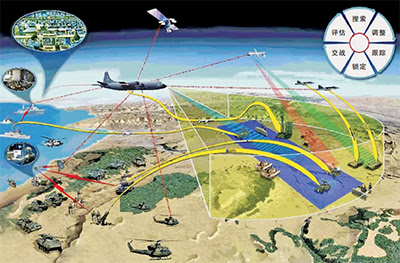
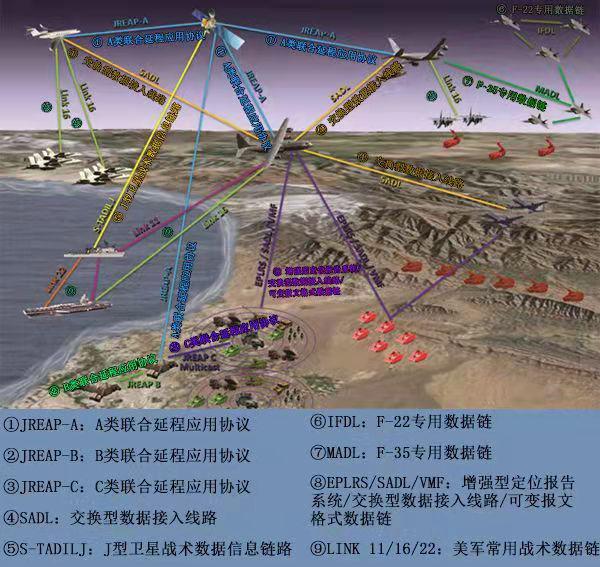
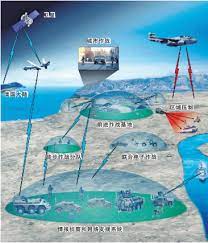
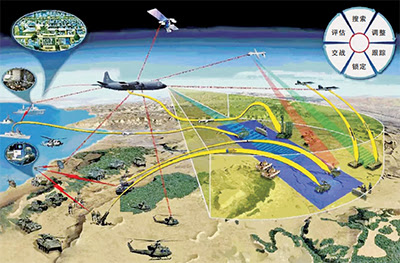
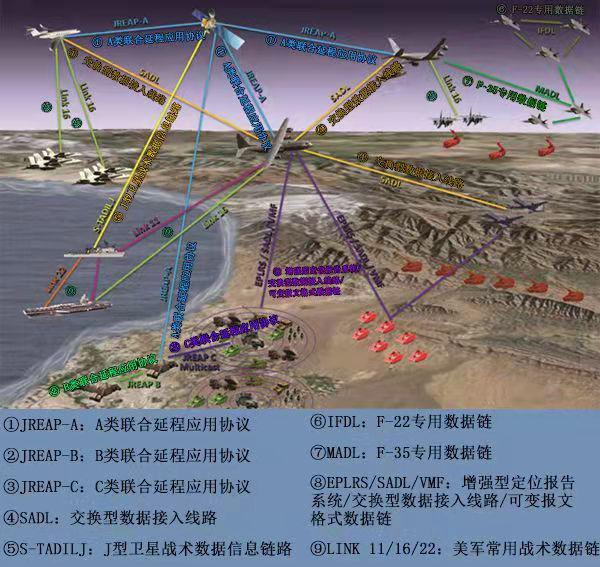
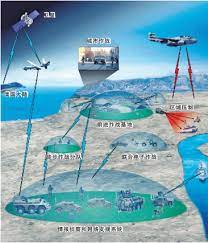
Chinese Military Designs & Development for Operational Concepts Focusing on Future Warfare
原始國語(繁體):
自21世紀以來,隨著世界新軍事革命的深入,世界軍事強國提出了一系列新的作戰概念,並在戰爭實踐中不斷完善,導致戰爭加速演變。 隨著雲端運算、區塊鏈、人工智慧、大數據等資訊科技的快速發展以及在軍事領域的廣泛應用,人們認識戰爭的模式逐漸從總結實戰經驗轉變為研究判斷未來戰爭。 目前,作為軍事能力建構的源泉,作戰理念發展能力的強弱將直接影響戰爭的勝負。 特別是世界新軍事革命方興未艾,時刻呼喚作戰理論創新。 只有建立新的作戰理念,前瞻性地設計未來戰爭,才能贏得軍事鬥爭準備的主動權。
作戰理念從根本解決如何打仗
一流的軍隊設計戰爭,二流的軍隊應對戰爭,三流的軍隊跟隨戰爭。 所謂“真正的戰爭發生在戰爭之前”,就是在戰爭開始之前,戰爭的理論、風格、戰鬥方式就已經設計好了。 照設計打仗怎麼可能打不贏呢? 設計戰爭的關鍵是在認識戰爭特徵和規律的基礎上,設計和發展新的作戰理念,推動作戰方式和戰術創新,從根本上解決「如何打戰爭」。
在設計戰爭時,理論是第一位的。 近年來,美軍提出“網路中心戰”、“空海戰”、“混合戰”等新概念,俄軍提出“非核遏制戰略”、“戰略空天戰役”和“國家資訊安全主義”,體現了世界軍事強國正大力研究作戰理論,搶佔軍事制高點。 從某種程度上來說,作戰概念是作戰理論形成的「組織細胞」。 沒有完整的概念生成能力,就很難產生先進的理論。 當一種作戰理論提出後,需要發展相關的作戰概念,使作戰理論能夠具體“下沉”,更好地完善,轉化為軍事實踐。 在沒有作戰理論概念的情況下,作戰概念創新可以為作戰理論研究提供「原料」。 軍事領域是最不確定的領域,人們對戰爭的認知總是不斷演變。 然而,作戰理論的創新不能等到認識成熟之後才開始。 相反,需要在現有認識的基礎上積極發展和創新作戰理念,建構未來作戰圖景,探索未來制勝機制,指導和指導軍事實踐。 掌握戰爭主動權。 因此,作戰理念創新正在成為軍隊建設和發展的戰略支點和槓桿。
營運概念開發著重於設計核心營運概念。 核心作戰理念是作戰理念的核心與胚胎。 它體現了作戰的本質要求,蘊含著作戰理念成長的「基因」。 整個概念體係都是由此衍生發展出來的。 目前,對資訊化、智慧化戰爭制勝機制的認識逐漸清晰,戰爭設計的著力點應該集中到主要作戰理論和關鍵作戰理念的發展。
經營理念是經營思想的抽象表達。
