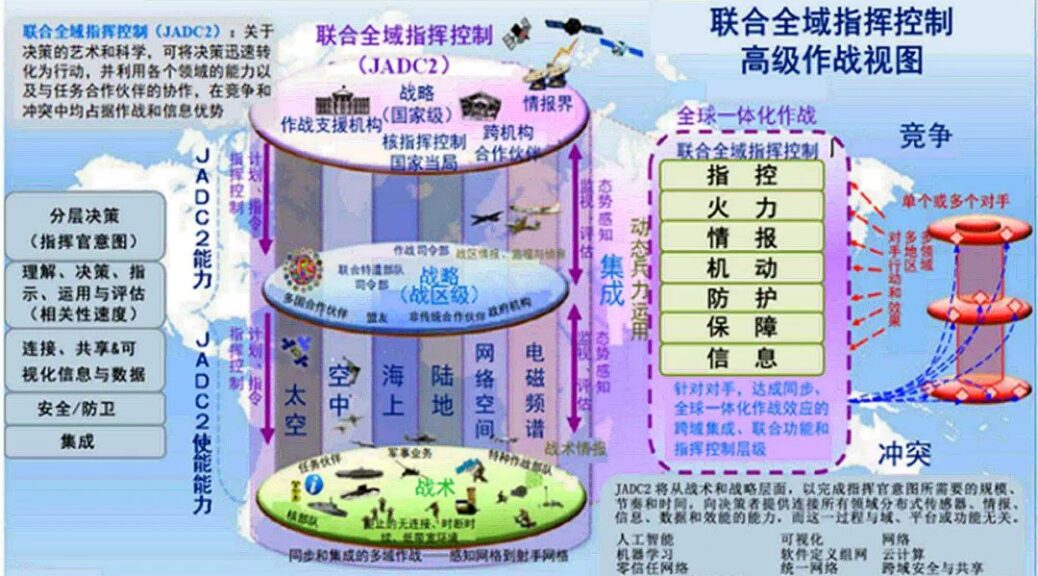
軍事大數據:驅動中國未來軍事轉型
現代英語:
Military Big Data: Driving Future Military Transformation
—Answering questions from reporters during the Third Military Big Data Forum
In recent years, the Chinese military has continuously promoted the application of big data technology in the military field. Big data has been gradually integrated into joint operations, construction management, and military scientific research, bringing new momentum to military innovation practices.
Based on the new situation and new requirements, and with a view to accelerating the construction and development of military big data, and to build an academic exchange platform for mutual communication, sharing and win-win cooperation between the military and civilian sectors, the 3rd Military Big Data Forum, hosted by the Academy of Military Sciences and themed “Frontiers and Prospects of Military Big Data Development”, was held in Beijing on September 16.
During the forum, a reporter from the PLA Daily interviewed Geng Guotong, Director of the Military Science Information Research Center of the Academy of Military Sciences, along with Deputy Directors Bai Xiaoying, Luo Wei, Li Xiaosong, and Li Congying, on topics related to military big data.
Military big data applications face complex challenges
Reporter: Globally, big data is developing rapidly, with key technologies accelerating breakthroughs and applications, deeply integrating with industrial development, and giving rise to a series of new technologies, applications, business models, and patterns. What are the main challenges facing the application of military big data?
Geng Guotong: Big data provides a new model, method, and means for understanding complex systems. The high complexity of the environment, the strong adversarial nature of competition, the high real-time response, the incompleteness of information, and the uncertainty of boundaries inherent in military activities determine the complexity of military big data applications. The combination of big data, high computing power, and large-scale models has achieved great success in civilian applications such as machine translation, human-computer dialogue, and autonomous driving. However, artificial intelligence driven by big data still struggles to achieve satisfactory application results when facing uncertain environments, especially complex military adversarial environments.
In the future era of intelligent warfare, the widespread use of unmanned systems and autonomous weapons will not only change traditional combat modes but also introduce new complexities. Therefore, unlike in the civilian sector, complexity will dominate the future military big data application environment. How to observe, intervene in, and measure the complex mega-systems of warfare using big data technologies is the main challenge facing military big data applications.
