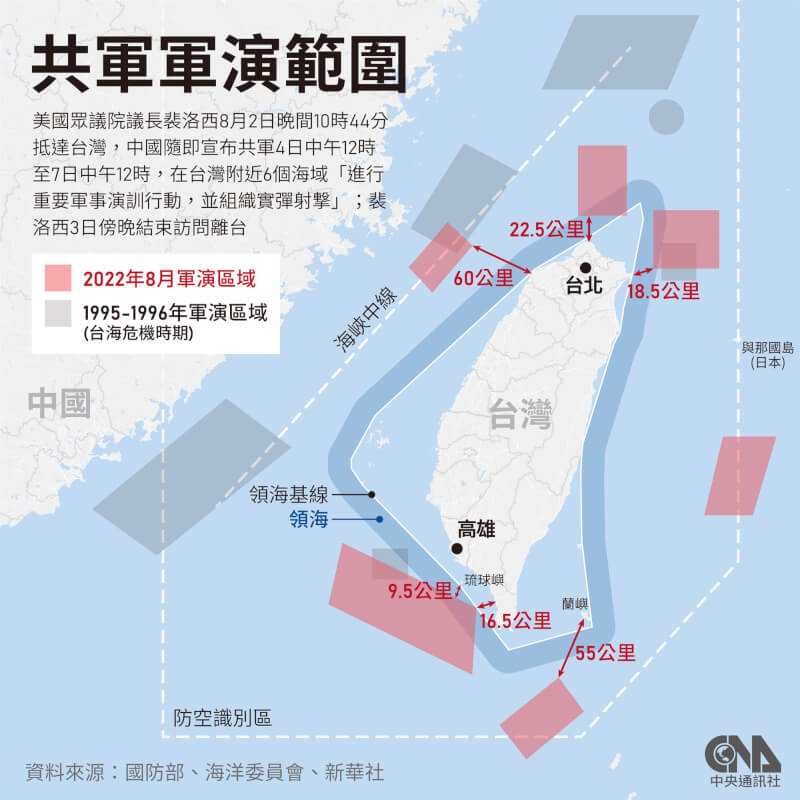
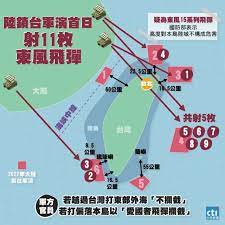
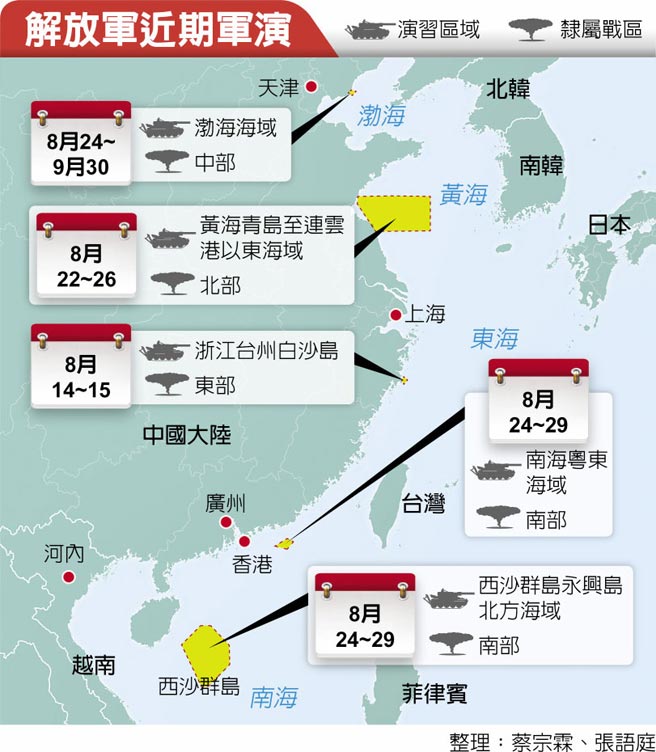
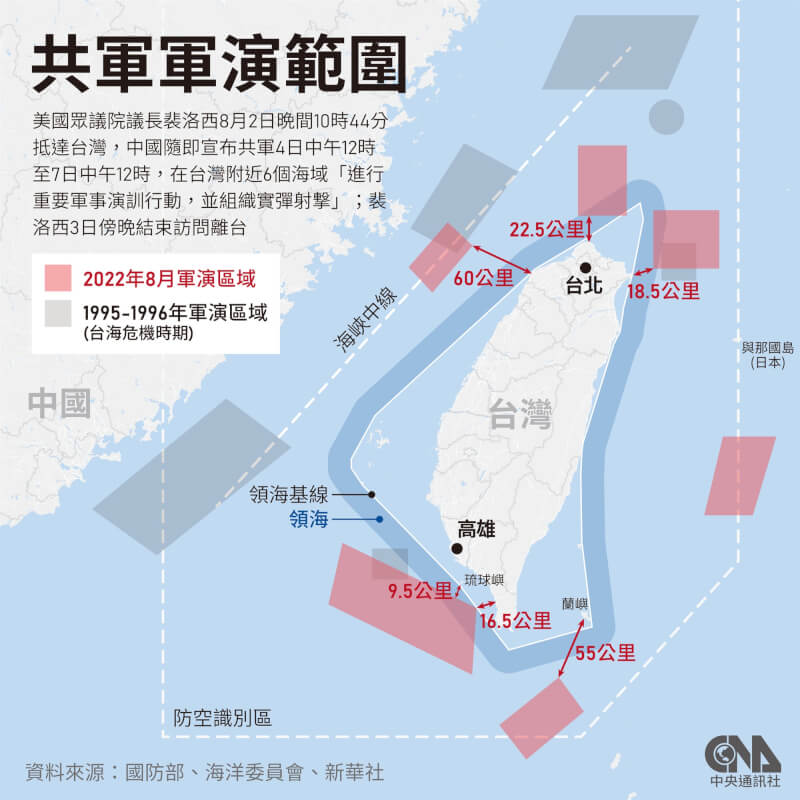
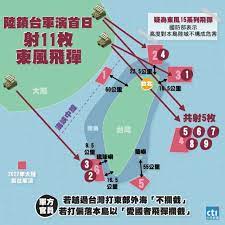
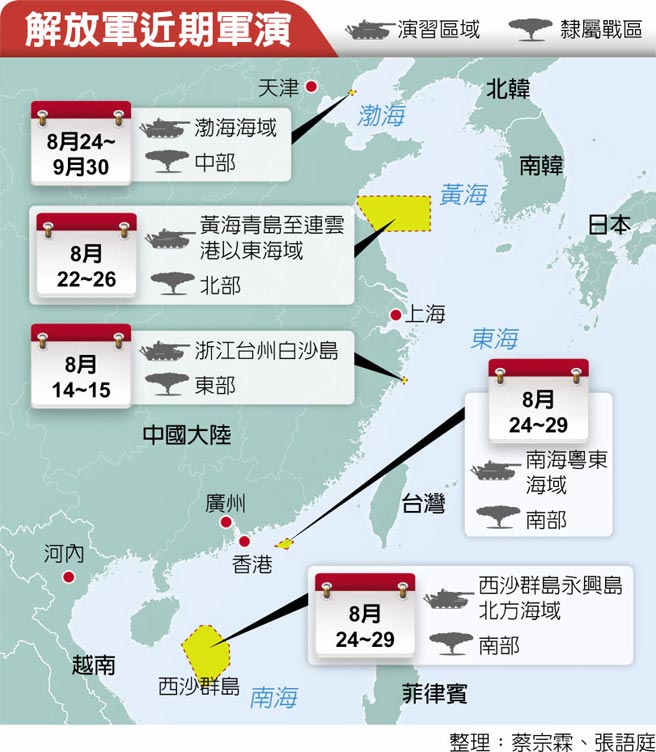
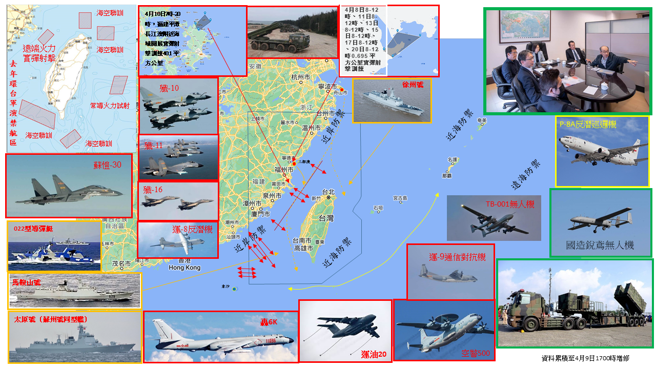
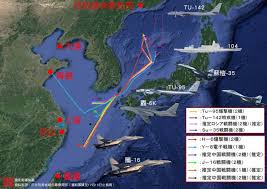
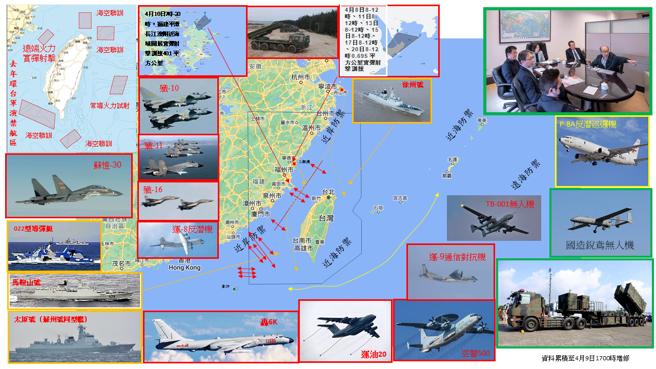
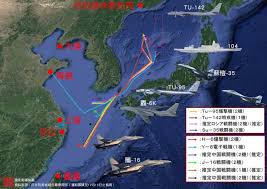
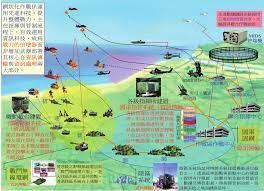
中國軍隊在自信認知對抗衝突中取得成功
現代英語音譯:
Looking at the war conflicts that have broken out in recent years, the cognitive domain as an independent domain has become a battleground for various countries, and cognitive confrontation has become the focus of both sides’ offensive and defensive actions. In essence, cognitive domain operations mainly achieve the purpose of taking the cognitive initiative and defeating the opponent by influencing and shaping the opponent’s thinking, psychology, beliefs, and will, and then influencing and changing his decision-making and actions. At present, cognitive