「作戰概念」一詞源自美軍。 這是對未來如何戰鬥的描述。 日益成為推動軍隊建設發展的重要抓手。 美國陸軍訓練與條令指揮概念發展指南指出,作戰概念是一種概念、一種想法、一種整體理解和基於作戰環境中具體事件的推論。 它概述了最廣泛的意義和更具體的措施。上面描述了戰鬥是如何進行的。 美國海軍陸戰隊作戰發展司令部作戰發展和整合指令指出,作戰概念表達瞭如何打一場戰爭,用於描述未來的作戰場景以及如何利用軍事藝術和科學能力來應對未來的挑戰。 美國空軍作戰概念發展條令指出,作戰概念是戰爭理論層面的概念描述。 它實現了既定的營運理念和意圖
透過有序組織作戰能力和作戰任務。
綜上所述,作戰理念可以理解為對當前或未來具體作戰問題的作戰思路和行動方案的抽象理解。 一般來說,作戰構想包含三個部分:一是作戰問題的描述,即作戰構想的背景、作戰環境、作戰對手等;二是作戰構想的描述。 二是解決方案的描述,即概念內涵、應用場景、動作風格。 、制勝機制、能力特性及優勢等; 三是能力要求描述,即實施作戰理念所需的裝備技術、基本條件、實施手段等。 可見,作戰概念應具有針對性、科學性、適應性和可行性等特點,其內涵和外延會隨著戰略背景、軍事政策、威脅對手、時空環境、能力條件和作戰能力的變化而不斷調整。其他因素。
從某種意義上說,作戰理念實際上是作戰理論的一種過渡形式,其最終價值在於指導和拉動軍事實踐。 發展新作戰理念的目的和歸宿是挖掘和增強軍隊戰鬥力。 將作戰理念轉化為作戰條令、作戰方案,其價值才能充分發揮。
作戰理念創新驅動作戰方式變革
進入21世紀以來,世界軍事強國根據國家戰略要求,應對新威脅新挑戰,把發展新作戰理念作為軍事能力轉型的關鍵步驟,推動軍事力量變革。作戰風格,並尋求在未來戰場上獲得勝利的機會。 為了進一步加強軍事領導力,世界軍事強國正加速推出一系列新的作戰概念。
美軍積極抓住科技進步帶來的機遇,綜合運用新一代資訊科技、人工智慧技術、無人自主技術等尖端技術,提出馬賽克戰爭、多域作戰、分散式殺傷、決策作戰等。集中作戰、聯合全局指揮控制。 等一連串新的作戰概念,推動作戰思想、作戰方式、作戰空間、作戰體系發生根本性變革。
與美軍不同,俄軍在軍事實踐中實行作戰理念迭代創新。 近期,俄軍致力於推動聯合作戰能力建設,加速新型無人裝備研發部署,著力打造網路資訊化戰場優勢,不斷豐富傳統作戰理念內涵,與新時代融合發展。混合戰和心理戰等作戰概念。 用於指導戰爭實踐。
總體而言,近年來,世界軍事強國提出的新作戰理念正在導致作戰方式的深刻變化。 其能力、特徵和優勢主要體現在以下五個方面:一是無人作戰裝備,基於新作戰理念的無人裝備系統比重顯著增加,有人與無人協同作戰成為主要作戰方式之一。風格,形成利用無人系統控制有人部隊的優勢。 其次,部署方式是去中心化的。 基於新作戰概念的兵力部署是分散式的、系統間互聯的、具有互通能力的,形成單獨系統和組合的優勢; 第三,殺傷網絡複雜。 基於新作戰理念的殺傷網絡,功能更加多元。 單一系統可以執行多種任務,其故障對作戰系統影響較大。 規模小,形成多用控制單單的優勢; 四是反應時間敏捷,新作戰概念強調快速決策,出其不意,形成以快慢的優勢; 五是作戰領域多維度,新作戰理念更重視多域連動,將戰場從傳統的陸、海、空拓展到電磁、網路、認知領域,形成無形、有形的優勢。
營運理念開發應堅持系統化設計思路
以營運理念指導建設
f軍事力量是世界軍事強國的普遍做法。 相較而言,美軍擁有較為完善的作戰概念發展機制,建構了較為完整的作戰概念發展體系,由概念類型、組織結構、規範標準、支撐手段等組成。
