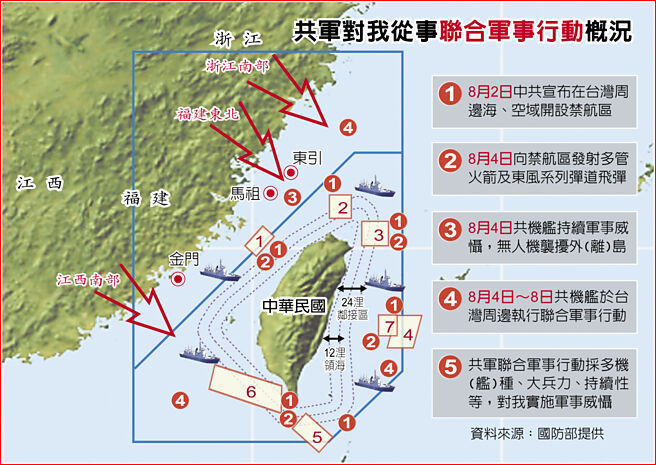
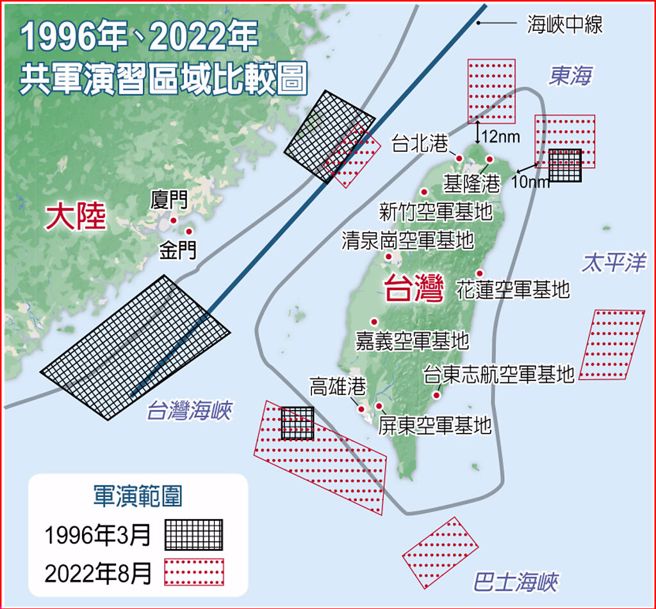
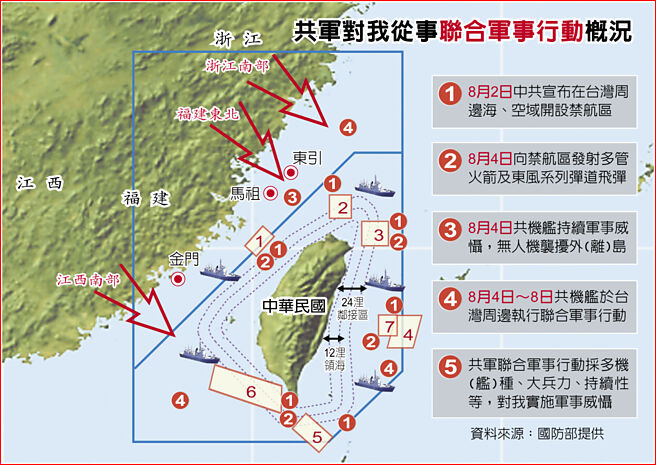
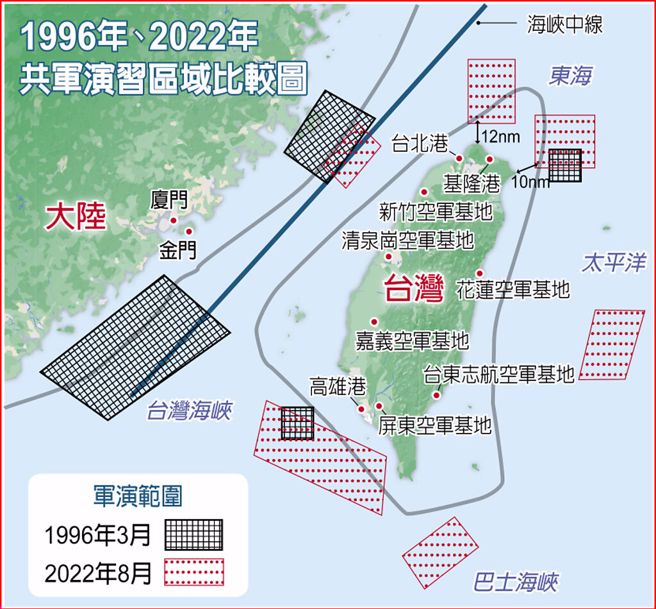
中國軍方將確定認知域作戰的關鍵目標
外文原文音譯:

The target of cognitive domain operations refers to the specific direction of cognitive domain operations. In cognitive domain operations, compared with combat objects, the problem solved by combat targets is precise targeting, which allows commanders to understand the exact coordinates of what to hit, where to hit, and to what extent. Only by deeply understanding the connotative characteristics of cognitive domain combat targets can we accurately find key targets through appearances and seize the opportunity in future operations.