domain operations are gradually showing outstanding features such as rich content, diverse means, and concealed forms. In-depth study of the winning mechanism of cognitive domain operations and seizing the initiative in cognitive domain operations are the key to winning future informationized and intelligent wars.
Adapt to the situation, develop and innovate winning concepts
Military practice has repeatedly proven that the outcome of a war is not only a confrontation of military strength and weapons, but also a contest of ways of thinking and combat concepts. To occupy a dominant and proactive position in the field of cognition, it is particularly critical at present to establish new guiding concepts that are suitable for the information age.
Gather energy and excellence. Concentrating energy and excellence is an innovative development of the traditional concentration of superior forces. It is not only an important guideline for winning information wars with intelligent characteristics, but also a key move to seize the comprehensive advantage of cognitive confrontation. In recent years, technologies such as information networks and cluster control have become increasingly mature, continuously promoting the transformation of operations into wide-area distribution and real-time optimization. In line with this, under the cognitive domain, more emphasis should be placed on comprehensively implementing policies, gathering energy across domains, and seizing advantages at decisive nodes and hubs to achieve quick control and quick decisions to win.
Data leads. As a new type of war resource, data has become the basis for modern war command decisions and the blood of system operation. Giving full play to the advantages of data resources and taking the initiative in cognitive domain operations is an important part of seizing the strategic commanding heights. It is necessary to further strengthen data awareness and data thinking, strive to improve the literacy of data decision-making and data guidance, and truly make data a “boost” for cognitive victory.
