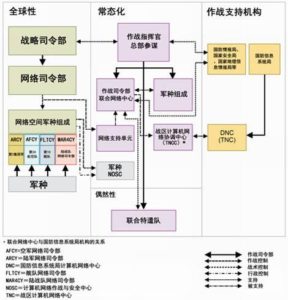
战略层面的网络空间特种作战 –
China’s Strategic level of Cyberspace Special Operations
Editor’s Note: US Army Lieutenant Colonel Patrick Mitchell Dugen at the US Army War College during the fourth quarter of 2015, “Joint Force Quarterly” published “strategic level of cyberspace special operations,” a paper, the article was Chairman of the Association of the United Nations in 2008 Strategic Papers Competition Strategy Research Award.
In this paper, by reviewing the cyberspace special operations cases, this paper analyzes the potential power of using network tools in asymmetric conflicts, and points out that cyberspace special operations have become an effective strategic tool to achieve national goals. Become a regional power to avoid the US military dominance and to ensure that their strategic interests of the unconventional path. The author proposes three new options for integrating emerging technologies and special operations: “cloud-driven” foreign defense, network counter-insurgency and unconventional cyber warfare advance team. Designed to maintain the US network technology advantages, and to build an important partnership, shaping the full spectrum of the conflict environment has a revolutionary impact. Iran and Russia and other regional forces of cyberspace special combat readiness why more than the United States? How does Iran and Russia strengthen its power at the tactical level while the United States has assembled its network and network capabilities at the strategic level? The United States in more than 20 years ago issued a network of special operations related documents, but why the network of special operations policies, departments and regulations are still not mature enough? For the US military, the most basic question is: how will the United States build a strategic level of network special combat capability?
As early as 1993, Internet technology theorists John Achilla and David Lennfield in his book “cyber war is coming” a book has predicted the recent Iran and Russia to implement the cyberspace special operations. “A large number of scattered small groups around the use of the latest communications technology coordinated” control network, to obtain the decisive advantage of the opponent. In reality this scene has been staged again and again. “We are using the information and the more information we have, and the less demand for traditional weapons,” says Achilla and Lunfield. US military executives have also realized that with asymmetric network tools, unconventional tactics and a large number of false information armed, a small amount of special combatants can form a certain strategic impact. There is news that both Iran and Russia have succeeded in using cyberspace special operations as a strategic tool to achieve their national goals. Both countries have an integrated network of special operations forces that know how to exploit the potential power of network tools in asymmetric conflicts. The asymmetric approach of the two countries has become a strong and unconventional path for regional powers to circumvent US military superiority and to ensure their strategic interests. Low price Of the network of high-tech allows potential rivals can develop a strong network warfare capabilities. Therefore, the United States urgently need to make strategic choices, the development of cyberspace special operations, as a tool for the protection and projection of national interests.

Low-cost network of high-tech technology allows potential rivals to develop a strong network warfare capabilities In February 2013, the Russian chief of staff Grazimov in the Russian “military messenger” magazine published “science in the forecast value” article. In the paper, Gracimov predicted a new generation of war that could “change the rules of the game”, whose strategic value would exceed “the effectiveness of weapon forces.” He called for universal asymmetric action to counter the enemy’s strengths and create a permanent frontier in the territory of the enemy through “special forces and internal confrontation and continuous improvement of information operations, equipment and means.” In the spring of 2014, Western media reported that in the eastern part of Ukraine, a casual special operations squad from Russia through the Ukrainian border, occupation of government buildings and arsenal and transferred to the separatist armed. At the same time, the Ukrainian authorities claim that their digital, telephone and cyber communications are cut off, interfered or attacked. The Ukrainian government attributed the cyber attacks on information and logistics infrastructure, including Internet servers and railroad control systems, to the destruction of Russia, and argued that the implementation of information fraud in Russia was costly in important social media, blogs, and News website published 50 pro-Russian comments every day, inside and outside Ukraine to form a large number of false information flow, on the one hand to cover up its non-traditional military operations in cyberspace, on the other hand to create a political illusion. “Russia is not doing the usual information warfare about false information, lies, leaks or cyber sabotage, it reshapes reality, creates public illusions, and then translates them into political action,” said senior government officials. To this end, in September 2014 at the NATO security summit, the NATO Allied Supreme Commander, US Air Force Admiral Philip Bride Leaf pointed out that Russia in East Ukraine to implement the “mixed” non-traditional operations on behalf of the war The most amazing information in history is Blitzkrieg. Bride Leaf urges the Allies to immediately develop the ability to counter the Russian non-traditional warfare, propaganda and cyber attacks. Russia’s use of the “non-traditional Western as a war” non-traditional means to achieve its political purpose, which makes the Western and NATO countries by surprise. Russia is not a fragmented way to use special forces, information operations or network capabilities.