Bai Xiaoying: We can also examine the challenges currently faced by military big data applications from the perspective of causal science. Viktor Mayer-Schönberger, in his book *Big Data*, argues that “the biggest shift in the big data era is abandoning the pursuit of causality and instead focusing on correlation.” Currently, widely used deep learning and reinforcement learning methods are essentially data-driven algorithms that seek patterns and correlations through observation, thus having inherent limitations in revealing the essential laws governing things.
In future military operations, true and false data will be intricately intertwined, and data fog and deception will be prevalent. Focusing solely on correlations without considering causality risks getting lost in the fog and focusing on trivial details while neglecting the essentials. Therefore, how to organically integrate big data technology with causal inference to see through data relationships and understand the true nature of data is a major challenge facing the application of military big data.
The world’s major military powers are sparing no effort in promoting the development of military big data.
Reporter: Currently, big data development has become a crucial “blood-generating and intelligence-enhancing” project for major military powers worldwide to build military superiority, and a new pathway and driving force for combat capability growth. So, what new practices are major military powers adopting in promoting military big data development?
Li Xiaosong: Faced with the challenges of the era of artificial intelligence, the world’s leading military powers, represented by the United States, believe that artificial intelligence and big data are “two sides of the same coin.” They have continuously strengthened the integrated development of artificial intelligence and big data through measures such as issuing special plans, establishing research and development institutions, and strengthening the overall coordination of resources, in order to seize the initiative in the development of future intelligent warfare. They have successively issued documents such as the “Ministry of Defence Digital Modernization Strategy” and the Ministry of Defence’s “Data Strategy.” The United Kingdom recently also released its first “Ministry of Defence Digital Strategy,” comprehensively promoting a data-centric strategic transformation.
In order to implement strategic requirements, the United States has further proposed to achieve goals such as data visibility, accessibility, interconnectivity, trustworthiness, and interoperability. By formulating standards and specifications, increasing R&D investment, and adopting advanced commercial technologies, the United States has systematically addressed the bottlenecks that have long constrained data sharing efficiency, operational effectiveness, interoperability, and data analysis capabilities. The benefits of military big data construction are gradually becoming apparent.
In June of this year, the U.S. Department of Defense launched the “Artificial Intelligence and Data Acceleration Initiative,” adding specialized teams such as “Operational Data Teams” and “Artificial Intelligence Expert Teams” to 11 joint combatant commands, striving to gain faster judgment, decision-making, and action capabilities than adversaries in the ever-changing battlefield environment.
Li Congying: In addition to strengthening strategic guidance, major military powers have launched a series of projects to accelerate the transformation of big data technology research and development results into combat capabilities. For example, the U.S. Department of Defense implemented the “Big Data to Decision” project, focusing on the research and development of big data management and utilization technologies to build an autonomous system capable of independent operation and decision-making, thereby automating operations and decisions; the U.S. Special Operations Command launched Project Avatar, which uses automatic keyword searches on various public data sources such as the Internet and databases to enable combat personnel to obtain relevant battlefield data and build real-time battlefield environment images as much as possible; the U.S. Air Force developed the F-35 fighter jet integrated seamless support system, which integrates massive amounts of data such as historical status monitoring, fault diagnosis, and maintenance mission planning, and receives flight data in real time to achieve intelligent fault diagnosis, efficient maintenance mission planning, and precise allocation of maintenance resources. Russia’s combat command information system has made breakthroughs in intelligent analysis technology of battlefield situation big data and has been deployed and applied.
Big data drives the transformation of future warfare styles
Reporter: Artificial intelligence technology is rapidly penetrating the military field, profoundly changing the mechanisms of victory, force structures, and combat methods in future warfare. How should we understand and grasp the key role of big data in future intelligent warfare?
Geng Guotong: Data-driven artificial intelligence will inevitably become a new engine for future military transformation. “No data, no victory” has become the essential law and prominent feature of intelligent warfare.
First, data empowers intelligent equipment. This will drive the deep integration of hardware and algorithms through data flow, and the profound combination of machine intelligence and human wisdom, breaking through the limitations of traditional equipment systems in terms of time, space, mobility, and cost, thus unleashing the combat effectiveness of weapon systems. The US “Third Offset Strategy,” focusing on intelligent armies, autonomous equipment, and unmanned systems, plans to fully realize the intelligentization or even unmanned operation of combat platforms, information systems, and command and control by 2050, creating a new generation of equipment and achieving true “robot warfare.” In the latest round of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Israel, leveraging its advantage in artificial intelligence technology, has integrated and aggregated multi-source intelligence information and battlefield data to assist in combat operations, gradually revealing the beginnings of intelligent warfare.
