China Analysis of Analysis of the US Central Command Network War During Iraq War
浅析伊拉克战争中美军网络中心战
The network center war was first proposed by the US Navy in 1997, initially reflected in the war in Afghanistan, it is the core of the future of US military joint operations.
As early as 1997, the Navy put forward the concept of network-centric warfare. In 2001, the Pentagon upgraded it into the war form of the information age. In 2002, the Bush administration regarded the network center warfare capability as the focus of the military transformation and the core of the future joint operations. In view of the network center war in the war in Afghanistan in the initial results, the US military in the Iraq war to further test the new concept of combat.
· Construction of the US military network centric warfare architecture
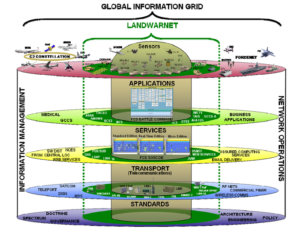
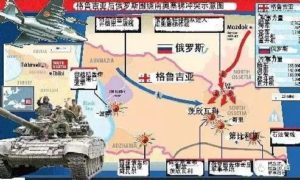
in the Iraq war, the US military stressed that network-centric warfare, and the prominence of the role of information, with an agile and efficient digital network structure information gathering, command and control and communications, firepower three systems integration, Shortened the time from the detection of the target, the formation of operational instructions to combat the destruction of the target. The networked combat structure can improve the level of information sharing, enhance situational awareness, speed up command and decision speed, achieve combat coordination, enhance the lethality, viability and responsiveness, thus greatly improving the combat effectiveness and shorten the war process. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the network structure of the US military network structure and three-tier network structure diagram.
Full-dimensional detection network to seize the information advantage is to give full play to the network center war the first condition. The US military used almost all high-tech means of detection, the establishment of the days, air, sea and land integration of full-dimensional detection network. In addition to the outer space constitutes a huge satellite surveillance network, the air at the same time there are low altitude, hollow, high altitude three reconnaissance aircraft on the Iraqi military positions to scan, the ground also deployed a large number of sensors. It is with the full-dimensional detection network, the US military captured the asymmetric information advantage, and its conversion into asymmetric firepower advantage, arbitrary implementation of the long-range strike, not only makes the Iraqi air force can not fight, ground forces are not large-scale assembly , In a passive position. <A I = 5> flexible allegations In the Gulf War, the message in the chain after a few hours or days after the transfer, the commander to issue an attack command, so the US military even through the reconnaissance found a mobile missile launcher, can not Timely strike. In this Iraq war, the US military used a flexible allegation network to effectively integrate the allegation system, greatly reducing the combat preparation time. Through the network, the commander can at the same time with the subordinate forces at all levels to contact, while commanding scattered in the regional combat forces, the formation of the overall force.
Efficient combat network At present, the US military services are more than half of the equipment to achieve the information, these information equipment on the battlefield constitutes an interconnected, interoperable network environment, different services, deployed in different spaces of various weapons platforms and fire units Equivalent to a node in the network, you can exchange the battlefield information in a timely manner, indicating the target, in accordance with the unified fire plan to implement precision strike, more effective performance. In this battle, DDG-75 “Aegis” destroyers for the “Patriot” missiles to provide early warning information, the platform through the network to achieve an example of interoperability.
In the Iraq war, the US military with the network structure for the first time to achieve a real sense of the land, sea, air and marines combat operations. Soon after the war, the US military to effectively implement the space cooperation, air force in the use of precision guided weapons to combat the implementation of the enemy at the same time, the ground forces to provide effective close support. Enhanced one-way transparency and situational awareness Since the war, the US military to use the most advanced and most powerful network technology, access to transparent and sustained battlefield charts. US Joint Operations Center is located in Qatar, is the command of the nerve center of war against Iraq. A variety of information after nearly 700 intelligence officers of the analysis, sent to the highest commander on the screen, six display battlefield information on a few minutes to update. Through the display can watch the battlefield situation, such as the movement of Iraqi tanks, deployed in Baghdad’s commando and in the flight section of the “Tomahawk” cruise missiles. <A I = 10> Realize the battlefield real-time Gulf War, the US air raid from the discovery to attack target takes 3 days, if the temporary target is difficult to adjust the air raid plan. In the Kosovo war, this time is shortened to 2h, making a considerable part of the air raid mission can be re-adjusted after the plane lift. Afghanistan war time to further shorten to 19min, the attack real-time greatly improved. In this war, this time control in 10min. The high-speed digital network system enables the US military to make faster and more responsive responses to the rapid changes in the battlefield, and to command and control the coordination of arms and operations efficiently and efficiently, which greatly improves the ability to respond quickly to changes in operational plans.