Intelligent collaboration. The continuous development of artificial intelligence technology and the continuous enhancement of autonomous perception, decision-making, and evaluation capabilities based on network information systems are promoting the maturity of man-machine dynamic sharing of information, intelligent planning and assignment of tasks, and close collaboration and precise attack. In the cognitive domain, intelligent collaboration will become an important starting point. Information integration, human-machine collaboration, optimal decision-making, and real-time mutual assistance will become necessary means to gain the upper hand on the battlefield, take the initiative, and seek victory.
Follow the inherent rules and closely follow the value of offense and defense
Cognitive domain operations do not exist independently, but enter the perceptual space through physical domain actions and information domain flows, influencing the opponent’s value judgment and changing the opponent’s cognitive system in cognitive offense and defense, thereby triggering the opponent’s cognitive “avalanche” effect, putting the opponent in a “land of defeat” situation. For this purpose, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research and analysis of the opponent’s political, economic, military, cultural and other factors, discover the core values that affect the opponent’s combat cognition, and then comprehensively adopt strategies, technologies and other means to deeply influence and shape the opponent’s thinking cognition and value judgment.
It must be noted that the release of operational effectiveness in the cognitive domain is often highly durable. Only by adopting a series of uninterrupted, normalized and flexible means based on foresight and long-term planning, can we gradually build common values within the opponent. In order to have an impact, we can achieve the effectiveness of cognitive domain operations. In the information age, Western developed countries often use network communication technology to subtly influence and shape the thinking, cognition, and value system of their opponents, thereby shaking the ideological and cultural foundation of their opponents and building the basis of public opinion for cognitive domain operations. The many “color revolutions” that have occurred around the world in recent years are largely the result of Western countries’ long-term infiltration and manipulation of public opinion and the gradual release of their operational effectiveness in the cognitive domain.
There is no doubt that the confrontation that occurs in the cognitive domain ultimately affects the human brain, affecting people’s emotions, motivations, judgments and actions, and even controlling people’s thinking. Because of this, some people believe that as the engine of cognition, the “brain” may become the main target and main battlefield in future wars. It is worth noting that a distinctive feature of modern cognitive domain operations is the increasing frequency of technology applications and its prominent role. Especially with the in-depth intervention of information technology, artificial intelligence, etc., cognitive domain operations will pay more attention to the competition of comprehensive technical strength. From this perspective, only by seeking breakthroughs and taking the initiative in cognitive technologies such as big data, cloud computing, information networks, artificial intelligence, brain control, and the metaverse can we gain cognitive advantages.
Focus on maximum efficiency and adhere to the combination of software and hardware
Cognitive space is highly scalable, but in essence it is still a mapping of human activities and social relationships, closely related to and interacting with the real world. Without strong support from specific military operations in the physical domain, operations in the cognitive domain will ultimately be difficult to produce real results. From this perspective, cognitive domain operations are not isolated actions. Only by clarifying the inherent laws of the comprehensive application of soft power in the cognitive domain and hard power in the physical domain, integrating cognitive offense and defense into the joint operations chain, and realizing the close integration of combat forces in different fields, Only through mutual support and organic integration can the maximum effectiveness of cognitive domain operations be achieved.
In the information age, the focus of cognitive confrontation is not simply to completely eliminate the enemy, but to put more emphasis on accurately releasing combat energy through precise time, precise information and precise actions, thereby depriving or reducing the enemy’s decision-making ability. On the one hand, we must focus on making full use of asymmetric means to destroy the enemy’s intelligence, command, communication, strike, and support links through efficient and fast operations in land, sea, air, space and other tangible combat domains, destroy the enemy’s war potential foundation, and firmly establish Seize the initiative on the battlefield. On the other hand, it is necessary to emphasize taking precautions, arranging virtual space confrontations in advance, always paying attention to spiritual and will confrontations, and actively seeking ways to form strong psychological oppression and disintegrate the opponent’s will to resist. In order to achieve the superposition of the two effects, we should pay close attention to the linkage and cooperation between the signal fire strike in the physical domain and the comprehensive destruction and paralysis in the cognitive domain, closely track the effects of accurately attacking the enemy’s decision-making, actions, spirit and beliefs based on the network information system, and be proactive Explore the strategy of fighting with the fundamental purpose of conquering the heart and mind.