從概念類型來看,美軍作戰概念基本上可分為三類:一是各軍種主導下發展的一系列作戰概念。 他們主要從本軍種角度出發,研究潛在敵人和未來戰場,重新定義作戰方式,尋求勝利。 新方法。 二是參謀長聯席會議領導下所發展的一系列聯合作戰概念,主要由頂層概念、作戰概念、支撐概念三個層次組成。 第三類是學術界、智庫等發展出來的操作概念,這類操作概念的數量雖然沒有前兩類那麼多,但仍是操作概念體系的重要組成部分。 透過此體系,美軍將大軍事戰略透過作戰理念層層落實到部隊的各項作戰行動、各項作戰能力、各項武器裝備性能中,指導聯合部隊和各軍兵種建設。
在組織架構上,以聯合作戰理念的發展為例,美軍建立了由五類組織組成的工作體系。 一是聯合概念工作小組,主要職責是檢視概念大綱和概念發展的整體問題; 二是聯合概念指導委員會,主要職責是監督指導概念發展計畫; 三是核心編寫團隊,主要職責是編制概念大綱,將概念中原有的概念轉化為聯合可操作的概念; 四是概念研發團隊,主要職責是提供可操作的概念開發方法和方案; 五是獨立紅隊,主要職責是獨立評估,判斷概念的嚴謹性和科學性。
在規範標準方面,對於聯合作戰理念的發展,美軍有完整的製度體系約束和指導,將概念發展規範化、規範化、程序化,這主要體現在參謀長聯席會議主席的一系列指令和聯合出版物中。 例如,《聯合概念制定和實施指南》旨在建立聯合概念制定的治理結構,明確聯合作戰概念規劃、執行和評估的框架,推動聯合作戰概念的實施; 「聯合條令準備流程」旨在製定聯合條令準備流程,並為將作戰概念轉化為作戰條令提供明確的流程架構。
從支援手段來看,營運概念的設計、開發和驗證是一個系統工程,離不開各種開發工具和手段的支援。 例如,DODAF2.0模型、IDEFO模型、SYSML建模語言等工具可以為戰鬥概念設計者提供標準化的結構化分析模型和邏輯描述模型; 基於模型的系統工程方法可以為作戰概念設計者和評估驗證者提供作戰概念中裝備要素的能力模型,用於設計和建構作戰概念架構。 美軍聯合作戰概念開發採用基於網路的數位軟體,具有很強的互聯能力。 參與開發的各機構可即時分享訊息,提高開發效率。
營運理念的成熟發展需要多方的配合
制定作戰概念是一項多學科、多領域的工作,涉及軍事學、哲學、運籌學、系統科學等許多領域。 它需要多方合作,確保在理論層面上具有先進性、前瞻性,在實踐層面上具有適用性和可行性。
建立小核心、大外圍的研究團隊。 主導制定作戰理念的部門要充分發揮主導作用,統籌協調與調度研究工作; 建立聯合研發團隊,充分發揮群體智慧與作用
d 廣泛獲取各方對作戰理念研究的新思路、新思路。 方法與新視角; 成立跨領域、跨部門的專家委員會,多角度監督、審查、指導相關工作。
形成多部門連動工作機制。 為了確保各部門之間溝通順暢、有效率運轉,首先要明確各自的任務與職責。 例如,概念發起部門負責總體規劃和實施,實驗室負責技術驗證,工業部門負責裝備研發,作戰部隊負責實戰測試。 其次,要製定相關規範文件,確保各項工作有秩序地進行,並為可操作理念的研發提供製度支撐。 最後,要建立需求牽引機制、協同研究機制、迭代回饋機制等,打通作戰概念從研發到實際運用的環節。
促進理論與實務的有機結合。 只有透過「設計研究-推演驗證-實戰測試」的循環迭代,才能逐步調整、優化、完善作戰理念,帶動戰爭理論的發展。 因此,操作理念的發展必須特別注重理論創新與實際應用的結合。 透過理論與實踐的相互驅動,才能達到引領新一代優質作戰能力生成的根本目的。 具體方法包括將成熟的作戰理念及時納入作戰條令,編寫相應的訓練大綱或教材,逐步向部隊推廣; 組織相關演練或試驗,在接近實戰的條件下檢驗作戰理念的成熟度和可行性。 自然,發現問題並解決問題; 以作戰理念確定的能力指標作為裝備需求論證的參考,帶動裝備技術發展,促進作戰能力提升。