Secondly, data empowers the formation of new forms of warfare. With data analysis and processing at its core, it will change the way forces are organized, the relative strengths and weaknesses of adversaries, and give rise to a series of new combat styles, forming an intelligent form of warfare centered on data.
Secondly, data empowers and transforms combat command. With the advancement and application of cognitive artificial intelligence, data-driven intelligent staff will extract high-value information from the “data deluge” in the shortest time and in the most effective way. In particular, it will be able to autonomously perceive, judge, decide, and respond to corresponding threats, forming a rapid decision-making advantage against the enemy in the command and control chain, achieving “strategic planning within data and decisive victory above data,” and realizing a true “decision-centered war.”
Luo Wei: In the current context of the integrated development of mechanization, informatization, and intelligentization, embedding big data technology into the kill chain and modularizing and integrating combat force formations can fully unleash combat capabilities. At the same time, we should also be clearly aware that the key factor determining the outcome of war remains people. Big data and artificial intelligence technologies cannot completely replace people, nor can they change the decisive role of people in war.
Big data powerfully supports the revolution in military management
Reporter: Currently, a military management revolution centered on efficiency is being actively promoted. So how can big data be used to transform the military’s construction and management model?
Li Xiaosong: As national defense and military modernization enter a new era, data is becoming an important basis for construction management and scientific decision-making. To explore new models of integration and coordinated development between big data and military construction management, and to support the advancement of a military management revolution centered on efficiency and guided by precision, we must grasp the following three aspects:
First, we must adhere to demand-driven principles. The booming fields of big data are all closely coupled with business scenarios. Only by clarifying the needs can we understand what data to build, what models to develop, and what products to create; otherwise, we’ll be “grasping at everything at once.”
Second, we must focus on embedding data into processes. Military management activities are complex and diverse. Only by integrating data thinking into the entire chain of planning, execution, supervision, and evaluation, and into business systems such as strategic planning, equipment management, logistics support, and personnel management, can we achieve business process reengineering and precise resource allocation.
Third, we must strengthen integration and sharing. Departmental barriers and fragmentation have always been significant factors affecting the realization of data value. We must comprehensively strengthen the development of laws and standards, actively promote the online deployment of business operations and data, effectively solve the challenges of sharing and utilization, and lay the foundation for a data-driven new model of military construction and management.
Bai Xiaoying: The development of technologies such as knowledge graphs, natural language processing, data mining, data computing, and data governance has also provided technical support for building a data-driven military construction and management model. For example, the U.S. Department of Defense, in collaboration with MIT, developed a “semantic data lake” technology for defense acquisition operations. Based on cleaning and processing massive amounts of fragmented business text data, they established a defense acquisition knowledge system through comparative analysis, correlation retrieval, and comprehensive judgment. This automatically discovers and mines the interdependencies between defense acquisition and operational capability requirements, quickly identifies capability deficiencies, optimizes acquisition investment projects, and provides effective reference for defense acquisition management and decision-making.
Big data drives a paradigm shift in military scientific research innovation.
Reporter: Marked by AlphaFold’s accurate prediction of protein structure, big data-driven artificial intelligence technologies, represented by deep learning, are revolutionizing modern scientific research models. Could you share your understanding of building a data-intensive paradigm for military scientific research innovation?
Luo Wei: Turing Award winner Jim Gray proposed that human scientific research activities have gone through the “experimental science paradigm” at the beginning of the development of science and technology, the “theoretical science paradigm” characterized by models and induction, the “computational science paradigm” characterized by simulation, and are now developing into the “data-intensive science paradigm” characterized by big data analysis.
In the era of big data, scientific research is grappling with a data divide and is essentially drowning in data. Take the biomedical field as an example: over one million papers are published annually, yet scientists read only about 250 on average each year. Simultaneously, as the total amount of human knowledge continues to expand, scientists’ hypotheses are based on only a small fraction of that knowledge, and human creativity increasingly depends on the randomness of prior experience. In this context, automating scientific research using big data and artificial intelligence technologies has become the catalyst for a paradigm shift in scientific research.