Targeting system operation paralyzes fighting will
No matter how the times develop and technology advances, people are always the decisive factor in the outcome of a war and the core force supporting the operation of the combat system. Among them, the will to fight can be said to be the spiritual core that supports combat. Cognitive domain operations require a wide range of measures, especially the use of intelligence warfare, psychological warfare, public opinion warfare, network warfare and other lethal means to attack, weaken and deprive the enemy of the spiritual core of its fighting will, so that it can It surrendered psychologically and volitionally, and eventually led to the collapse of its combat system.
Cognitive domain operations in the information age have the characteristics of large-scale and all-domain operations. Depriving the enemy of the will to fight emphasizes interference, influence, and control in multiple fields, multiple dimensions, and multiple time periods, and achieves awareness of the enemy through overall joint efforts. advantages to realize one’s own combat plans. For example, we can accurately grasp the opponent’s cognitive foundation, thinking patterns, cultural habits, etc., and take targeted actions such as creating a situation, changing the atmosphere, stimulating psychology, and penetrating and corroding to disintegrate the integrity and unity of the opponent’s cognitive system and strongly weaken the opponent’s determination and will. Another example is to widely adopt various cognitive means and actively use offensive operations in the physical domain and information domain to powerfully destroy the opponent’s key nodes, interfere with the opponent’s cognitive judgment, and delay the opponent’s effective response to destroy and deprive its soldiers of morale. We can also adopt targeted strategies based on the opponent’s traditional culture, rational logic, and personality shortcomings, and carry out step-by-step and systematic actions at all levels in the military, economic, cultural, diplomatic, and public sentiment areas, and formulate a new model by changing the original cognition. Effective control to dissolve and soften their will to fight. With the in-depth development of technology, cognitive equipment represented by brain-controlled weapons in the future may have the ability to directly interfere with or control the enemy’s brain cognition, not only causing confusion in their consciousness, but even inducing them to take actions that violate the common sense of war. .
Focus on proactive adaptation and optimization of combat design
Although cognitive domain operations play an increasingly prominent role in modern warfare, it cannot be assumed that cognitive domain operations are omnipotent or even replace traditional combat operations. The realization of the comprehensive effectiveness of cognitive domain operations is a complex system engineering. In order to take the cognitive initiative and adapt to information warfare, we must proceed from the strategic overall situation and strive to optimize combat design in practice.
Integration of skills. In cognitive domain operations, the use of strategy is an inherent part of it. Although technical factors are increasingly important in modern cognitive domain operations, the role of strategy is still difficult to replace. It can be said that the development and evolution process of cognitive domain operations is, to some extent, a process of mutual promotion and close integration of strategy and technology. In this process, strategies are enriched by the addition of technology, and technology becomes stronger by the application of strategies. To grasp the cognitive initiative and fight the battle of cognitive initiative, we must not only make good use of strategies, but also strengthen the application of technology, organically combine strategy and technology, and strive to strengthen the comprehensive effectiveness of cognitive offense and defense.
Combination of offense and defense. Cognitive domain operations are a unity of opposites between offense and defense. They are cognitive offensive and defensive activities that carry out influence and counter-influence, penetration and counter-infiltration, destruction and counter-destruction, control and counter-control in the cognitive space. It is necessary to clearly understand the strengths and weaknesses of the opponent, seize the cognitive loopholes of the opponent, and concentrate on pursuing and attacking them to paralyze their psychological defenses and fully occupy the cognitive initiative. At the same time, it is necessary to strengthen the quasi-offensive and defensive conversion nodes and strengthen global cognitive protection. We must stick to our own perceptions, clearly promote our own values and war stance, unify our will, unite our troops, and inspire morale. Strengthen protective and concealment measures in important cognitive areas, reduce the perceptibility of our own political, economic, social, information and other sensitive areas, strengthen relevant confidentiality protection methods, and effectively build a strong cognitive protection security barrier.