On the contrary, as General Glashimov said, “the war does not need to be publicly announced, when the special forces with advanced technology and a lot of information for the traditional forces in the maintenance of peace and crisis under the cover of strategic objectives to create good conditions, the war on “Cybercrime deception and cyber attacks are special forces in” war and peace ”

Network information spoofing and cyber attack action for special combat forces in the “war and peace” between the implementation of non-traditional warfare to win the time and space lessons learned from the Russian case can draw four major experience, for the United States special operations Action and network capacity integration to provide a viable theoretical framework. First, there are tactical and strategic differences in the offensive network tools used by the Russian Special Forces, targeting tactical “closed networks”, such as local communications, social media, regional networks and logistics infrastructure, while retaining Its more advanced open network tools as a backup. Second, the network special operations are primarily an agent behavior, emphasizing the minimization of the source tracking. As Gracimov described, “the long-distance, non-contact action against the enemy is becoming the primary means of the tactical battle.” Network special operations usually avoid direct contact with people, but in peace and war in the gray area to start action. Third, information and communication technology, network attacks and information operations in the network to form a non-conventional warfare play an important role. As long as the appropriate implementation, the traditional special operations can go far beyond its original function, “which involves the comprehensive application of a wide range of capabilities to achieve policy objectives.” To be effective, it must also be integrated to synchronize other areas of expertise. Fourth, the network special operations can both deter the conflict, can also be used to deal with the whole spectrum of conflict, because “it is suitable for all stages of action, from shaping the environment to the intense war to post-war reconstruction.” Although the network war to destroy the original intention, but also has a constructive side. The widespread dissemination of low-cost information and communication technologies is conducive to strengthening the security of partner countries and thus helping to prevent the occurrence of conflicts.

“‘Foreign help defense’ (FID) under ‘cloud drive’ is both a concept of cloud computing and a metaphorical description of partnering and trust through virtual means. “The concept of” cloud-driven “FID” has not yet been clearly defined, but it can be integrated into an interdisciplinary field to better understand people, geography and virtual worlds and to act together on related goals. Technically, the “cloud-driven” FID “strengthens the partnership, consolidates data through the federated facilities, enhances automation, and disseminates the analysis process. “Cloud-driven” is flexible and can be developed in private, public, community, or mixed form, using different software, platforms, and infrastructure. Security personnel use intelligent technology to drive confidential mobile applications, analyze tools and share data through “cloud-driven” FIDs. Although the data associated with the virtual cloud, but its real value is to make the timely dissemination of information to the hands of tactics. “The cloud-driven” FID “can also be likened to a persistent, active partnership, the data never stops, the network has been busy. Technology is only a tool to drive deeper, extensive socio-cultural, political and historical factors that are often prone to conflict. “Cloud-driven” FID “can build more sustainable competencies and trust with partner countries. “The cloud-driven” FID “lay a virtual foundation for the future establishment of various institutions, centers and laboratories to bridge the benefits of inter-agency across the United States. From the strategic point of view of the US government, “cloud-driven” FID “is a pragmatic” partnership-centered approach designed to target the core interests of partner countries rather than to Way to change the partner country “. “The cloud-driven” FID “is also a prudent strategic move to” prevent the US partner countries from becoming a public relations crisis due to domestic political problems. ” “The cloud drive ‘FID’ also offers other opportunities. The technology and networks it forms can react quickly to emergencies, such as humanitarian relief or relief operations, prevent mass killings, or evacuate personnel from non-combatants. This saves time, money and manpower by providing information for the decision-making process. For the construction of the partnership, the cloud-driven FID can store local non-US social media information, rich social network analysis, social network maps, and behavioral and opinion trends analysis. Most importantly, the “cloud drive ‘FID” builds trust in an innovative and extremely powerful way to build lasting influence on allies and partners.