For data-intensive military scientific research and innovation paradigms, on the one hand, based on massive amounts of data and models, simulations of military activities are conducted to explore data relationships and value, and to build a “bottom-level channel” for the integration of theory and technology. Data serves as a bridge to achieve mutual attraction and deep integration between military theory and military technology. On the other hand, through research such as automated reasoning of scientific knowledge, exploration of scientific mechanisms, and the construction of a human-machine symbiotic research ecosystem, data is used to enhance efficiency and stimulate vitality, thereby realizing the digitalization and intelligentization of military scientific research activities. This deeply taps into the innovative potential of military researchers and enhances the military’s scientific research productivity.
Li Congying: To build a data-intensive military scientific research innovation paradigm, we should focus on two aspects: First, we should accumulate a solid data foundation by strengthening the multi-source collection, classification, integration, verification, and validation of various data resources related to military scientific research, and integrating widely distributed data with different ownership into a logically unified data resource pool. Second, we should strengthen algorithm innovation by grasping the evolutionary laws and development trends of military scientific research paradigms, developing targeted intelligent algorithms and models, and integrating our understanding of the essence of war, the rules of combat, and the mechanisms of victory to efficiently support data-driven military scientific research applications.
The innovative development of military big data requires collaboration from all parties.
Reporter: Big data technology has strong versatility. So, how can we effectively utilize all technological resources to solve the challenges of military big data research and application?
Geng Guotong: For the development and construction of military big data, it is necessary to strengthen communication, collaboration, and integration, emphasize cooperation among all parties, and enhance the supply of high-quality big data technologies. Specifically, three key aspects need to be addressed:
First, we must strengthen top-level guidance. Major military powers worldwide have elevated data from a technological level to a “high-value-added strategic asset” and a “high-profit product” in the military field, promoting the large-scale use of military and civilian data by drawing on commercial practices to gain comprehensive military advantages. In light of this, we should strengthen top-level guidance, clarify supporting conditions such as data integration and sharing, on-demand secure use, and compensation for benefits, to achieve efficient use of national big data infrastructure, technological products, and high-end talent.
Second, innovate application mechanisms. Given the characteristics of big data technology products—short update cycles, rapid iteration, and flexible integration and deployment—some of the world’s leading military powers emphasize fully utilizing commercial big data technology frameworks to build agile information system architectures that apply data faster than their competitors. To this end, a rapid procurement channel for military big data technologies and products can be established, exploring models such as direct procurement, trial-before-you-buy, service purchase, and joint research and development to promote the rapid application and efficient transformation of big data technology research results.
Third, strengthen collaborative efforts. Given the versatility of big data technology, we can explore the establishment of new research and development institutions to focus on fundamental and forward-looking technologies, product development, and industrial incubation related to big data, thereby seizing the high ground for innovation in big data research and application.
Bai Xiaoying: Talent is the primary resource for data construction. Building a professional talent team that is proficient in data knowledge and familiar with national defense and military operations is the key to the development of military big data construction.
In recent years, some of the world’s leading military powers have adopted methods such as introducing civilian talent, training existing personnel, and strengthening qualification certification to focus on cultivating talent in military data theory research and technology development. The U.S. Defense Acquisition University has partnered with Stanford University, Johns Hopkins University, Google, and others to jointly cultivate military big data talent with expertise in both data science and technology.
現代國語:
軍事大數據:驅動未來軍事變革
——第三屆軍事大數據論壇期間有關專家答記者問
■雷 帥 解放軍報特約記者 王 晗 記者 邵龍飛
近年來,我軍持續推動大數據技術在軍事領域的應用,大數據逐步融入聯合作戰、建設管理和軍事科研之中,為軍事創新實踐帶來了新動能。
立足新形勢新要求,著眼加快軍事大數據建設發展,搭建軍地互通共享、互促共贏的學術交流平台,由軍事科學院主辦、主題為“軍事大數據發展前沿與展望”的第三屆軍事大數據論壇,於9月16日在京舉行。
論壇期間,解放軍報記者就軍事大數據相關話題,采訪了軍事科學院軍事科學信息研究中心主任耿國桐研究員、副主任白曉穎研究員、羅威研究員、李曉松高級工程師和李聰穎副研究員。
軍事大數據應用面臨復雜性挑戰
記者:在世界范圍內,大數據發展日新月異,關鍵技術加速突破應用,與產業發展深度融合,催生了一系列新技術、新應用、新業態和新模式。請問軍事大數據應用主要面臨哪些挑戰?
