場應用。有人認為,該模型存在層次數量與內容不是最佳、會話層和表示層幾乎為空、相應的服務定義和協議複雜等技術缺點。
而因特網技術先天不足導致的諸多顯而易見的不安全問題,已為各國和各國際組織普遍關注。從根本上改變因特網的單一控制中心框架結構、TCP/IP協議、標識與安全認證機制等,已經成為全球重大的關鍵核心技術創新攻關課題。
也許正因為此,目前各國還沒有形成在主權網絡空間基礎上構建全球互聯網(internetwork)的條件、資源和依托,還沒有能力與因特網“劃江而治”、“平分秋色”、“共享太平”,只能“寄人籬下”,在接入因特網、租用因特網服務、防止因特網過分滲透等方面,投入巨大成本與美國討價還價地周旋,試圖盡量減少危害和損失。各國平等參與互聯網治理、公平分配互聯網基礎資源、共同管理互聯網根服務器等關鍵信息基礎設施、加強發展中國家的代表性和發言權等,好像口號,又好像海市蜃樓,喊喊罷了,觸不可及。
在美國因特網一張網的框架內、在美國賽博空間主權和安全的嚴重威懾下,和平發展為主題的網絡空間國際合作戰略很可能只是一廂情願的奢談,前提和基礎錯了,方向與路線偏頗。耗費巨大的人力物力財力追隨美國的因特網升級部署及賽博空間戰略,拼精力、拼時間、拼智商、磨牙口,終將導致我國及世界各國繼續在網絡空間長期落後於美國、受制於美國、屈從於美國,並將實際上喪失網絡空間主權、痛失發展良機和戰略契機,得不償失,悔不當初。
4、網絡空間國際合作權衡

與中文網絡空間對應的英文是Net Space,科學的定義是:信息基礎設施連接、覆蓋及承載信息處理的時空域。
這個定義,指明了因特網、互聯網、賽博網絡空間以及其它任何網絡空間最基本的共性,不以某個國家、某個利益集團的意志為轉移,不局限於專指某一張網、某一個國家構建的網絡空間。
以這個定義為前提,支持各國加強主權網絡空間的建設與發展,推動國際社會本著相互尊重的精神開展對話與合作,才有資源保障公眾在網絡空間的知情權、參與權、表達權、監督權,才有條件構建多邊、民主、透明的全球網絡空間治理體系,才有可能實現科學合理、公平有序、平等互惠、安全制衡的網絡空間國際合作。
我國在超級計算機研製、航天計算機系統應用等方面已經沖在了世界的前列,可以兼容覆蓋IPV6和IPV4的IPV9技術體系試運行測試令人滿意。俄羅斯在國內網絡信息控制和防範外來網絡侵襲等方面積累了很好的經驗、建立了良好的系統。歐盟已經著手製衡因特網的潛在威脅,致力於打造獨立自主的網絡空間體系。越來越多的國家提出網絡空間主權訴求,贊成習近平主席“共同構建網絡空間命運共同體”的主張。
在當前有限的條件、基礎和可預期的前景下,我國的網絡空間國際合作舉措應當審時度勢、量力而行、精心運籌操作,不可貿然鑽進他國的套路里。應當一手搶占與美國及他國談判國際網絡空間治理的外交先機、未雨綢繆,一手以舉國之力打造足以製衡美國因特網和賽博空間的我國主權公眾網絡體系。同時,採取果斷有力的措施,堅決處置來源於境內外的網絡安全風險和威脅,堅決懲治網絡違法犯罪活動,堅決打擊危害我國網絡空間主權、出賣國家和民族利益的行為,堅決糾正長期被動受制的網絡空間追隨戰略和策略。
三、世界網絡空間安全態勢

美國因特網主導下的世界網絡空間安全形勢日益嚴峻。穿戴“互聯網”衣帽的因特網安全問題千瘡百孔,越來越成為各國網絡空間難以救藥的頑疾和久治不癒的“心病”。