Today’s global environment drives the United States to use cyber special operations as a strategic tool network for national military strategies Anti-riot counterintelligence network Anti-riot operations (CNCOIN) aims to use social media networks to achieve the purpose of rebellion. To break the asymmetric information superiority of the enemy, CNCOIN uses non-technical means to combat the relevant crowd and control its perception, behavior and action. It adds a military color to the cyber space’s ubiquitous anti-social network. Although these means are not clearly defined, this article believes that it actually refers to the manipulation of social media, cover up the true identity, to achieve ulterior motives. While social media provides a wide range of opportunities for anti-social networks, such as malicious use, intentional misconduct, but from the military point of view, social media provides a wealth of information resources to affect the psychological vulnerability, but also an ideal attack platform. There are several technologies that contribute to its implementation in each functional category. The scope of action includes, but is not limited to, cyber-pseudo operation and cyber-herding operation. Network fraud is a classic counter-insurgency strategy, “government forces and technical staff will pretend to be insurgents, into the enemy network after the use of advanced intelligence technology in the network within the implementation of the destruction.” Internet expulsion means that “individuals, groups, or organizations deport other individuals, groups, or organizations to the default network area.” The magic of the two technologies is the expulsion of insurgents in the virtual network by exploiting the inherent flaws of the communication technology and communication platform. The two tactics are aimed at rebel activist online communities, manipulating or disrupting them, and ultimately providing more opportunities for cyberbullying. The virtual world magnifies the environmental factors, because the characters in the network are more difficult to determine their authenticity. Planning command control, communication frequency and equipment platform and other elements will become the key to the implementation of network fraud or network expulsion operations to manipulate, mislead or expel the target group to the desired results. The scope of information includes, but is not limited to, Crowdsourcing and Social Networking Analysis, SNA). Crowdsourcing is the use of large-scale knowledge base, provided by the participants voluntarily, to solve the problem to provide new ideas, services or observation, you can quickly expand the organizers of the field of vision. Social network analysis depicts and measures the relationships, strengths, and cores of social links in a visual way to illustrate the social network structure. Social network visualization or social networking maps can provide a unique window for assessing, depicting and even predicting the intensity, time, space, and relationship dimensions of relationship events. In September 2013, during the crisis in the Philippines, the anti-government armed Moro National Liberation Front (hereinafter referred to as “the dismount”) was dissatisfied with the situation of national reconciliation, hijacked more than 200 civilians as hostages, attacked commercial shops and burned urban buildings. Throughout the crisis, crowdsourcing and social network analysis are very successful non-traditional tactical means. The Philippine security forces use crowdsourcing tactics to encourage Zamboang residents to discover and report on the “melodic” members of the hiding place. FEI security forces, together with crowdsourcing information and intelligence analysis, provide information for security operations and humanitarian operations. The use of social network analysis to assess the “Mobility” of the public support, and in the social media against the “interpretation” declaration, to ban the violation of social media user agreement propaganda site, but also the use of crowds of information blockade ” Troops, attacking their temporary command post. The Philippine security forces used solid media to track the key information and lead the use of social media, and then use the solid forces to defeat the “interpretation” of the asymmetric advantage. The information warfare category includes but is not limited to cyber intrusion (cyber Aggression, forum vest (sock-puppeting), astro-turfing and so on. Three tactics are anonymous use of social media to implement misleading, false information to manipulate behavior, public opinion and action. The cyber-invasion is proposed by Teanna Felmyr, which refers to “an electronic or online act that is intended to cause psychological harm to others or damage its reputation by using e-mail, instant messaging, cell phones, digital information, chat rooms