耿國桐:大數據提供了一種認識復雜系統的新模式、新方法和新手段。軍事活動所具有的環境高復雜性、博弈強對抗性、響應高實時性、信息不完整性、邊界不確定性等特點,決定了軍事大數據應用的復雜性。大數據、大算力、大模型三者結合,在機器翻譯、人機對話、自動駕駛等民用領域應用取得了巨大成功。但是,大數據驅動下的人工智能在面臨不確定性環境、特別是軍事復雜對抗環境時,仍難以達到令人滿意的應用效果。
未來智能化戰爭時代,無人系統、自主武器等廣泛運用,不僅會改變傳統作戰模式,也將引入新的復雜性。因此,與民用領域不同,復雜性將主導未來軍事大數據應用環境。如何通過大數據技術手段觀察、干預、度量戰爭復雜巨系統,是軍事大數據應用所面臨的主要挑戰。
白曉穎:我們也可從因果科學的角度來看待當前軍事大數據應用所面臨的挑戰。維克托·邁爾·舍恩伯格在《大數據時代》一書中提出:“大數據時代最大的轉變就是,放棄對因果關系的渴求,而取而代之關注相關關系。”目前,廣泛應用的深度學習和強化學習方法,本質上還是數據驅動的算法,通過觀察尋找規律、尋求相關關系,在揭示事物本質規律方面存在固有局限性。
未來軍事活動中,真假數據錯綜交織,數據迷霧、偽裝欺騙現象普遍存在。如果只重相關不重因果,很有可能陷入迷霧之中,去舍本逐末。因此,如何將大數據技術與因果推斷有機融合起來,透視數據關系、認清數據本質,是軍事大數據應用面臨的一大挑戰。
世界各軍事強國不遺余力推進軍事大數據建設
記者:當前,大數據建設已成為世界各軍事強國構築軍事優勢的“造血增智”工程,成為戰斗力增長的新途徑新動能。那麼,各軍事強國在推進軍事大數據建設方面有哪些新做法?
李曉松:面對人工智能時代的挑戰,以美國為代表的世界軍事強國認為,人工智能和大數據是“一枚硬幣的兩面”。其通過出台專項規劃、建立研發機構、加強力量統籌等舉措,持續強化人工智能與大數據的融合發展,搶佔未來智能化戰爭的發展先機,先後出台了《國防部數字現代化戰略》、國防部《數據戰略》等。英國近期也發布了首部《國防部數字戰略》,全方位推進以數據為中心的戰略轉型。
著眼落實戰略要求,美國進一步提出要實現數據可見、可訪問、可互聯、可信、互操作等目標,並通過制定標准規范、加大研發投入、引用商業先進技術等方式,體系化破解長期制約數據共享效率、服務作戰效能、互操作水平、數據分析能力等方面的瓶頸問題,軍事大數據建設效益逐步凸顯。
今年6月,美國防部啟動了“人工智能與數據加速計劃”,為11個聯合作戰司令部增派“作戰數據小組”和“人工智能專家小組”等專業團隊,力求在瞬息萬變的戰場環境中,獲得比對手更快的判斷力、決策力和行動力。
李聰穎:除強化戰略引領外,各軍事強國紛紛布局開展系列項目,加速大數據技術研發成果向作戰能力轉化。比如,美國防部實施“大數據到決策”項目,重點研發大數據管理和利用技術,構建能獨立完成操控並做出決策的自治式系統,以實現操作和決策的自動化;美軍特種作戰司令部啟動“阿凡達”工程,通過在各種互聯網和數據庫等公開數據源上自動運行關鍵詞搜索的方式,使得作戰人員獲取相關戰場數據,盡可能構建實時的戰場環境圖像;美空軍研發的F-35戰機綜合無縫保障系統,整合歷史狀態監控、故障診斷、維修任務規劃等海量數據,實時接收飛行數據,以實現智能故障診斷、維修任務高效規劃與維修資源精准調配。俄羅斯研發的戰斗指揮信息系統,突破戰場態勢大數據智能分析技術,已配發應用。
大數據驅動未來作戰樣式變革
記者:人工智能技術正加速向軍事領域滲透,深刻改變著未來戰爭的制勝機理、力量結構和作戰方式。請問應該怎樣認識把握大數據在未來智能化戰爭中的關鍵作用?