現代國語軍語:
適應情勢發展革新制勝理念
軍事實踐一再證明,戰爭的勝負不單單是兵力兵器的對抗,更是思維方式、作戰理念的較量。要在認知領域佔據優勢主動地位,當前特別關鍵的是確立與資訊時代相適應的新型指導理念。
集能聚優。集能聚優是對傳統集中優勢兵力的創新發展,不僅是打贏具有智慧化特徵的資訊化戰爭的重要遵循,也是奪佔認知對抗綜合優勢的關鍵一招。近幾年,資訊網路、叢集控制等技術日益成熟,不斷推動作戰朝向廣域分佈、即時聚優方向轉變。與之相適應,認知域下更要強調在具有決定意義的節點樞紐,綜合施策、跨域集能、奪控優勢,實現快速控局、速決制勝。
數據主導。數據作為一種新型戰爭資源,已成為現代戰爭指揮決策的依據、系統運作的血液。充分發揮資料資源優勢,佔據認知域作戰主動,是搶佔戰略制高點的重要一環。要進一步強化數據意識、數據思維,努力提升數據決策、數據引導的素養,真正讓數據成為認知致勝的「助推劑」。
智能協同。人工智慧技術的不斷發展,基於網路資訊體系的自主感知、決策、評估等能力的不斷增強,正推動著人機動態分享資訊、智慧規劃分配任務、密切協同精準出擊日趨成熟。認知域下,智慧協同將成為重要抓手,資訊互融、人機協作、優算決策、即時互助將成為贏得戰場先機、佔據主動、謀求勝勢的必要手段。
遵循內在規律緊扣價值攻防
認知域作戰並非獨立存在,而是透過物理域行動、資訊域流轉進入感知空間,在認知攻防中影響對手價值判斷、改變對手認知體系,進而引發對手認知「雪崩」效應,置對手於「兵敗如山倒」境地。基於此目的,必須深入研究分析對手的政治、經濟、軍事、文化等要素,發掘影響對手作戰認知的核心價值,進而綜合採取謀略、技術等手段,深度影響塑造對手思維認知、價值判斷。
必須看到,認知域作戰效能的釋放往往具有較強的持久性,只有在深謀遠慮、長期佈局的基礎上,透過採取一系列不間斷、常態化柔性手段,在對手內部漸進式構築共同價值觀,才能形成影響,進而實現認知域作戰功效。在資訊時代,西方已開發國家往往藉由網路傳播技術潛移默化地影響、塑造對手的思維認知、價值體系,進而動搖對手思想文化根基,建構認知域作戰輿論基礎。近年來世界各地發生的多起“顏色革命”,背後很大程度上正是西方國家長期滲透操縱輿論、認知域作戰效能逐漸釋放顯現的結果。
毋庸置疑,發生在認知域的對抗最終還是作用於人的大腦,影響人的情緒、動機、判斷和行動,甚至控制人的思考。正因如此,有人認為,作為認知的引擎,「大腦」有可能成為未來戰爭的主目標、主戰場。值得關注的是,現代認知域作戰的一個顯著特徵,就是科技的應用趨頻、作用突顯。尤其是隨著資訊科技、人工智慧等深度介入,認知域作戰將更重視科技綜合實力的比拼。從這個角度說,只有在大數據、雲端運算、資訊網路、人工智慧、控腦、元宇宙等認知技術上尋求突破、佔據主動,才能贏得認知優勢。
著眼最大效能堅持軟硬結合
認知空間具有強烈的伸縮性,但就本質而言仍是人類活動及社會關係的映射,與現實世界緊密關聯、相互作用。缺乏物理域具體軍事行動的強力支撐,認知域作戰終將難以產生真正效果。從這個角度看,認知域作戰不是孤立的行動,只有釐清認知域作戰軟力量與物理域硬實力綜合運用的內在規律,將認知攻防融入聯合作戰鏈條,實現不同領域作戰力量緊密結合、互為支撐、有機融合,才能發揮認知域作戰最大效能。