As well as social media, video, game sites, etc. “. It is much broader than the range of ordinary cyber-aggressive behavior. Its anonymity may cause substantial psychological harm and negative consequences, as the relevant information will be repeatedly sent to the target or published in the social media. Its value to CNCOIN is that it can use sensitive digital information to humiliate, defame or hurt the target, causing psychological barriers. This powerful cyber-invading action can reduce the credibility, influence and power of the target, and ultimately lose the power of the target or other insurgents. The other two tactics, the forum vest and the fake are all fictitious online propaganda tools used to spread distorted views to create a wider range of support or opposition to the illusion. In fact, with the forum vest is the same concept, but more complex, more organized, larger. Both tactics use virtual characters to distribute false information in cyberspace, with the aim of initiating group reactions or actions. Combining massive amounts of text, images, and video with a planned misleading network activity will significantly enhance the effectiveness of CNCOIN’s action. The third way to advance the US network’s special operations is the unconventional cyber warfare team (cyber-UW Pilot Team, using social media networks to shape the physical environment, the establishment of regional mechanisms, in the implementation of non – conventional war before the regional connectivity. The core of the unconventional network warfare team is the special forces, with a number of professional organizations to provide technical support, its task is in the field of network security for the preparation of unconventional operations. The penetration of the traditional advance team is the target of enemy territory, military facilities and other entities, rather than the conventional advance team is through the virtual means of infiltration, and then into the sensitive, hostile or refused to area. Through the virtual means, can reduce the United States and partner countries armed forces in time, risk, equipment and other aspects of the loss and risk. Conceptually, unconventional cyber warfare teams use web tools and advanced technology to build people, entities, intelligence, and information infrastructures on social media. While deepening understanding of the local human terrain, the team can strengthen its local language and cultural skills, as well as identify resistance leaders, assess motivation and resistance, and overall support for US government goals, while at the same time understanding Informal hierarchical distribution, psychology and behavior. In addition, you can also incorporate the Internet’s white noise into the social media network to “improve the cultural understanding of potential collaborators in the United States and the local situation before action.” While the US national security strategy has long recognized the strategy of cyber warfare Role, but this understanding is not fully translated into a clear strategic level of thinking and combat capability. For example, the US Department of Defense cyberspace action strategy did not give much solution or specific measures, only from five aspects of the previous repeated network ideas. Lack of clear ideas lead to our network strategy is flawed, making the United States advanced network technology advantages to hand over to the potential rival risk. In contrast, Iran and Russia’s asymmetric innovation modeled other regions and global forces, trying to circumvent the US military advantage by unconventional means to ensure their strategic interests. Cyberspace special operations are a must to fill the strategic level of the blank. Obviously, the United States must actively seek a tactical level of unconventional combat into the cyber space operations in the form of special operations. Rand’s recent study of special operations concluded that “the United States needs to use a more advanced form of special operations to ensure national interests, taking into account the recent US and its interests facing the security threat situation, special operations
Become the most appropriate form of ensuring national interests “. In an increasingly interconnected global environment, the physical infrastructure is quickly allocated Internet protocol addresses, accessory networking. By 2020, there will be 50 billion “machine-to-machine” equipment (currently 1 3 billion units) will be through the “embedded computer, sensor and Internet capabilities” access to network space. Cyberspace special operations Unicom virtual and reality, through the modern information network and with the traditional face-to-face combination of special operations partnership. Today’s global environment has prompted the United States to use cyber special operations as a strategic tool for national military strategies. Potential rivals combine offensive network capabilities with unconventional tactics to set a terrible example for other enemies in the United States, and they will follow suit quickly. This paper presents three new options for integrating emerging technologies and special operations: foreign-assisted defense under “cloud-driven”, anti-riot operations in the network, and non-conventional cyber warfare advance teams. Full play of these three tactics will not only maintain the advantages of the US network technology, but also to build an important partnership, shaping the whole spectrum of combat environment have a revolutionary impact. If successful implementation, network special operations will become the United States a strong new strategic options
Original Mandarin Chinese:
编者按:美国陆军中校帕特里克·米歇尔·杜根在美陆军战争学院就读期间,于2015年第4季度《联合部队季刊》发表《战略层面的网络空间特种作战》一文,该文曾获得2015年度参联会主席战略论文竞赛战略研究类奖。本文通过回顾网络空间特种作战案例,分析了在非对称性冲突中利用网络工具的潜在力量,指出网络空间特种作战已经成为达成国家目标的有效战略工具。成为地区强国用以规避美国军事主导权以及确保本国战略利益的非常规性路径。作者提出了融合新兴技术与特种作战的三种新选项:“云驱动”下的国外协助防御,网络反暴乱平叛行动与非常规网络战先遣队。旨在维持美国的网络技术优势,并对构建重要伙伴关系、塑造全频谱冲突环境产生革命性影响。伊朗和俄罗斯等地区力量的网络空间特种作战战备为何比美国更为充分?