據《中國網絡空間安全報告(2016)》藍皮書,2015年以來,基於因特網和賽博空間的網絡衝突和攻擊,成為國家間對抗的主要形式。俄羅斯卡巴斯基公司指責美國“方程式小組”通過植入間諜軟件,感染伊朗、俄羅斯、中國等30多個國家的軍事、金融、能源等關鍵部門的上萬台電腦。伊朗稱挫敗了美國對其石油部門的網絡攻擊。意大利“Hacking Team”公司逾400G的數據被公開後發現,美國、摩洛哥、埃塞俄比亞等20多個國家的機構向其購買了網絡間諜和漏洞工具。美國火眼公司指責俄羅斯“APT28”組織利用零日漏洞,攻擊北約和美國國防機構。
藍皮書披露,美國設立“網絡威脅情報整合中心”,並擴大國務院“反恐戰略信息中心”的規模,中情局設立“數字革新部”加強網絡情報蒐集能力。以色列國防部啟動網絡安全孵化器計劃,英國政府拓展其網絡安全研究能力,美國海軍籌備攻擊性網絡行動,北約宣布進行網絡混合戰準備等,各國註重網絡攻防與軟硬實力建設,力求安全保障與攻擊能力雙向提升。媒體披露,全球已經有50多個各個國家組建的網絡戰部隊,全球網絡空間“軍備賽”不斷升級。
另據披露,依托美國因特網技術、協議和基礎設施建設發展起來的“中國互聯網”,政府、銀行、能源等機要要害部門的網絡信息系統普遍無法實現安全可控,國內工業控制系統更是“安全漏洞百出”。 2015年出現的支付寶、攜程網數據丟失,網易郵箱信息洩漏等鬧得沸沸揚揚,近年來通過短信、微信實施的金融詐騙每天都在大量發生。工信部長苗圩告訴記者,現在平均一個月能夠搜索到1.73億條電信詐騙的信息。
據“國家互聯網信息中心”《網絡安全信息與動態週報》,2017年2月13日-19日,境內感染網絡病毒的主機數量為40萬台,比上週上升6.6%;境內被植入後門的政府網站上升47.1%;針對境內網站的仿冒頁面數量上升165.2%;新增信息安全高危漏洞上升26.2%。監測發現,網絡病毒傳播的源頭放馬站點,涉及的68個域名中30.9%為境外註冊,且頂級域為.com的約佔83.8%,大部分放馬站點通過域名訪問實施病毒傳播。
國防大學教授戴旭指出,今天的世界已在一張“網”中。軍事領域的變化已經發生。從以傳感器為核心、以電磁空間為邊界的電子信息戰(可稱之為“電信戰”),到以網絡為核心、以心理空間開闢為特徵的網絡、心理戰(可稱之為“網心戰”),“網絡”化為基本特徵的第七代戰爭,正在成為大國博弈的主戰場。從攻城略地到攻心掠民,中國的傳統戰略優勢正成為被對手破解的重點,中國又一次處於無自然屏障可以依賴的危險境地,面對被網絡訛詐的狀態。關於戰爭和反戰爭的傳統認知體系,亟須升級換代。在網絡化多形態混合戰爭的新軍事時代,中國必須也有能力牽住時代的“牛鼻子”。
2、網際空間戰略已提上日程

網絡空間(Net Space),是人類創造的時空體系,是泛指的名稱概念,是信息處理與交換的承載空間。它概括了構成網絡空間的三大要素:屬性、連接覆蓋範圍和承載處理信息的功能。無論金融網、企業網、政府網,無論因特網、互聯網、網間網,無論陸基網、航空網、太空網,無論有線網、無線網、量子網,無論公網或私網涉及的相關服務提供商和運營商的專用接入網絡,等等,都有自主連接覆蓋的時空域和承載處理交換不同信息的網絡空間。
地球各種網絡空間並存構成的集合體,已經大大超出了網絡空間泛指的概念和定義,“網絡空間”已不能嚴謹、規範、準確地反映和包容其全部的內在特徵、延伸範疇與在全新的條件和基礎上發展變化的規律。這種網絡與網絡之間構成的超級網絡空間,喚生了“網際空間”(Nets Space)的學說。網際空間是網絡空間的集成域。