耿國桐:數據賦能人工智能,必將成為未來軍事變革的新引擎。“無數據不勝”已成為智能化戰爭的本質規律和顯著特征。
首先,數據賦能智能化裝備。將通過數據流驅動硬件與算法深度融合、機器智能與人類智慧深度結合,突破傳統裝備系統在時間、空間、機動、成本上的限制,釋放武器裝備體系作戰效能。美軍“第三次抵消戰略”,以智能化軍隊、自主化裝備和無人化系統為重點,計劃在2050年全面實現作戰平台、信息系統、指揮控制等智能化甚至無人化,形成新的裝備“代差”,實現真正的“機器人戰爭”。在新一輪巴以沖突中,以色列利用其人工智能技術優勢,融合匯聚多源情報信息與戰場數據,輔助實施作戰行動,漸露智能化戰爭端倪。
其次,數據賦能形成新的戰爭形態。以數據分析與處理為核心,將改變部隊力量編成方式、對抗的強弱關系以及催生系列新型作戰樣式,形成以數據為中心的智能化戰爭形態。
再次,數據賦能變革作戰指揮。隨著認知人工智能的進步和應用,以數據為核心的智能參謀將在最短時間內,以最有效方式從“數據洪流”中提取高價值信息。特別是自行感知、判斷、決策、應對相應威脅,在指揮控制鏈條中形成對敵快速決策優勢,達成“運籌於數據之中、決勝於數據之上”,實現真正的“決策中心戰”。
羅威:在當前機械化信息化智能化融合發展的形勢下,將大數據技術嵌入殺傷鏈,對作戰力量編成進行模塊化、一體化改造,可充分釋放作戰能力。同時,也應該清醒認識到,決定戰爭勝負的關鍵因素仍然是人,大數據和人工智能技術不可能完全取代人,不能改變人在戰爭中的決定性地位。
大數據有力支撐軍事管理革命
記者:當前,正在積極推進以效能為核心的軍事管理革命。那麼如何運用大數據來變革軍隊建設管理模式?
李曉松:隨著國防和軍隊現代化建設進入新時代,數據正成為建設管理和科學決策的重要依據。探索大數據與軍隊建設管理融合滲透、協同發展的新模式,借助大數據精算、深算、細算發展路徑,支撐推開以效能為核心、以精准為導向的軍事管理革命,要把握以下三個方面:
一是堅持需求牽引。大數據蓬勃發展的領域,都與業務場景緊密耦合。只有把需求弄清楚,才能明白要建設什麼數據、開發什麼模型、形成什麼產品,否則就是“眉毛胡子一把抓”。
二是注重嵌入流程。軍事管理活動復雜多樣,只有把數據思維貫穿於規劃、執行、監督、評估等全鏈條,融入戰略規劃、裝備管理、後勤保障、人員管理等業務體系,才能實現業務流程再造和資源精准配置。
三是強化融合共享。部門壁壘和條塊分割一直是影響數據價值效用發揮的重要因素。要通過全面加強法規標准建設,積極推動業務上網、數據上線,有效破解共享利用難題,為數據驅動的軍隊建設管理新模式奠定基礎。
白曉穎:知識圖譜、自然語言處理、數據挖掘、數據計算、數據治理等技術的發展,也為構建數據驅動的軍隊建設管理模式提供了技術支撐。比如,美國防部與麻省理工學院合作,開發面向國防采辦業務的“語義數據湖”技術。他們在清洗處理海量碎片化業務文本數據基礎上,通過對比分析、關聯檢索和綜合研判,建立國防采辦知識體系,自動發現和挖掘國防采辦與作戰能力需求之間的相互依賴關系,快速查找能力缺陷,優化采辦投資項目,為國防采辦管理與決策提供有效的參考借鑑。
大數據推動軍事科研創新范式變革
記者:以AlphaFold准確預測蛋白質結構為標志,以深度學習為代表的大數據驅動人工智能技術正在顛覆著現代科學研究模式。那麼,對於構建數據密集型的軍事科研創新范式,請談一下您的理解。