美国在战略层面集结其网络部门和网络能力的同时,伊朗和俄罗斯又是如何在战术层面强化其力量的呢?美国在20多年前就发布了网络特种作战的相关文件,但为何其网络特种作战的政策、部门和条令仍然不够成熟呢?对于美军而言,最基本的问题是:美国将如何打造战略层面的网络特种作战能力?早在1993年,互联网技术理论家约翰·阿奇拉和大卫·伦菲尔德在其著作《网络战争即将来临》一书中就已经预言了最近伊朗和俄罗斯所实施的网络空间特种作战行动。“大量分散各地的小规模团体利用最新的通信技术协调一致”控制网络,取得对对手的决定性优势。现实中这一情景一再上演。阿奇拉和伦菲尔德认为,“战争中我们投向敌人的不再是质量和能量;如今我们使用的是信息,掌握的信息越多,对传统武器的需求就越少”。
美军高层也已经意识到,有了非对称性网络工具、非常规战术以及大量虚假信息的武装,少量的特种作战人员就可以形成一定的战略影响。目前有消息表明,伊朗和俄罗斯均已成功地将网络空间特种作战作为一种战略工具来达成其国家目标。两国都拥有一体化的网络特种作战部队,知道如何在非对称性冲突中利用网络工具的潜在力量。两国的非对称性手段成为地区强国用以规避美国军事优势以及确保本国战略利益的强大非常规性路径。价格低廉的网络高新技术使得潜在对手可以发展出强大的网络战能力。因此,美国亟需做出战略选择,发展网络空间特种作战,作为保护和投射国家利益的工具。

价格低廉的网络高新技术使得潜在对手可以发展出强大的网络战能力2013年2月,俄罗斯总参谋长格拉西莫夫在俄《军工信使》杂志发表了《科学在预测中的价值》一文。文中,格拉西莫夫预测了能够“改变游戏规则”的新一代战争,其战略价值将超过“武器力量的效能”。他号召普遍开展非对称性行动,以抵消敌方的优势,通过“特种作战力量和内部对抗以及不断完善的信息行动、装备和手段,在敌国的领土中创造一个永久活动的前线”。2014年春,有西方媒体报道,在乌克兰东部的乱局中,一支便装的特种作战小分队从俄罗斯境内穿越乌克兰边界,占领政府建筑和武器库并转交给分裂主义武装。与此同时,乌克兰当局声称,其全境的数字、电话及网络通信均遭到切断、干扰或攻击活动。乌克兰政府将信息和物流基础设施(包括互联网服务器和铁路控制系统)遭受的网络攻击归因于俄方的破坏,同时还认为,俄罗斯实施信息欺骗行动,花费巨资在重要的社交媒体、博客以及新闻网站每天发布50条亲俄评论,在乌克兰内外形成大量的虚假信息流,一方面掩盖其在网络空间的非传统军事行动,另一方面制造了政治假象。乌政府高级官员表示,“俄罗斯所做的并不是通常的信息作战所涉及的虚假信息、谎言、泄漏机密或网络破坏活动,它重新塑造现实,造成大众幻象,然后将之转化为政治行动”。为此,在2014年9月召开的北约安全峰会上,北约盟军最高司令、美国空军上将菲利普·布里德莱弗指出,俄罗斯在东乌克兰实施的“混合型”非传统作战代表了战争史上最惊人的信息闪电战。布里德莱弗敦促盟军立即发展相应的能力以反制俄罗斯的非传统战、宣传战及网络攻击行动。俄罗斯使用“根本不被西方视为战争的”非传统手段达成其政治目的,这使得西方及北约国家措手不及。俄罗斯并不是以碎片化的方式来使用特种力量、信息作战或网络能力。相反,正如格拉西莫夫将军所言,“发动战争不再需要公开宣布,当配备先进技术和大量信息的特种力量为传统部队在维持和平与危机的掩护下达成战略目标创造好条件,战争就发生了。”言外之意,网络信息欺骗和网络攻击行动为特种作战力量在“战争与和平之间”实施非传统战赢得了时间和空间。俄罗斯的网络赋能非传统战极为成功,不仅是其网络特种力量的混成,而且还成功地侵入欧盟成员国,甚至没有引起西方有效的军事反应。