Try the effect-based operations and fast decisive combat Unlike the Gulf War, the US war in Iraq warn of information warfare using information-based weapons, not only to ensure victory, but also to achieve rapid decisive combat. To this end, the US military rely on the network of combat structure, the pursuit of effect-based operations, the target to combat more selective and targeted. US military straight to the goal of two: First, Saddam Hussein and other senior officials and the main defenders, “beheading action” from beginning to end throughout the war; the second is the Iraqi capital Baghdad, the US military did not like the traditional city war as the first to seize And occupation of the suburbs, and then step by step, layers of advance, but the first to capture the city’s strategic location.
Quickly hit time sensitive targets When time-sensitive targets appear on the battlefield, the time-sensitive targeting team within the Joint Air Combat Center of the Saudi Air Force Base will be able to identify the target in just a few minutes and determine the best attack. On 20 March, two mobile missile launchers in Iraq launched the “Abubel” -100 missile in Kuwaiti territory, which was discovered by the US airborne reconnaissance plane at a temporary US Air Force Base at 40 km from the launch site To fly the aircraft combat mission, the aircraft took off after the bombing of the missile launch vehicle bombing.
The first test of the digitalization of the United States after the Gulf War put forward the “digital network as the center of the war” concept, and at the end of the last century put forward the “digital battlefield and digital forces” concept. In 2001, the fourth machine division became the world’s first digital division, it can share the location and target information, has a unique battlefield access to tactical Internet capabilities, but has not yet been tested. April 13, the US military step 4 division vanguard arrived in Ticritt, to accept the actual test. <A (FBCB2)
The basic components of the system include the computer hardware / software, GPS receiver and communication interface, the main function is the main function of the system is the core of the war, To the commander, squad and individual show enemy position, send and receive combat command and logistical data, improve the battlefield situational awareness, target recognition. FBCB2 can provide e-mail service, connected with the Army’s high-level tactical communications system, allowing combatants to send a large number of news and digital reconnaissance reports to field commanders.
Tactical Internet Tactics The Internet is made up of three main tactical communications systems, namely, airborne radio systems, enhanced location reporting systems and mobile user equipment, including radio, communications satellites, mobile phones, fiber optic cables and switching facilities. Tactical Internet enables seamless connectivity between tactical users, voice, data, image and real-time video transmission, support for text, network management and security, and e-mail services, delivering fast and accurate information and instructions to each Combat unit.
“Global Command and Control System” (GCCS-J) to support the war against Iraq, the US military pre-war with the latest version of GCCS-J6. 0 The global command and control system enhances the intelligence capabilities so that the data from the common operations map can be better synchronized. GCCS-J combines the command and control systems of all arms and arms and correlates the data of unmanned aerial vehicles, terrestrial and satellite sensors to the integrated image and intelligence system, which can assist the commander in analyzing operational intelligence data, Generate target data and plan tasks. ”Can be deployed joint command and control system” (DJCCS) In this war, the US military for the first time using the DJCCS. The system is a computer information sharing platform, with a video conference, Internet and send and receive e-mail function, the battlefield commander in the state of movement in an unprecedented way to monitor the progress of action, keep abreast of the arms and operations of the situation, the timely release of combat orders.
JFN is a network-centric combat system for the US Navy, consisting of the TES, the Global Command and Control System (GCCS) and the Joint Operations Image Processing System, (JSIPS) to provide real-time information interaction, sensor control, target generation, mission planning and combat damage assessment capabilities, can identify and attack target time from a few hours to 10nin, to combat time-sensitive targets. TES allows the theater command center to receive target information directly from the wu1 man-machine or U-2 reconnaissance platform, and the pilots of the attack aircraft can receive the target indication data from the theater command center. GCCS provides the commander with a command and control network to issue target attack orders. JSIPS for data processing. In the future, JFN will be able to process intelligence data into targeted data more quickly, to achieve the goal of moving all people in the network, sharing common operational charts and requesting fire support.