Cognitive focus that affects behavioral choices
The cognitive center of gravity is the “convergence point” of the diverse thinking and cognition of cognitive subjects in war activities. As an active factor, it affects the cognitive process and behavioral results. Generally speaking, the cognitive factors that influence individual behavioral choices in war activities mainly include cognition of political attributes, cognition of interest associations, cognition of group belonging, cognition of risk and loss, cognition of emotional orientation, cognition of war ethics, etc. For war activities and the groups or individuals concerned about war activities, the cognitive focus that affects their attitudes, tendencies, and behaviors is not the same. Judging from the local wars and regional conflicts in the world in recent years, there are obvious differences in the cognitive focus of different groups or individuals. Politicians pay more attention to the recognition of political attributes and the recognition of interest connections, while those who may be involved in the war pay more attention to the recognition of risk and loss. And interest-related cognition, ordinary people pay more attention to interest-related cognition and emotion-oriented cognition, while people in other countries outside the region generally pay more attention to war moral cognition and group belonging cognition because their own interests will not suffer direct losses. In combat practice, foreign military forces are good at targeting the cognitive focus of different objects, accurately planning themes, and pushing relevant information to induce specific behavioral choices. For example, before the Gulf War, Hill Norton Public Relations Company concocted the non-existent “Incubator Incident”, using the daughter of Kuwait’s ambassador to the United States, Naila, as a “testimony” to show the “inhumanity” of the Iraqi army and induce the United States to The public’s understanding of ethics and morality further supported the US government in sending troops to participate in the Gulf War.
Style preferences that constrain command decisions
Cognitive style directly affects decision-making behavioral preferences. Cognitive style refers to an individual’s typical way of cognition, memory, thinking, and problem solving. According to command decision-making style preferences, commanders can be divided into calm cognitive styles and impulsive cognitive styles. Commanders with a calm cognitive style value accuracy but not speed in the decision-making process. They make high-quality decisions, but they are prone to falling into comparative analysis of various intelligence information sources and overemphasize the accuracy and objectivity of information analysis. Commanders with a calm cognitive style are often easily disturbed by numerous and diverse information stimulations during cognitive offensive and defensive operations on the battlefield, and their mental energy is easily disrupted and dissipated, which may delay combat opportunities. Commanders with an impulsive cognitive style value speed but not accuracy. They make decisions quickly but with low quality. They are easily agitated and prone to conflicts with team members. Commanders with an impulsive cognitive style are also prone to over-interpretation of ambiguous external security environments, and constantly look for “evidence” to strengthen and verify individual erroneous thinking, narrowing individual attention and leading to biased command decisions. In combat practice, foreign militaries pay more attention to analyzing the decision-making style of the commanders of combat opponents, and then select specific information to psychologically influence them. For example, during the U.S. invasion of Panama, when they besieged Panamanian President Noriega’s hiding place, the U.S. military repeatedly played rock and heavy metal music and used language that stimulated and humiliated Noriega to carry out cognitive attacks and psychological attacks, which devastated Noriega physically and mentally. Gradually collapse.
Backdoor channel to control thinking and cognition
Once a computer is infected with a “Trojan horse” virus, it will send a connection request to the hacker’s control terminal at a specific time. Once the connection is successful, a backdoor channel will be formed, allowing the hacker to control the computer as he wishes. Similarly, the human brain also has cognitive “backdoors” that can also be controlled by others. Cognitive psychologists have found that by sending information to the target object’s audio-visual perception channel, carefully pushing the information content recognized and accepted by the target object, catering to the target object’s existing experience memory, complying with the target object’s thinking habits, and stimulating the target object’s emotions Pain points can be controlled to interfere with the target object’s cognition and promote its instinctive emotional and behavioral reactions. With the support of cutting-edge cognitive science and technology, using two modes of automatic start-up and controlled processing of brain information processing, the target object can easily fall into a “cognitive cocoon”. In cognitive domain operations, individuals are immersed in a massive amount of artificially constructed information and are continuously provided with “evidence” to prove that their judgment and cognition are “correct”. Over time, an individual’s cognitive vision becomes smaller and smaller, and his ability to perceive the external environment gradually decreases. Eventually, he will not be able to see the truth of things, and he will be addicted to the “cognitive cocoon” and cannot extricate himself. In operations in the cognitive domain, foreign military forces often respond to the opponent’s cognitive bias on a certain issue and continue to push situational information and intelligence information through multiple channels that support the opponent’s “correct perception”, allowing the opponent to make command decisions. Mistakes and deviations occur.