网络信息欺骗和网络攻击行动为特种作战力量在“战争与和平之间”实施非传统战赢得了时间和空间 经验教训从俄罗斯的案例中可以得出四个方面的主要经验,可为美国特种作战行动与网络能力整合提供一个可行的理论框架。第一,俄罗斯特种部队所使用的进攻性网络工具存在战术和战略层面的差别,主要以战术层面的“封闭网络”为目标,如本地通讯、社交媒体、区域网络和后勤基础设施等,同时保留其更为先进的开放网络工具作为备用。第二,网络特种作战主要是一种代理人行为,强调最小化的来源跟踪。正如格拉西莫夫所描述的那样,“对敌方的远距离、无接触行动正在成为战术战役目标的主要手段”。网络特种作战通常避免人员的直接接触,而是在和平与战争的灰色地带展开行动。第三,信息与通信技术、网络攻击及信息作战等在网络赋能的非常规战中发挥着重要作用。只要恰当的实施,传统的特种作战可以远远超出其原有的功能,“这涉及到对广泛能力的综合运用,以达成政策目标”。要发挥效能,还必须整合同步其他领域的专门知识。第四,网络特种作战既可以慑止冲突,也可用于应对全频谱冲突,因为“它适合行动的各个阶段,从塑造环境到剧烈战争再到战后重建等”。虽然网络战以破坏为初衷,但也具有建设性的一面。低成本的信息和通信技术的广泛传播有利于强化伙伴国安全,从而有助于阻止冲突的发生。

网络空间特种作战是一种必须填补的战略层面的能力空白,美国必须积极寻求一种在战术层面的非常规作战中融入网络空间作战的特种作战形式 “‘云驱动’下的‘国外协助防御’(FID)”既是一种云计算概念,也是通过虚拟手段增强伙伴能力和信任的一种比喻性描述。“‘云驱动’FID”概念虽然还未经明确界定,但是它却可以联接整合跨学科领域,以更好地理解人员、地理及虚拟世界,并对相关目标展开共同行动。从技术上而言,“‘云驱动’FID”可以强化伙伴关系,通过联合设施,实时共享数据,增强自动化,传播分析过程。“云驱动”是灵活多变的,能够以私人、公共、社区或混合形式出现,各自使用不同的软件、平台和基础设施等。安全人员通过“‘云驱动’FID”使用智能技术驱动保密的移动应用软件、分析工具和共享数据。虽然数据与虚拟云相联,但其真正价值在于使信息及时传播到战术人员手中。“‘云驱动’FID”也可比喻为一种持续的、活跃的伙伴关系,数据永不停止,网络一直忙碌。技术仅仅是一种工具,用以驱动更深入、广泛的社会文化、政治和历史因素的理解,这些往往是容易造成冲突的因素。“‘云驱动’FID”可以与伙伴国构建更具持续性的能力和信任。“‘云驱动’FID”为未来建立各种机构、中心和实验室弥合美国各跨机构间的利益打下一个虚拟的基础。从美国政府的战略视角而言,“‘云驱动’FID”是一种实用主义的“以伙伴国为中心的方式,旨在围绕伙伴国的核心利益设计行动,而不是寄希望于以短视的方式来改变伙伴国”。“‘云驱动’FID”还是一种审慎的战略举措,“以防美国的伙伴国由于国内政治问题出现公共关系危机”。“‘云驱动’FID”也提供了其他的机会。它所形成的技术和关系网络可以迅速对紧急事件做出反应,如人道主义救援或救灾行动、阻止大规模屠杀,或者非战斗人员撤离任务等。这样可以通过为决策过程提供信息而节约时间、金钱和人力等。对于伙伴关系的构建而言,“‘云驱动’FID”可以存储当地的非美国社交媒体信息、丰富的社交网络分析、社会网络地图以及行为和舆论趋势分析等信息。最为重要的是,“‘云驱动’FID”以富有创新性和极为有力的方式构建信任,打造对盟友及伙伴国的持久影响力。