新時代科學技術快速發展,為軍事能力建構帶來許多新的機會與挑戰。 發展新的作戰概念,有利於敏銳抓住科技進步帶來的軍事機遇,積極應對科技發展帶來的威脅和挑戰,及時掌握戰爭形態演變的方向和規律,為戰爭形態的演變提供指導。引領未來戰爭風格,抓住勝利機會。 重要的支持。 目前,國際安全情勢複雜多變。 打贏未來資訊化戰爭,需要把作戰理念發展作為國防和軍隊建設的抓手,積極開展軍事技術創新,推動武器裝備升級換代,實現跨越式發展,從而引領新時代。 軍事革命趨勢。
(作者單位:中國航太科工集團第二研究院)
現代外語英語翻譯:
Since the 21st century, with the deepening of the world’s new military revolution, the world’s military powers have proposed a series of new combat concepts and continuously improved them in war practice, thus leading to the accelerated evolution of war. With the rapid development of information technologies such as cloud computing, blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data, as well as their widespread application in the military field, people’s mode of understanding war has gradually changed from summarizing actual combat experience to studying and judging future wars. At present, as the source of military capability building, the strength of operational concept development capabilities will directly affect the opportunity to win the war. In particular, the new military revolution in the world is booming, calling for innovation in combat theory all the time. Only by developing new combat concepts and designing future wars with a forward-looking perspective can we gain the initiative in preparing for military struggles.