“Tactical Input System” (TIS) TIS has been installed on the “Nimitz” aircraft carrier, and is expected to deploy to other US Navy aircraft carrier and the main amphibious ship. The system can receive digital images via terrestrial and sea-based airborne sensor platform radio lines, including optoelectronic, infrared and synthetic aperture radar images. Navy intelligence personnel can click on the interface to analyze the image, get important information, mark the potential target. TIS gives the US Navy a complete, end-to-end electronic image that greatly enhances the ability to collect, identify and target targets throughout the battlefield, reducing sensor-to-shooter time. <A (CEC) system April 7, equipped with CEC system, the US Navy “Nimitz” aircraft carrier into the designated waters, which is the first time the actual deployment of the system. CEC system is mainly composed of data distribution system and collaborative combat processor, is a network center war concept more mature a system, will make the sea air defense combat revolution, it will be aircraft carrier battle group formation in the platform (including ships and early warning aircraft ) The target detection system, the command and control system and the weapon system are organically linked to allow the platform to share all the data acquired by the various detection devices in the formation with a very short delay, so that the combat system breaks through the single ship, Within the realization of integration.
Tactical data information chain In the network center war, the tactical data information chain is one of the important means for the US military and allied forces to realize the information superiority, mainly including Link-16 and Link-11. Link-16 can transmit all kinds of tactical data information between command and control system and aircraft, missile and other weapons system platform and between combat units, effectively connect information source, accusation center and weapon system platform to realize battlefield resource sharing. The tactical data information chain using time division multiple access technology, with relative navigation and anti-jamming capability to relay the way of communication, the working frequency band 960MHz-1215MHz, the data rate of 115.2lkbps-238kbps. Link-11 operates at high frequency / UHF band, data rate is 1.8kbps, can be used for real-time exchange of early warning information, air / ground / underwater target data, control instructions and the status of the unit weapons, and has a certain degree of confidentiality , The entire network under the control of the network control station network communication, the use of master-slave polling, can be over-the-horizon transmission.