当今的全球环境促使美国采用网络特种作战作为国家军事战略的战略性工具 网络反暴乱平叛行动网络反暴乱平叛行动(CNCOIN)旨在利用社交媒体网络达成平叛的目的。为打破敌人的非对称性信息优势,CNCOIN使用非技术手段打击相关人群,控制其感知、行为和行动。它为网络空间无处不在的反社交网络手段增添了军事色彩。虽然这些手段没有明确界定,本文认为,它实际上就是指操纵社交媒体,掩盖真实身份,达成不可告人的目的。虽然社交媒体为反社交网络提供了广泛的机会,如恶意利用、有意误导等,但从军事角度而言,社交媒体提供了丰富的信息资源以影响心理脆弱性,也是一个理想的攻击平台。每种功能性范畴中都有几种有助于其实施的技术。行动范畴包括但不局限于网络欺骗行动(cyber-pseudo operation)和网络驱逐行动(cyber-herding operation)。网络欺骗行动是一种经典的平叛策略,“政府军和技术人员将自己假扮为叛乱分子,渗入敌方网络后使用先进的谍报技术在该网络内部实施破坏”。网络驱逐行动就是指,“个人、团体或组织把其他的个人、团体或组织驱逐到预设的网络区域”。两种技术的奇妙之处在于,通过利用通信技术与通信平台的内在缺陷来驱逐虚拟网络中的叛乱分子。两种战术以叛乱分子活跃的网络社群为目标,对其进行操控或者瓦解,最终为网络平叛提供更多的机会。虚拟世界放大了环境因素,因为网络中的人物更难确定其真实性。规划指挥控制、通信频率以及设备平台等要素将成为网络欺骗行动或网络驱逐行动实施的关键点,用以操纵、误导或者驱逐目标群走向预想的结果。情报范畴包括但不局限于众包(Crowdsourcing)和社交网络分析技术(Social Networking Analysis, SNA)。众包就是利用大规模的知识库,由参与者自愿提供的,为解决问题提供新思路、服务或观察,可以迅速扩展组织者的视野。社交网络分析以可视的方式描绘和测量社交链接的关系、强度及核心性以说明社会网络结构。社交网络可视化或者社网图可以提供独特的窗口用以评估、描绘甚至预测关系事件的强度、时间、空间和关系维度。2013年9月,菲律宾三宝颜危机期间,反政府武装摩洛民族解放阵线(以下简称“摩解”)对民族和解状况感到不满,挟持200多名平民为人质,袭击商业店铺,烧毁城市建筑。整个危机期间,众包和社交网络分析都是非常成功的非传统战术手段。菲律宾安全部队使用众包战术鼓励三宝颜居民发现并报告“摩解”成员的藏身地点。菲安全部队结合众包信息和情报分析,为安全行动和人道主义行动提供信息。使用社交网络分析来评估“摩解”的民众支持度,并在社交媒体上反制“摩解”宣言,封禁违反社交媒体用户协议的宣传网站,还使用众包信息封锁“摩解”小股部队,攻击其临时指挥哨所。菲安全部队通过使用社交媒体跟踪关键信息和领导节点,随后使用实体部队挫败了“摩解”的非对称性优势。信息作战范畴包括但不局限于网络入侵(cyber aggression)、论坛马甲(袜子手偶sock-puppeting)、以假乱真(Astro-turfing)等。三种战术都是匿名利用社交媒体实施误导、假信息等来操纵行为、舆论及行动。网络入侵是由蒂安娜·菲尔姆利提出,是指“一种电子或在线行为,旨在对他人实施心理伤害或损毁其名誉,通过使用电子邮件、即时信息、手机、数字信息、聊天室以及社交媒体、视频、游戏网站等”。它比普通的网络攻击性行为的范围要广泛得多。它的匿名性可能会引起实质性的心理伤害和负面后果,因为相关信息会被重复发送给目标或者在社交媒体发布。