The concept of combat fundamentally solves how to fight a war
First-rate armies design wars, second-rate armies respond to wars, and third-rate armies follow wars. The so-called “real war happens before the war” means that before the war begins, the theory, style, and fighting methods of the war have already been designed. How can it be unwinnable to fight a war according to the design? The key to designing a war is to design and develop new combat concepts based on understanding the characteristics and laws of war, promote innovation in combat styles and tactics, and fundamentally solve “how to fight a war.”
In designing a war, theory comes first. In recent years, the US military has proposed new concepts such as “network-centric warfare”, “air-sea warfare” and “hybrid warfare”, and the Russian military has proposed theories such as “non-nuclear containment strategy”, “strategic air and space campaign” and “national information security doctrine”, reflecting The world’s military powers are vigorously studying combat theories and seizing the military commanding heights. To a certain extent, operational concepts are the “organizing cells” for the formation of operational theories. Without complete concept generation capabilities, it is difficult to generate advanced theories. When a combat theory is proposed, relevant combat concepts need to be developed so that the combat theory can be “sinked” concretely, better improved, and transformed into military practice. When there is no operational theory concept, operational concept innovation can provide “raw materials” for studying operational theory. The military field is the most uncertain field, and people’s understanding of war is always evolving. However, innovation in combat theory cannot wait until the understanding matures before starting. Instead, it needs to actively develop and innovate combat concepts on the basis of existing understanding, construct a future combat picture, explore future winning mechanisms, and guide and guide military practice. Take the initiative in war. Therefore, innovation in operational concepts is becoming a strategic fulcrum and lever for military construction and development.
Operational concept development focuses on designing core operational concepts. The core combat concept is the nucleus and embryo of the combat concept. It reflects the essential requirements of combat and contains the “gene” for the growth of the combat concept. The entire concept system is derived and developed from this. At present, the understanding of the winning mechanisms of informatization and intelligent warfare is gradually becoming clearer, and it is time to focus the focus of designing wars on the development of main combat theories and key combat concepts.
The operational concept is an abstract expression of operational thoughts.
The term “operational concept” originated from the US military. It is a description of how to fight in the future. It is increasingly becoming an important starting point to promote the construction and development of the military. The U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command Concept Development Guide points out that an operational concept is a concept, an idea, an overall understanding, and an inference based on specific events in the operational environment. It outlines what will be done in the broadest sense, and in more specific measures The above describes how the battle is fought. The US Marine Corps Combat Development Command Operational Development and Integration Directive states that an operational concept expresses how to fight a war and is used to describe future combat scenarios and how to use military art and scientific capabilities to meet future challenges. The US Air Force Operational Concept Development Doctrine points out that an operational concept is a conceptual description at the theoretical level of war. It realizes established operational concepts and intentions through the orderly organization of combat capabilities and combat tasks.
To sum up, the operational concept can be understood as an abstract understanding of operational ideas and action plans for specific current or future operational problems. Generally speaking, the operational concept includes three parts: first, the description of the operational problem, that is, the background of the operational concept, operational environment, operational opponents, etc.; second, the description of the solution, that is, the conceptual connotation, application scenarios, and action styles. , winning mechanism, capability characteristics and advantages, etc.; the third is the description of capability requirements, that is, the equipment technology, basic conditions, implementation means, etc. required to implement the operational concept. It can be seen that the operational concept should have the characteristics of pertinence, scientificity, adaptability and feasibility, and its connotation and extension will be continuously adjusted with changes in strategic background, military policy, threatening opponents, time and space environment, capability conditions and other factors.
In a sense, the operational concept is actually a transitional form of operational theory, and its ultimate value is to guide and pull military practice. The purpose and destination of developing new combat concepts is to tap into and enhance the military’s combat effectiveness. Only by transforming combat concepts into combat doctrine and combat plans can their value be fully exerted.