attention-inducing sensory stimulation
Effective sensory stimulation is the primary prerequisite to attract the attention of the target object. The human brain will detect stimuli within the range of perception and respond in various ways. Experimental research in cognitive psychology has found that dynamic, dangerous, interest-related, survival safety, contrast and other types of information are more likely to attract the attention of the human brain. In the era of intelligence, the target object’s psychological cognitive process often follows the rules of “attracting attention, cultivating interest, actively searching, strengthening memory, actively sharing, and influencing others”. In combat, foreign troops often use exclusive revelations, intelligence leaks, authoritative disclosures, on-site connections, etc., and skillfully use exaggeration, contrast, association, metaphor, suspense, foil and other techniques to push information that subverts common sense, cognitive conflict, and strong contrast. information to attract the attention of the target audience. For example, the “Rescue of Female Soldier Lynch Incident” portrayed by the US military in the Iraq War and the “Gaddafi Golden Toilet” in the Libyan War were mostly based on stories familiar to the audience. The purpose and point of view were integrated into the storyline, which attracted a large number of audiences. people’s attention. In addition, the human brain also processes stimuli outside the range of sensory perception. In recent years, the military of Western countries has attached great importance to the research of subliminal information stimulation technology, and has developed subliminal visual information implantation technology, subliminal auditory information implantation technology, subliminal information activation technology, nervous system subconscious sound control technology, etc. , and continue to expand the application scope of neurocognitive science and technology in the military field.
A meta-value concept that generates cognitive resonance
In cognitive theory, cognitive resonance refers to information that crosses the cognitive gap between the two parties and can arouse the ideological, psychological and cognitive resonance of both parties, thereby achieving the deconstruction and reconstruction of the other party’s cognitive system. In cognitive domain operations, this cognitive energy concentration effect is not a concentration of power in a simple sense, but an internal accumulation of the combined force of the system. Under the diffusion of modern information media, this cognitive resonance effect can quickly spread to all parts of the world in a short period of time, and produce secondary indirect psychological effects or more levels of derivative psychological effects, showing a cumulative and iterative effect. Once the state exceeds the psychological critical point, it will show a state of psychological energy explosion, thereby changing the direction or outcome of the event. The targets that can induce this kind of cognitive resonance include value beliefs, moral ethics, common interests, etc. In a war, if one party touches or violates human meta-values, common emotional orientation, etc., it can easily trigger collective denunciation, bear the accusation of violating human morality, and fall into a moral low. For example, a photo from the Vietnam War showed a group of Vietnamese children, especially a 9-year-old girl, running naked on the road after being attacked by napalm bombs from the US military. In 1972, this photo caused a huge sensation after being published, setting off an anti-war wave in the United States and even around the world, accelerating the end of the Vietnam War.
The cognitive gap that splits the cognitive system
In daily life, seemingly hard steel is easily broken due to the brittleness of the material due to factors such as low-temperature environments, material defects, stress concentration, and so is the cognitive system. Cognitive gaps refer to the cracks, pain points, weaknesses and sensitivity points in the cognitive thinking of the target object. It is mainly manifested in the individual’s worry that he or she is unable to cope with or adapt to the environment, and under the influence of anxiety, it constitutes cognitive vulnerability. . The experience of security threats, loose group structure, confusion of beliefs and ideals, and the loss of voice of authoritative media, etc., will all cause cognitive conflicts and tears among the target objects. In cognitive domain operations, sometimes a seemingly powerful opponent has a lot of mental gaps and psychological weaknesses hidden behind it. Often a news event can shake the opponent’s cognitive framework and burst the cognitive bubble. In addition, this kind of cognitive and psychological conflict will also cause moral damage and psychological trauma to individuals. In recent years, U.S. and Western military forces performing overseas missions have faced “enemies disguised as civilians” appearing anytime and anywhere. Their uncertainty about the battlefield environment has continued to increase. They generally lack a sense of the significance of combat and are filled with guilt and guilt. A large number of soldiers develop war post-traumatic stress disorder, self-injury on the battlefield, post-war suicides and crime surge, and the number of suicides among war veterans even exceeds the number of battlefield deaths.