The analysis of the characteristics of the US military development network center war shows that the concept of network-centric warfare has gradually become a new form of combat for the US military in the 21st century. In the development and application of network-centric warfare concept, the US military showed the following characteristics:
In the Iraq war, the US military uses a variety of detection and communication means to make the entire battlefield transparent, from beginning to end are information-led. This shows that in the future war who can have the advantage in the detection and communication, to seize the right to information, who will be able to achieve greater battlefield initiative.
Pay attention to the digitalization of weapons and equipment, information construction Digital is the basis of network-based warfare, is expected to US military services in 2010-2020 to achieve full digital. Weapon and equipment information is to achieve the network as the center of the joint operations of the core, the US military will be further in the world to take the lead in the information age of information technology. To strengthen the network center warfare related equipment R & D The US military effective implementation of the network center war relies on in recent years targeted research and development of various related equipment, such as joint fire network, collaborative combat capability, tactical Internet, tactical input system, global command and control system, Data information chain and so on.
(Source: “National Defense Technology” 2003 the first 18)
Original Mandarin Chinese:
中国日报网站消息:网络中心战最早由美国海军于1997年提出,在阿富汗战争中初步体现出优越性,它是美军未来联合作战的核心。
海军早在1997年就提出网络中心战概念,2001年五角大楼将其提升为信息时代的战争形态,2002年布什政府将网络中心战能力视为军队转型的重点和未来联合作战的核心。鉴于网络中心战在阿富汗战争中初见成效,美军在伊拉克战争中进一步检验了这一全新的作战概念。
在伊拉克战争中,美军强调网络中心战,突出信息的地位和作用,借助灵敏高效的数字化网络结构将信息收集、指挥控制与通信、火力打击三大系统融为一体,缩短了从侦察发现目标、形成作战指令到打击摧毁目标的时间。网络化的作战结构可提高信息共享水平,增强态势感知能力,加快指挥和决策速度,实现作战协同,增强杀伤力、生存能力和响应能力,从而极大地提高作战效能,缩短战争进程。图1和图2分别显示了美军构建的网络中心战的网络结构原理图和三层网络结构图。
全维的探测网 夺取信息优势是充分发挥网络中心战的首要条件。美军动用了几乎所有高技术探测手段,建立了天、空、海、陆一体化全维探测网。除在外层空间构成庞大的卫星监视网外,空中同时有低空、中空、高空三个层次的各种侦察飞机对伊军阵地进行扫描,地面上也部署了大量传感器。正是借助全维的探测网,美军夺取了不对称的信息优势,并将其转化为不对称的火力优势,随心所欲地实施远程打击,不但使得伊拉克空军无法作战,地面部队也不敢大规模集结,陷于被动境地。
灵活的指控网 在海湾战争中,信息在指控链中需经过数小时或数天的传递后,指挥官才能下达攻击命令,因此美军即使通过侦察发现了机动导弹发射车,也无法及时实施打击。这次伊拉克战争中,美军利用灵活的指控网有效整合了指控系统,大大缩短打击准备时间。通过网络,指挥官可以同时与下属各级部队进行联络,同时指挥分散在各地域的作战部队,形成整体合力。
高效的作战网 目前,美军各军种均有一半以上的装备实现了信息化,这些信息化装备在战场上构成互联、互通的网络环境,不同军种、部署在不同空间的各种武器平台和火力单元相当于网络中的一个节点,可以及时交换战场信息,指示目标,按照统一的火力计划实施精确打击,更有效地发挥效能。在这次作战中,DDG-75“宙斯盾”驱逐舰为“爱国者”导弹提供预警信息,是平台通过网络化途径实现互通的一个例证。
·伊拉克战争中网络中心战的具体应用
检验联合作战的协同性 伊拉克战争中,美军借助网络化结构首次实现了真正意义上的陆、海、空和海军陆战队协同作战。开战不久,美军就有效地实施空地协同,空中力量在使用精确制导武器对敌军实施打击的同时,对地面部队提供有效的近距离支援。
增强单向透明度和态势感知能力 自开战以来,美军运用最先进、最强大的网络技术,获取透明持续的战场态势图。美军联合作战中心位于卡塔尔,是指挥对伊作战的神经中枢。各种信息经过近700名情报人员的分析,传送到最高指挥官的显示屏上,6个显示屏上的战场信息几分钟就更新一次。通过显示屏可观察战场情况,如运动中的伊拉克坦克、部署在巴格达的突击队以及处于飞行段的“战斧”巡航导弹。