Innovation in combat concepts drives changes in combat styles
Since the beginning of the 21st century, the world’s military powers, in accordance with national strategic requirements and in response to new threats and challenges, have regarded the development of new operational concepts as a key step in the transformation of military capabilities, promoted changes in operational styles, and sought to gain opportunities for victory in future battlefields. In order to further strengthen their military leadership, the world’s military powers are accelerating the launch of a series of new combat concepts.
The U.S. military actively seizes the opportunities brought by scientific and technological progress, comprehensively uses cutting-edge technologies such as new generation information technology, artificial intelligence technology, and unmanned autonomous technology to propose mosaic warfare, multi-domain operations, distributed destruction, decision-centered warfare, and joint full-domain command and control. and a series of new operational concepts, promoting fundamental changes in operational thinking, combat styles, combat spaces and combat systems.
Unlike the US military, the Russian army implements iterative innovation in operational concepts in military practice. Recently, the Russian military has been committed to promoting the construction of joint combat capabilities, accelerating the development and deployment of new unmanned equipment, focusing on creating network information battlefield advantages, constantly enriching the connotation of its traditional combat concepts, and integrating them with new combat concepts such as hybrid warfare and mental warfare. Used to guide war practice.
Generally speaking, in recent years, the new combat concepts proposed by the world’s military powers are leading to profound changes in combat styles. Their capabilities, characteristics and advantages are mainly reflected in the following five aspects: First, unmanned combat equipment, based on the new combat concepts The proportion of unmanned equipment systems has increased significantly, and manned and unmanned coordinated operations have become one of the main combat styles, forming the advantage of using unmanned systems to control manned forces. Second, the deployment method is decentralized. The deployment of forces based on new combat concepts is distributed and inter-system They are interconnected and have interoperability capabilities, forming the advantage of separate systems and combinations; third, the kill network is complex. The kill network based on new combat concepts has more diverse functions. A single system can perform a variety of tasks, and its failure has a greater impact on the combat system. Small, forming the advantage of using more to control single orders; fourth, the response time is agile, and the new combat concept emphasizes quick decisions, taking the enemy by surprise, and forming the advantage of using speed to control the slow; fifth, the combat field is multi-dimensional, and the new combat concept Pay more attention to multi-domain linkage, expanding the battlefield from traditional land, sea and air to electromagnetic, network and cognitive domains, forming intangible and tangible advantages.
Operation concept development should adhere to systematic design ideas
Using operational concepts to guide the construction of military forces is a common practice among the world’s military powers. Comparatively speaking, the U.S. military has a relatively complete operational concept development mechanism and has built a relatively complete operational concept development system, which consists of concept types, organizational structures, specifications and standards, and support means.
In terms of concept types, U.S. military operational concepts can be basically divided into three categories: First, a series of operational concepts developed under the leadership of each service. They mainly start from the perspective of their own services to study potential enemies and future battlefields, redefine combat styles, and seek to win. new ways. The second is a series of joint operations concepts developed under the leadership of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, which are mainly composed of three levels: top-level concepts, operational concepts and supporting concepts. The third is the operational concepts developed by academia, think tanks, etc. The number of such operational concepts is not as large as the first two categories, but it is still an important part of the operational concept system. Through this system, the US military implements grand military strategies layer by layer through operational concepts into various combat operations, various combat capabilities, and various types of weapons and equipment performance for the troops, guiding the construction of joint forces and various services and arms.
In terms of organizational structure, taking the development of joint operations concepts as an example, the US military has established a working system composed of five types of organizations. The first is the Joint Concept Working Group, whose main responsibility is to review the concept outline and overall issues of concept development; the second is the Joint Concept Steering Committee, whose main responsibility is to supervise and guide the concept development plan; the third is the core writing team, whose main responsibility is to compile the concept outline The original concepts in the concept are transformed into joint operational concepts; the fourth is the concept research and development team, whose main responsibility is to provide operational concept development methods and plans; the fifth is the independent red team, whose main responsibility is to carry out independent evaluation to judge the rigor and scientificity of the concept.