它对CNCOIN的价值在于,可以利用敏感的数字信息来羞辱、诽谤或伤害目标,造成心理障碍行为。这种强大的网络入侵行动可以降低目标的可信度、影响力和权力,最终使目标或其它叛乱分子丧失实力。其它两种战术,论坛马甲和以假乱真都是虚构的在线宣传工具,用来散布扭曲的观点,以制造更广范围的支持或者反对的假象。以假乱真实际上跟论坛马甲是同一个概念,只不过更为复杂、更有组织、规模更大。两种战术都使用虚拟人物在网络空间散布虚假信息,目的是引发群体反应或行动。以假乱真的网络信息作战行动包含海量文字、图片和视频,与有计划的误导性网络活动相结合,将显著增强CNCOIN行动的效果。 非常规网络战先遣队推进美国网络特种作战的第三种方式是非常规网络战先遣队(cyber-UW Pilot Team),利用社交媒体网络塑造实体环境,建立区域机制,在实施非常规战之前将各区域联通起来。非常规网络战先遣队的核心是特种部队,拥有多个专业机构提供的技术支持,其任务是在网络安全领域进行非常规作战的准备。传统先遣队的渗透目标是敌方领土、军事设施等实体目标,而非常规先遣队则是通过虚拟手段进行渗透,再潜入敏感、敌对或拒止区域。通过虚拟手段,可以减少美国及伙伴国武装力量在时间、风险、装备等方面的损失和风险。从概念上讲,非常规网络战先遣队利用网络工具和先进技术在社交媒体上打造人员、实体、情报以及信息基础设施。在加深对当地人文地形理解的同时,小组可以强化其本地语言和文化技能,还可识别抵抗活动领导者、评估动机和抵抗能力以及对美国政府目标的总体支持度,与此同时,还可以了解非正式的层级分布、心理及行为等。此外,还可以通过接入社交媒体网络混入互联网白噪音,以“提高美国对潜在合作者的文化理解以及在采取行动之前的当地形势。”虽然美国国家安全战略中早就承认了网络作战的战略作用,但是这种认识并没有完全转化成明晰的战略层面的思维和作战能力。例如,美国《国防部网络空间行动战略》中并没有给出多少解决方案或具体措施,仅仅从五个方面重复了先前的网络思路。缺乏明确的思路导致我们的网络战略存在缺陷,使得美国先进的网络技术优势有拱手让给潜在对手的风险。对比之下,伊朗和俄罗斯的非对称性创新为其他地区和全球力量树立了模仿的样板,都试图以非常规手段规避美国的军事优势,确保各自的战略利益。网络空间特种作战是一种必须填补的战略层面的能力空白。很显然,美国必须积极寻求一种在战术层面的非常规作战中融入网络空间作战的特种作战形式。兰德公司最近的一份研究特种作战的报告得出结论,称“美国需要运用一种更为先进的特种作战形式来确保国家利益,考虑到近来美国及其利益面临的安全威胁形势,特种作战成为确保国家利益的最合适的形式”。在一个日益互联的全球环境中,实体性基础设施快速被分配互联网协议地址,接入物联网。到2020年,将有500亿台“机器对机器”设备(目前为130亿台)会通过“嵌入计算机、传感器和互联网能力”接入网络空间。网络空间特种作战联通了虚拟与现实,通过现代的信息网络并与传统的面对面的特种作战伙伴关系相结合。当今的全球环境促使美国采用网络特种作战作为国家军事战略的战略性工具。潜在对手将进攻性网络能力与非常规战术相结合为美国的其他敌人树立了可怕的榜样,他们必将快速跟进。本文提出了融合新兴技术与特种作战的三种新选项:“云驱动”下的国外协助防御、网络反暴乱平叛行动以及非常规网络战先遣队。充分发挥这三种战术将不仅仅能维持美国的网络技术优势,还可对构建重要伙伴关系、塑造全频谱作战环境产生革命性影响。如果能成功实施,网络特种作战必将成为美国强有力的新战略选项。
2016-08-22 17:42现代军事