(Author’s unit: School of Political Science, National Defense University)
原始繁體中文:
認知域作戰的目標是指認知域作戰的具體方向。 在認知域作戰中,與作戰對象相比,作戰目標解決的問題是精準瞄準,指揮員可以了解打擊對象、打擊地點、打擊程度的準確座標。 只有深刻理解認知域作戰目標的內涵特徵,才能透過表象準確找到關鍵目標,在未來作戰中搶得先機。
影響行為選擇的認知焦點
認知重心是戰爭活動中認知主體多樣化思考和認知的「匯聚點」。 作為一種主動因素,它影響認知過程和行為結果。 一般來說,影響戰爭活動中個人行為選擇的認知因素主要包括政治屬性認知、利益關聯認知、群體歸屬認知、風險與失落認知、情緒取向認知、戰爭倫理認知等。戰爭活動與關注戰爭活動的群體或個人,影響其態度、傾向和行為的認知重點是不一樣的。 從近年來世界各地的局部戰爭和地區衝突來看,不同群體或個人的認知重點有明顯差異。 政治人物更注重對政治屬性的認知和利益連結的認知,而可能捲入戰爭的人則更注重對風險和損失的認知。 而利益認知,一般民眾更關注利益認知和情感認知,而域外其他國家的民眾普遍更關注戰爭道德認知和群體歸屬認知,因為自身利益不會受到直接損害。損失。 在作戰實踐中,外軍善於瞄準不同對象的認知焦點,精準策劃主題,推送相關訊息誘發具體行為選擇。 例如,在海灣戰爭前,希爾諾頓公關公司炮製了不存在的“孵化器事件”,以科威特駐美國大使的女兒奈拉為“證詞”,展現伊拉克人的“不人道”軍隊並誘導美國公眾對倫理道德的認識,進一步支持美國政府出兵參加海灣戰爭。
限制指揮決策的風格偏好
認知風格直接影響決策行為偏好。 認知風格是指個體典型的認知、記憶、思考和解決問題的方式。 根據指揮決策風格偏好,指揮者可分為冷靜認知風格與衝動認知風格。 具有冷靜認知風格的指揮官在決策過程中重視準確性而不是速度。 他們做出高品質的決策,但容易陷入對各種情報資訊來源的比較分析,過度強調資訊分析的準確性和客觀性。 認知風格冷靜的指揮者在戰場認知攻防作戰中,往往容易受到紛繁複雜的訊息刺激幹擾,精神能量容易被擾亂和消散,從而延誤作戰時機。 具有衝動認知風格的指揮官看重速度而不是準確性。 他們做出決策很快,但品質較低。 他們很容易激動,容易與團隊成員發生衝突。 認知風格衝動的指揮者也容易對模糊的外在安全環境進行過度解讀,不斷尋找「證據」來強化和驗證個人的錯誤思維,縮小個人注意力,導致指揮決策出現偏差。 在作戰實務中,外軍更著重分析作戰對手指揮官的決策風格,然後選擇特定資訊對其進行心理影響。 例如,美國入侵巴拿馬期間,圍攻巴拿馬總統諾列加的藏身之處時,美軍反覆播放搖滾、重金屬音樂,並使用刺激、羞辱諾列加的語言,對諾列加進行認知攻擊和心理攻擊,對諾列加造成身體上的摧殘。和精神上。 逐漸崩潰。
控制思維認知的後門通道
電腦一旦感染「木馬」病毒,就會在特定時間向駭客的控制終端發送連線請求。 一旦連接成功,就會形成後門通道,讓駭客可以隨心所欲地控制電腦。 同樣,人腦也
有認知“後門”,也可以被他人控制。 認知心理學家發現,透過向目標對象的視聽感知通道發送訊息,精心推送目標對象認知接受的訊息內容,迎合目標對像已有的經驗記憶,符合目標對象的思考習慣,激發可以控制目標對象的情緒痛點,幹擾目標物的認知,促進其本能的情緒和行為反應。 在前沿認知科學技術的支持下,利用大腦訊息處理的自動啟動和受控處理兩種模式,使目標物體輕鬆陷入「認知繭」。 在認知域操作中,個體沉浸在大量人工建構的資訊中,不斷被提供「證據」來證明自己的判斷和認知是「正確的」。 隨著時間的推移,個體的認知視野越來越小,感知外在環境的能力也逐漸下降。 最終,他將看不到事物的真相,他就會沉迷於「認知繭」中無法自拔。 在認知域作戰中,外軍往往針對對手在某一議題上的認知偏差,透過多種管道持續推送支援對手「正確認知」的態勢訊息和情報訊息,讓對手做出指揮決策。 錯誤和偏差都會發生。