In terms of norms and standards, for the development of joint operations concepts, the U.S. military has complete institutional system constraints and guidance to standardize, standardize and program the concept development, which is mainly reflected in a series of joint chiefs of staff chairman Directives and joint publications. For example, the “Joint Concept Development and Implementation Guide” aims to establish a governance structure for joint concept development, clarify the framework for joint operational concept planning, execution and evaluation, and promote the implementation of joint operational concepts; the “Joint Doctrine Preparation Process” aims to develop joint doctrine Standardize the preparation process and provide a clear process framework for transforming operational concepts into operational doctrine.
In terms of support means, the design, development and verification of operational concepts is a systematic project that cannot be separated from the support of various development tools and means. For example, tools such as DODAF2.0 model, IDEFO model and SYSML modeling language can provide standardized structured analysis models and logical description models for combat concept designers; model-based system engineering methods can provide combat concept designers and evaluation Verifiers provide capability models of equipment elements in the operational concept, which are used to design and build the operational concept framework. The U.S. military’s joint operations concept development uses network-based digital software, which has strong interconnection capabilities. All agencies involved in the development can share information in real time and improve development efficiency.
The mature development of operational concepts requires the cooperation of multiple parties
Developing an operational concept is a multi-disciplinary, multi-field work involving military science, philosophy, operations research, systems science and many other fields. It requires the cooperation of multiple parties to ensure that it is both advanced and forward-looking at the theoretical level and It is applicable and feasible at the practical level.
Establish a small core and large peripheral research team. The department initiating the development of operational concepts should give full play to its leading role and coordinate and schedule the research work from an overall perspective; establish a joint research and development team to give full play to the role of group wisdom and widely obtain new ideas and new ideas from all parties on the research of operational concepts. Methods and new perspectives; establish a cross-field and cross-department expert committee to supervise, review and guide related work from multiple perspectives.
Form a multi-departmental linkage working mechanism. In order to ensure smooth communication and efficient operation among various departments, it is necessary to first clarify their respective tasks and responsibilities. For example, the concept initiating department is responsible for overall planning and implementation, the laboratory is responsible for technical verification, the industrial department is responsible for equipment research and development, and the combat force is responsible for actual combat testing. Secondly, it is necessary to formulate relevant normative documents to ensure that all work is carried out in an orderly manner and to provide institutional support for the research and development of operational concepts. Finally, a demand traction mechanism, a collaborative research mechanism, an iterative feedback mechanism, etc. must be established to open up the link from research and development to practical application of combat concepts.
Promote the organic integration of theory and practice. Only through the cyclic iteration of “design research-deduction verification-actual military testing” can operational concepts be gradually adjusted, optimized and improved, and drive the development of war theory. Therefore, the development of operational concepts must pay special attention to the combination of theoretical innovation and practical application. Through the mutual driving of theory and practice, the fundamental purpose of leading the generation of new quality combat capabilities can be achieved. Specific methods include incorporating mature combat concepts into combat doctrine in a timely manner, preparing training syllabuses or teaching materials accordingly, and gradually promoting them to the troops; organizing relevant drills or tests to test the maturity and feasibility of combat concepts under conditions close to actual combat. nature, find and solve problems; use the capability indicators determined by the combat concept as a reference for equipment demand demonstration, drive the development of equipment technology, and promote the improvement of combat capabilities.
The rapid development of science and technology in the new era has brought many new opportunities and challenges to military capability building. Developing new combat concepts can help to keenly seize the military opportunities brought by scientific and technological progress, actively respond to threats and challenges caused by scientific and technological development, and timely grasp the direction and laws of the evolution of war forms, which can provide guidance for leading future war styles and seizing the opportunity to win. important support. At present, the international security situation is complex and ever-changing. To win future information-based wars, we need to regard the development of operational concepts as the starting point of national defense and military construction, actively carry out military technological innovation, promote the upgrading of weapons and equipment, achieve leapfrog development, and thus lead the new era. Military revolutionary trends.
(Author’s unit: Second Research Institute of China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation)
中國軍事原文來源:http://www.81.cn/gfbmap/content/2022-06/22/content_318888.htm