羅威:計算機圖靈獎獲得者吉姆·格雷提出,人類科研活動歷經科學技術發展之初的“實驗科學范式”、以模型和歸納為特征的“理論科學范式”、以模擬仿真為特征的“計算科學范式”,正發展到以大數據分析為特征的“數據密集型科學范式”。
可以說,大數據時代,科學研究正陷入數據鴻溝與淹溺之中。以生物醫學領域為例,每年發表論文超過100萬篇,科學家每年平均閱讀量卻只有250篇左右。與此同時,隨著人類的知識總量不斷擴大,科學家作出的假設只是基於知識總量的很小一部分,且人類創造力愈發取決於先前經驗的隨機性。在這種情況下,運用大數據和人工智能技術實現科學研究的自動化,成為當前科學研究范式變革的引爆點。
對於數據密集型軍事科研創新范式而言,一方面基於海量數據與模型,開展軍事活動的仿真模擬,挖掘數據關系和價值,搭建理技融合的“底層通道”,以數據為橋梁,來實現軍事理論和軍事科技的互牽互引、深度融合。另一方面,通過科技知識自動推理、科學機理探究、人機共生的科研生態構建等研究,以數據聚能增效,以數據激發活力,來實現軍事科研活動數字化、智能化,從而深度挖掘軍事科研工作者創新潛能,解放軍事科研生產力。
李聰穎:對於構建數據密集型的軍事科研創新范式,還應注重把握兩個方面問題:厚積數據基礎,加強軍事科研相關各類數據資源的多源采集、分類融合、校核驗證,將廣域分布、權屬不同的數據融合成邏輯一體的數據資源池;強化算法創新,把握軍事科研范式演進規律及發展趨勢,針對性研發智能算法和模型,融入對戰爭本質的認知、對作戰規則的理解和對制勝機理的把握,高效支撐數據驅動的軍事科研應用。
軍事大數據創新發展需要各方協作
記者:大數據技術具有很強的通用性。那麼,如何有效利用一切科技力量,破解軍事大數據研發與應用難題?
耿國桐:對於軍事大數據建設發展而言,需要加強交流、協作和融合,注重各方協作,強化高質量大數據技術供給。具體而言,需要重點把握三個方面:
一是加強頂層推進。世界各軍事強國已將數據從技術層面上升為“軍事領域高附加值的戰略資產”“高利潤產品”來認識,通過借鑑商業做法推動軍地數據的規模化使用,獲取全方位軍事優勢。鑑於此,可加強頂層指導,明晰數據融合共享、按需安全使用、利益補償等配套條件,實現國家大數據基礎設施、技術產品和高端人才等的高效使用。
二是創新應用機制。針對大數據技術產品更新換代周期短、迭代速度快、集成部署靈活等特點,世界一些軍事強國注重充分利用商業大數據技術框架,構建快於競爭對手數據應用的敏捷信息體系架構。為此,可構建軍事大數據技術與產品的快速采購通道,探索運用直接采購、先試後買、購買服務、聯合研發等模式,推動大數據技術研發成果的快速應用和高效轉化。
三是強化力量協同。針對大數據技術通用性強的特點,可探索成立新型研發機構,聚焦軍事應用場景開展大數據基礎性、前瞻性技術攻關、產品研發和產業孵化,搶佔大數據研發與應用的創新高地。
白曉穎:人才是數據建設的第一資源,打造一支既精通數據知識,又熟悉國防和軍隊業務的專業人才隊伍,是軍事大數據建設發展的關鍵。
近年來,世界一些軍事強國采取引進民用人才、培養現有人員、加強資格認證等方式,重點培養軍事數據理論研究與技術研發人才。美國防采辦大學與斯坦福大學、約翰斯霍普金斯大學、谷歌等合作,聯合培養“數業俱精”的軍事大數據人才。