实现战场实时化 海湾战争中,美军空袭从发现到攻击目标需要3天,若临时发现目标时很难及时调整空袭计划。在科索沃战争中,这一时间缩短到2h,使得相当一部分空袭任务可以在飞机升空后重新调整。阿富汗战争时这一时间进一步缩短到19min,攻击的实时性大大提高。而在这次战争中,这一时间控制在1Omin内。高速数字化网络系统使美军能对战场瞬息变化作出更快、更灵敏的反应,及时高效地指挥、控制与协调各军兵种的行动,大大提高了临时改变作战计划时的快速反应能力。
尝试基于效果的作战和快速决定性作战 与海湾战争不同,此次伊拉克战争美军提出用信息化武器装备打信息化战争,不仅要求确保胜利,而且要求实现快速决定性作战。为此,美军依靠网络化作战结构,追求基于效果的作战,对目标打击更有选择性和针对性。美军直取的目标有两个:一是萨达姆和其他高官以及主要捍卫者,“斩首行动”由始至终贯穿整个战争;二是伊拉克首都巴格达,美军没有像传统的城市战那样首先夺取和占领市郊,然后步步为营,层层推进,而是首先夺取市内的战略要地。
快速打击时间敏感目标 当战场上出现时间敏感目标时,美军在沙特空军基地的联合空中作战中心内的时间敏感瞄准小组只用几分钟时间就可准确识别目标,决定最佳攻击行动。3月20日,伊拉克两辆机动导弹发射车刚向科威特境内发射“阿巴比尔”-100导弹,即被美国空中侦察机发现,在距发射地点40km的一个美空军基地立即临时调整了几架待飞飞机的作战任务,飞机起飞后投掷炸弹将导弹发射车炸毁。
首次检验数字化师 美国在海湾战争后提出了“以数字化网络为中心的战争”概念,并于上世纪末率先提出了“数字化战场和数字化部队”的构想。2001年,第4机步师成为世界上第一支数字化师,它可以共享位置和目标信息,具有独一无二的战场接入战术因特网的能力,但尚未经过实战检验。4月13日,美军第4机步师先头部队到达提克里特,接受实战检验。
·伊拉克战争中网络中心战的部分装备
“21世纪旅及旅以下作战指挥控制系统”(FBCB2) 该系统的基本组件包括计算机硬/软件、GPS接收机和通信接口,主要功能是向指挥官、小分队和单兵显示敌我位置、收发作战命令和后勤数据、提高战场态势感知能力、进行目标识别等。FBCB2可提供电子邮件服务,与陆军的高层战术通信系统相连接,允许作战人员向战地指挥官发送大量消息和数字化侦察报告。
战术互联网 战术互联网由陆军3个主要的战术通信系统,即机载无线电系统、增强型定位报告系统和移动用户设备互联而成,包括无线电、通信卫星、移动电话、光缆和交换设施。战术互联网能够实现战术级用户间的无缝连接,提供语音、数据、图像和实时视频传输,支持文电、网络管理和安全以及电子邮件业务,可快速、准确地将战地情报和指示传递给每个作战单元。
“全球指挥与控制系统”(GCCS -J) 为支持对伊作战,美军战前采用了最新版本的GCCS-J6.0全球指挥和控制系统,提高了情报能力,使通用作战图传来的数据可以更好地同步。 GCCS-J联合了所有军兵种的指挥与控制系统,并使无人机、地面和卫星传感器的数据相互关联并传递到图像与情报综合系统,后者能够帮助指挥官分析作战情报数据、管理和生成目标数据以及规划任务。
“可部署的联合指挥与控制系统”(DJCCS) 在这次战争中,美军首次实战使用了DJCCS。该系统是一个计算机信息共享平台,具有召开电视会议、上网和收发邮件功能,可使战场指挥官在运动状态下以前所未有的方式监控行动进展,随时了解各军兵种作战情况,及时下达作战命令。
“联合火力网”(JFN) JFN是美海军的一个以网络为中心的作战系统,由“战术利用系统”(TES)、“全球指挥与控制系统”(GCCS)和“联合作战图像处理系统”(JSIPS)组成,能够提供实时信息交互、传感器控制、目标产生、任务计划制定以及作战毁伤评估功能,可将识别和攻击目标的时间从数小时减少到10nin,打击时间敏感目标。TES可使战区指挥中心直接从wu1人机或U -2等侦察平台接收目标信息,攻击机的飞行员能从战区指挥中心接收目标指示数据。GCCS为指挥官提供下达目标攻击指令的指挥控制网络。JSIPS进行数据处理。未来,JFN将能更快地把情报数据处理成瞄准数据,用于打击移动目标,最终实现使所有人员都置身于网络中,共享通用作战态势图和请求火力支援。
“战术输入系统”(TIS) TIS已安装在“尼米兹”号航母上,并有望部署到美海军其他航母和主要两栖舰上。该系统可通过陆基和海基机载传感器平台的无线电线路接收数字式图像,包括光电、红外及合成孔径雷达图像。海军情报人员可通过点击界面分析图像,获得重要信息,标记潜在目标。TIS使美海军拥有了完整的、端对端的电子图像,极大地提高在整个战场上搜集、识别和打击目标的能力,减少传感器到射手的时间。
“协同作战能力”(CEC)系统 4月7日,装有CEC系统的美海军“尼米兹”号航母进入指定海域,这是该系统首次实战部署。 CEC系统主要由数据分发系统和协同作战处理器组成,是网络中心战概念比较成熟的一个系统,将使海上防空作战发生革命性变化,它将航母战斗群编队中各平台(包括舰艇和预警机等)所装载的目标探测系统、指挥控制系统和武器系统有机联系起来,允许各平台以极短的延时共享编队内各种探测设备获取的所有数据,使作战系统突破单舰的限制,在编队内实现集成。
战术数据信息链 在网络中心战中,战术数据信息链是美军及盟军实现信息优势的重要手段之一,主要包括Link-16和Link -11。Link-16可在指挥控制系统与飞机、导弹等武器系统平台之间以及在各作战单元之间传输各种战术数据信息,有效连接信息源、指控中心与武器系统平台,实现战场资源共享。该战术数据信息链采用时分多址技术,具有相对导航和抗干扰能力,以中继方式进行通信,工作频段为960MHz-1215MHz,数据速率为115.2lkbps-238kbps。Link-11在高频/特高频频段工作,数据速率为1.8kbps,可用于实时交换预警信息、空中/地面/水下目标数据、控制指令以及各单元武器状况信息,并具有一定的保密能力,整个网络在网络控制站的管制下组网通信,采用主从式轮询,可进行超视距传输。
·美军发展网络中心战的特点
分析表明,网络中心战概念已逐渐成为美军面向21世纪的新型作战形式。在发展和应用网络中心战概念上,美军表现出以下特点:
建立全维的探测网,夺取制信息权 伊拉克战争中,美军运用多种探测和通信手段使整个战场透明化,从始至终都以信息为主导。这说明在未来战争中谁能够在探测和通信上占有优势,夺取制信息权,谁就能够取得更大的战场主动权。
注重武器装备的数字化、信息化建设 数字化是网络中心战的基础,预计美国各军种将在2010-2020年间全面实现数字化。武器装备的信息化是实现以网络为中心的联合作战的核心,美军将进一步在世界上率先建成信息时代的信息化军队。
加强网络中心战相关装备研发 此次美军有效实施网络中心战依赖于近年有针对性地研发各种相关装备,如联合火力网、协同作战能力、战术互联网、战术输入系统、全球指挥与控制系统、数据信息链等。(来源:《国防科技》2003年第18期)