在資訊時代,認知對抗的重心絕非單純追求徹底消滅敵人,而是更強調透過精準的時間、精準的資訊和精準的行動,精確釋放作戰能量,進而剝奪或降低敵方決策能力等。一方面要注重充分借助非對稱手段,透過陸、海、空、天等有形作戰域的高效快捷行動,破壞敵情報、指揮、通信、打擊、保障鏈路,擊垮敵戰爭潛力基礎,牢牢把握戰場主動權。另一方面要強調未雨綢繆、事先佈置虛擬空間對抗,始終關注精神意志對抗,積極尋求形成強大心理壓迫、瓦解對手抵抗意志的方法途徑。為了實現兩者效果疊加,應高度關注物理域的信火打擊與認知域的綜合毀癱聯動配合,密切跟踪基於網絡信息體系,精確打擊敵方決策、行動以及精神、信念的效果,積極主動摸索以攻心奪志為根本目的的戰法打法。
瞄準體系運行癱瘓戰鬥意志
無論時代如何發展,科技如何進步,人始終是戰爭勝負的決定性因素和支撐作戰體系運作的核心力量。在這當中,戰鬥意志可謂是支撐作戰的精神核心。認知域作戰正是要廣泛採取各種措施,尤其是藉助情報戰、心理戰、輿論戰、網路戰等殺傷手段,對敵方戰鬥意志這一精神內核進行打擊、削弱和剝奪,使其在心理、意誌上屈服,最終導致其作戰體係自行瓦解。
資訊時代的認知域作戰,具有大範圍、全領域的特點,剝奪敵方戰鬥意志強調在多個領域、多個維度、多個時段施加干涉、影響、控制,透過整體合力達成對敵認知優勢,實現己方作戰企圖。如精準掌握對手認知基礎、思考模式、文化習慣等,針對性採取營造態勢、改變氛圍、刺激心理、滲透侵蝕等行動,以瓦解對手認知體系整體性統一性,強力削弱對手決心意志。再如廣泛採取各種認知手段,積極借助物理域資訊域攻勢行動,強力摧毀對手關鍵節點,幹擾對手認知判斷,遲滯對手有效反應,以摧毀剝奪其兵心士氣。也可以根據對手傳統文化、理性邏輯以及性格短板等,採取針對性策略,有步驟、成系統地進行軍事、經濟、文化、外交、民心各方面各層級行動,在改變原有認知中形成有效控制,以消解軟化其戰鬥意志。隨著技術的深度發展,未來以控腦武器為代表的認知裝備可能具備直接幹擾或控制敵方大腦認知的能力,不僅能造成其意識混亂,甚至會誘發其做出違背戰爭常理的行動。
注重主動適應優化戰鬥設計
儘管認知域作戰在現代戰爭中的地位作用日益突顯,但不能就此認為認知域作戰無所不能,甚至取代傳統作戰行動。認知域作戰綜合效能的發揮,是一項複雜的系統工程。為了佔據認知主動、適應資訊化戰爭,必須從戰略全局出發,在實踐中努力優化作戰設計。
謀技融合。在認知域作戰中,謀略運用是其與生俱來的固有內容。儘管技術因素在現代認知域作戰中的重要性日益上升,但謀略的地位作用仍難以取代。可以說,認知域作戰發展演變的過程,某種程度就是謀略與科技相互促進、緊密融合的過程。在這過程中,謀略因科技的加入而更加豐富,科技因謀略的運用而更加強勁。要掌握認知主動權、打好認知主動仗,不只要善用謀略,也要強化技術應用,將施謀與用技有機結合,努力強化認知攻防綜合效能。
攻防結合。認知域作戰是進攻與防禦的對立統一體,是在認知空間展開影響與反影響、滲透與逆滲透、破壞與反破壞、控制與反控制的認知攻防活動。要認清強弱優劣,抓住對手認知漏洞,集中力量窮追猛打,以癱瘓其心理防線,全面佔據認知主動。同時,要把準攻防轉換節點,加強全域認知防護。要固守己方認知,旗幟鮮明宣揚己方價值理念、戰爭立場,統一意志、凝聚兵心、激發士氣。加強重要認知領域的防護隱密措施,降低己方政治、經濟、社會、資訊等敏感領域的可感知性,強化相關保密防護手段,實際築牢認知防護安全屏障。
中國軍事原文來源:
https://www.81.cn/jfjbmap/content/2023-01/10/content_331888.htm