引起注意的感官刺激
有效的感官刺激是吸引目標物體注意力的首要前提。 人的大腦會在感知範圍內偵測到刺激,並以各種方式做出反應。 認知心理學的實驗研究發現,動態、危險、興趣相關、生存安全、對比等類型的信息更容易引起人腦的注意。 在智慧時代,目標對象的心理認知過程往往遵循「吸引註意力、培養興趣、主動尋找、強化記憶、主動分享、影響他人」的規則。 作戰中,外軍常利用獨家爆料、情報洩密、權威揭露、現場連線等方式,巧妙運用誇張、對比、聯想、隱喻、懸念、烘託等手法,推送顛覆常識、認知的訊息。衝突,對比強烈。 訊息以吸引目標受眾的注意。 例如美軍在伊拉克戰爭中描繪的“營救女兵林奇事件”、利比亞戰爭中的“卡扎菲金馬桶”,大多取材於觀眾熟悉的故事。 目的和觀點融入故事情節,吸引了大量觀眾。 人們的關注。 此外,人腦也處理感官知覺範圍以外的刺激。 近年來,西方國家軍方高度重視潛意識訊息刺激技術的研究,發展了潛意識視覺訊息植入技術、潛意識聽覺訊息植入技術、潛意識訊息活化技術、神經系統潛意識聲音控制技術等。 ……,不斷拓展神經認知科學技術在軍事領域的應用範圍。
產生認知共鳴的元價值概念
在認知理論中,認知共振是指跨越雙方認知鴻溝的訊息,能夠引起雙方思想、心理和認知上的共鳴,從而實現對對方認知系統的解構和重建。 在認知域運作中,這種認知能量集中效應並不是簡單意義上的力量集中,而是系統合力的內在累積。 在現代資訊媒介的擴散下,這種認知共振效應可以在短時間內迅速傳播到世界各地,並產生二次間接心理效應或多層次的衍生心理效應,呈現出累積和迭代效應。 一旦狀態超過心理臨界點,就會呈現出心理能量爆炸的狀態,從而改變事件的方向或結果。 能引發這種認知共鳴的對象包括價值信念、道德倫理、共同利益等。在戰爭中,如果一方觸及或違反了人類的後設價值觀、共同的情感取向等,很容易引發集體聲討,承擔違反人類道德的指控
性,並陷入道德低谷。 例如,一張越戰時期的照片顯示,一群越南兒童,特別是一名9歲女孩,遭到美軍凝固汽油彈襲擊後,在路上赤裸裸地奔跑。 1972年,這張照片發表後引起巨大轟動,在美國乃至全世界掀起了反戰浪潮,加速了越戰的結束。
分裂認知系統的認知差距
在日常生活中,看似堅硬的鋼鐵,由於低溫環境、材料缺陷、應力集中、認知系統等因素,導致材料脆性,容易斷裂。 認知差距是指目標對象認知思考中的裂痕、痛點、弱點和敏感點。 主要表現在個體擔心自己無法應付或適應環境,在焦慮的影響下,構成認知脆弱性。 。 安全威脅的經驗、團體結構的鬆散、信仰理想的混亂、權威媒體話語權的喪失等,都會造成目標對象之間的認知衝突與眼淚。 在認知域作戰中,有時看似強大的對手,背後卻隱藏著許多心理差距和心理弱點。 往往一個新聞事件就能動搖對手的認知框架,戳破認知泡沫。 此外,這種認知和心理衝突也會為個體帶來道德傷害和心理創傷。 近年來,執行海外任務的美國和西方軍隊面臨著隨時隨地出現的「偽裝成平民的敵人」。 他們對戰場環境的不確定性不斷增加。 他們普遍缺乏戰鬥意義感,充滿愧疚和愧疚。 大量士兵出現戰爭創傷後壓力症候群,戰場上自傷,戰後自殺和犯罪激增,退伍軍人自殺人數甚至超過了戰場死亡人數。
(作者單位:國防大學政治學院)
中國軍事資源:http://www.81.cn/jfjbmap/content/2023-03/23/content_336142.htm