站在網際空間的高度、深度和廣度全維度、全視角地審視網絡空間,我們的視野將更寬更遠更清晰,我們的思維將更加容易跳出昨天和今天、展望明天,我們將會從因特網、“互聯網”、賽博空間造成的混沌中解放思想,走出一條超越計算機網絡時代的人類信息社會的全新道路。
一個由有線網絡、無線網絡、量子通訊、太空網絡等相互聯繫、相互作用、相互依托構成的網際空間時代,已經來臨並正在進入更加高級的階段。中國網際空間戰略的崛起,必將引起革命性的思想崛起、科技崛起、經濟崛起、民族崛起,國家崛起,惠及子孫後代,影響和帶動全球人類社會的跨越式進步。
網際空間戰略和技術準備已經提上日程,最佳時機也許就在眼前和今後的幾年之中。中國能不能搶占先機、把握良機,超越美國引領全新的超級網絡空間——網際空間時代,須只爭朝夕,須而今邁步從頭越,須數風流人物、還看今朝。
3、網際空間發展須舉國之力
美國以舉國之力推因特網、推IPV6、推賽博空間,在導致他國混沌和迷茫的同時,也確實創造了令人矚目的網絡科技、網絡經濟和網絡軍事輝煌。
我國已經成為世界第二大經濟體。我國完全有能力、有條件、有信心以舉國之力發展網際空間戰略和技術。
思想解放、體制改革是我國改革開放以來相輔相成的兩大舉措。由此出發,建議:
⑴ 建立黨中央、全國人大、國務院和全國政協共同領導和約束下的具高度權威性、法治化的決策糾錯機構和糾錯機制,堅決杜絕借混淆視聽左右決策之路。
少數追隨美國的“專家”、“權威”長期影響和乾預國家各網絡信息主管部門的身兼數職“一言堂”的怪事,再也不能允許發生、存在和繼續下去了,必須堅決扭轉和破除。
應當立即堅決糾正“全面引進、升級、部署IPV6”的重大戰略決策和規劃失誤,廢除與美國簽署的所有危害和危及我國網絡空間主權與安全的不平等協議;對網絡空間領域的國家投資項目逐一實施審計與後評價,明顯“為他人作嫁衣裳”的一律關停並轉。
⑵ 國家鼓勵和支持在民族自主知識產權前提和基礎上建設、發展與維護主權公眾網絡。
應當旗幟鮮明地允許在目前基於美國因特網的“中國互聯網“之外,建設發展獨立運行的中華公網等其它主權公眾網絡並提供服務,國民有選擇使用主權公眾網絡和非主權公眾網絡的權利。國家應出台傾向性的激勵政策和措施,允許主權公眾網絡採用IPV9、鄭碼、陶陳碼、CFL安全認證、MISC等等具有民族自主知識產權的技術。積極建設、發展與維護國內獨立運行的多網構成的互聯網,可以為構建全球網絡空間命運共同體探索模式、積累經驗、創造條件。
⑶ 不失時機地創建國家主導、社會參與、民間操作的“網際空間研究院”,全方位、多維度、深層次研究開發網際空間技術並製訂發展戰略和策略,打造世界一流的培養鍛煉網際空間人才基地,構建主權網絡/未來網絡/網際空間實驗、測試架構系統應用環境,探索與解決主權網絡、網絡空間和網際空間發展中的各種問題,大踏步地走在引領網際空間發展的世界前列。
⑷ 首先與俄羅斯、伊朗、德國、歐盟等致力於建設、發展、維護各自主權網絡空間的國家和國際組織積極進行構建網絡空間命運共同體的溝通、交流、洽談與合作,聯合多國積蓄力量,不以美國為主要談判對手。
掃清混沌,蕩滌迷茫,我們將不再受制於人、任其擺佈,我們將穩健地步入嚮往的網絡空間時代,我們將高瞻遠矚地奔向網際空間的未來。